

How to Manage Your Project: A Comprehensive Guide to Project Management






When a project is going well, it’s easy to get complacent and allow the process to go on autopilot. But when things go awry, you have to be ready to roll up your sleeves and jump right in.
Hey there! This blog is almost about 5000+ words long & not everyone likes to read that much. We understand that.
This is precisely why we made a podcast on the topic. Mitul Makadia, CEO & Founder of Maruti Techlabs, talks to Bikshita Bhattacharyya about his Agile implementation, strategy, and process during the nascent stages of the company.
He walks us through the challenges he faced, how the business benefited from scaling Agile, and how important is the scrum master in making Agile a success at the organizational level. Here is a small snippet from that episode. Check it out!
Even in the 21st century, we need excellent project management skills to get things done. The massive projects in technology and science — building a new computer operating system or sequencing the human genome — are at least as complicated as anything humanity has ever made or attempted before.
Though project management has been in the picture since the Egyptian era, people are still intimidated by its thought. For half a century now, organizations have started applying project management techniques to ensure that their projects run efficiently and smoothly from start to finish.
Every project is different, and the system will vary from team to team. But some tried-and-tested project management basics have withstood the test of time, and they are worth learning about.
Through this comprehensive guide on project management, you will learn how to effectively create a concrete action plan for your project and guide your team towards the path of success.
Project management is a strategic execution of everything a team has to do to accomplish all objectives with specific parameters. This includes your team objectives, tools, and techniques over the long term and your day-to-day work. Project management is all about setting up a plan, managing it, and controlling the project’s factors. It is a universal task for organizations, regardless of their sector, size, or complexity.
Project management is more than just scheduling events, tasks, or resources. It is about making sure that everyone on the team understands the goals, their roles in achieving those goals, and ensuring that there are no gaps in communication.
The execution of a project lifecycle can be ensured by monitoring and controlling the progress of all tasks, incorporating change requests as required, and managing any risks or threats that may arise.
The project management process must be in line with the triple constraints. However, managers often use project management tools and software to balance these constraints and schedules to meet project requirements.
Managing a project in the right way is crucial for the success of any project. If your team lacks lean and agile team management expertise, opting for agile software development services could be the best option.
Importance of Project Management
Project management encompasses many different aspects of running a business that is essential to its success. It helps you ensure that what you deliver is correct and provides real value against the business opportunity.
One of the crucial reasons to use project management is to align your project with your business strategy. Apart from strategic alignment, project management also helps set clear objectives, realistic project plans, quality control, and high-risk tolerance towards your project.
Did you know that 11.4% of every dollar invested in projects was wasted due to poor management in the year 2020? To overhaul such a situation, prioritizing project management methods helps continuously improve project workflow, eventually maintaining the organization’s highest efficiency and productivity.
The term project management was coined when the United States Navy employed a project management framework in their Polaris project during the 1950s. Later by the 1990s, the project management tools, techniques and theories became widely accepted by different organizations to interact and customize their products and services.
Businesses became more client-oriented by adopting and applying revolutionary technology changes to their project, which eventually led IT sectors to give birth to modern project management. Organizations started embracing these new project management basics to become more effective in managing and controlling the various aspects of the project.
According to the PMBOK (Project Management Body of Knowledge) by Project Management Institute, phases of software project management are categorized into five distinct phases. Let’s discuss those phases in detail below:

It is the first phase of Project Management. Initiating a project involves gathering background information, generating ideas, and forming an action plan. During project initiation, you have to create a business case and define your project on a large scale.
In the initiation phase, the Project Manager develops a project charter that provides a basic understanding of the project objectives, scope, and expectations. The project charter is an important document outlining the details of a particular project, such as the project constraints, goals, deadlines, budget, appointments of the project manager, etc.
It also includes a broad statement of potential project opportunities and challenges of a more extensive scope than planned. Once you have the project goals and objectives, the next step is to identify the key stakeholders interested in the project.
Note that the project charter is similar to the project brief. However, the difference is that the project charter is part of the PMBOK framework, whereas a project brief resembles the PRINCE2 methodology.
The project planning stage, the most crucial stage, is where you create a plan for your entire project. This phase aims to develop the action plan that will guide you through the subsequent two phases of the project management process. It helps set the key milestones and deadlines for the final project completion, ensuring that all your team members move towards the same goal.
The project plan must include every attribute of the project, including the budget baseline, deadlines, risk factors, resources, roles and responsibilities for each team member, etc., to avoid confusion when you encounter roadblocks during the project execution phase.
During this phase, the most pivotal thing is to identify the best Project Management tools and methodology that you and your team will follow throughout your project. There are various methods to choose from, such as Agile, Waterfall, Scrum, Kanban, etc.
If you choose the Scrum methodology, you can define your project scope using Scrum Board and break down your project into activities, deliverables, milestones by making it easy for the project manager and the team members to create and assign tasks.
Unless you use a modern methodology like an agile project management framework, this phase of the project management lifecycle covers almost half of the project’s timestamp.
Therefore, project managers often prefer to draw out their project plan using Gantt chart software, which shows how much work is required at each stage, such as research, development, or production, and when they should complete it.
Project execution is where all the preparation from project initiation and planning meets reality. It’s where the rubber meets the road, where you begin to see results from the work that has been done.
The project execution phase involves several activities that can help define your success or failure according to the clients’ and stakeholders’ satisfaction. It includes workflow management and corrective actions from the client, ensuring that everyone stays on the same page and the project runs steadily without any issue.
As the project manager, you will allocate all the resources to the working team and manage those resources to carry out the project successfully. Also, you have to maintain excellent and consistent collaboration between your team and stakeholders as a part of your job.
This stage coincides with the controlling and monitoring phase and, therefore, might include managing workflows and recommending corrective actions to meet and fix the issues as they arise.
This phase of the project management process ensures that the activities undertaken by teams have adhered to the project objectives and the project deliverables.
Project monitoring helps the manager identify the current project status vs. the actual project plan. During this phase, the manager is also responsible for quality control procedures to prevent the chances of disruptions and quantitative tracking of efforts and costs for the project.
In the project management process, the project execution and monitoring go inline to identify the progress and performance of the project. However, the decisive monitoring phase requires consistent project updates and proper tracking tools and frameworks to accomplish your task efficiently.
The most remarkable factors to consider while working on any project are time, cost, and scope, collectively known as triple constraints of project management. The purpose of this stage is to control these factors and make sure they never go off the rails.
The closure phase of the project management process is an essential part of completing a project successfully. This phase ensures that all loose ends are tied up, and the client walks with the final deliverables.
Once the client approves all resources and deliverables, the documentation is completed, and everything is signed off. This phase is an opportunity for the project manager to review what went well and what didn’t during the project to make any changes in future projects.
After completing the project, many teams also opt to hold reflection meetings to document the project learnings and identify the successes and failures of their project. This ensures that all team members know what they do well and what needs improvement, which helps them improve their performance in the future.
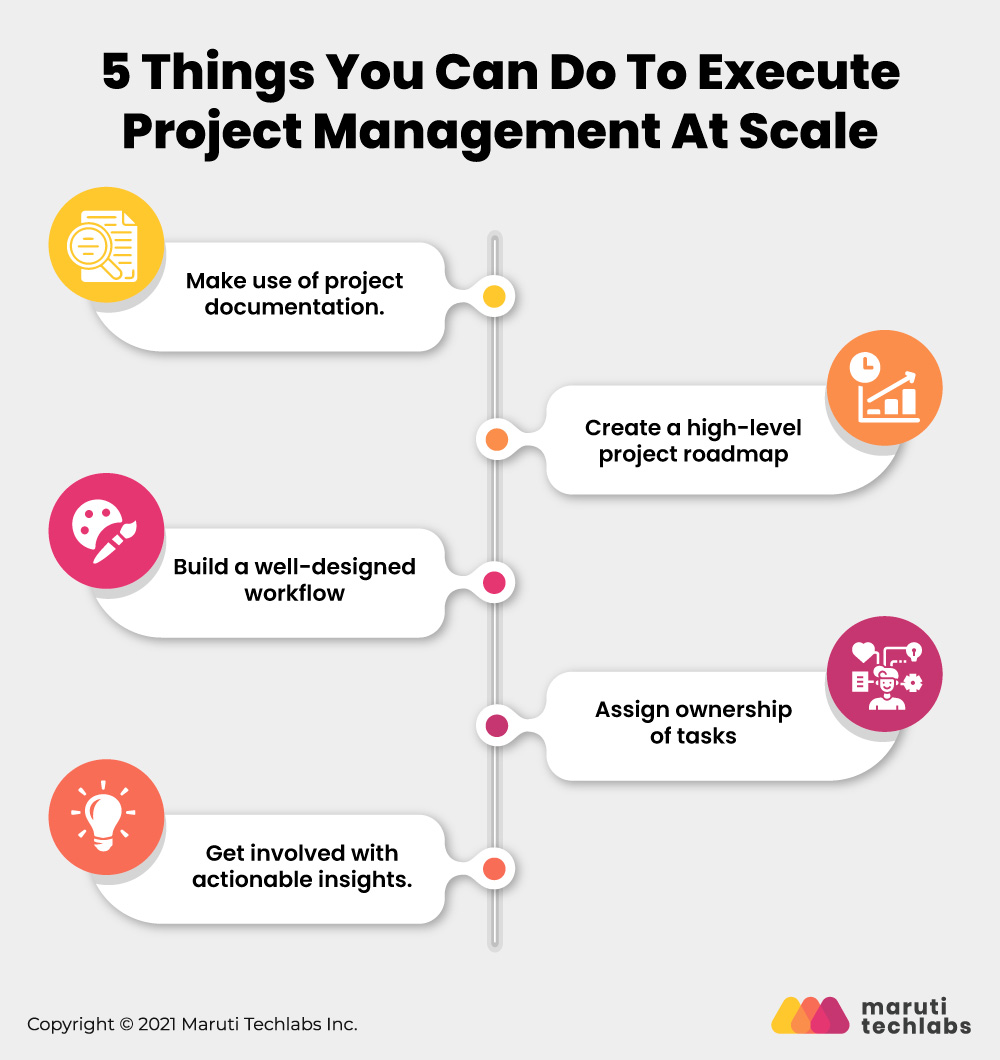
The more complex the project, the more robust the tools you need to manage it effectively. While spreadsheets and whiteboards can be helpful for small projects, for tracking simple things like tasks, issues, and due dates, complex projects demand robust project management systems and processes.
Here’s how you can execute your project management at a large scale:
Clear and easy-to-understand documentation is the key to the successful implementation of projects. Project documentation will help the project manager and the project team track their progress and verify that all activities are accomplished on time and within budget.
A project roadmap is a living document that iterates over time as plans change and goals shift. It is an important document that provides a high-level overview of the project’s goals and deliverables and a timeline for each milestone.
The project roadmap is designed to communicate strategy, status, and progress in a single, easy-to-digest visual format. It can help you manage stakeholders’ expectations and motivate your team to reach their goals.
Workflows are a central part of a project management process. They allow you to track and monitor your projects from start to finish, making it easier for everyone on the team to work together efficiently.
A well-designed workflow will keep your team from being overwhelmed by an overabundance of tasks and give them a clear understanding of how their work fits the larger project vision.
In a busy office, it’s often difficult to keep track of who’s working on what and who owns which tasks and projects. Using a robust work operating system, you can easily set up a people column for each project and assign ownership of the tasks and subtasks to individual employees and teams.
With this information at your fingertips, you can quickly redirect work if someone isn’t meeting expectations.
In addition, building transparency helps alleviate bottlenecks and make sure everyone is in the loop. It also builds momentum in your project; if everyone knows what’s happening in real-time, progress can be tracked more efficiently, and there’s less room for miscommunication or confusion.
It is easy to take your project to the next level using data-driven insights. Here are a few ways/ features to get the most insights from your data :
Once you build the workflows, you can easily create reports and dashboards. Evaluating project success at odds with KPIs, this data can lead to new decisions and projects.
The triple constraint, also called the iron triangle, is the classic project management triangle, featuring Scope, Time, and Cost as variables. Triple constraints of a project are the cornerstone of the project management process, and hence, special attention to the schedule, work breakdown, and budget is a must.
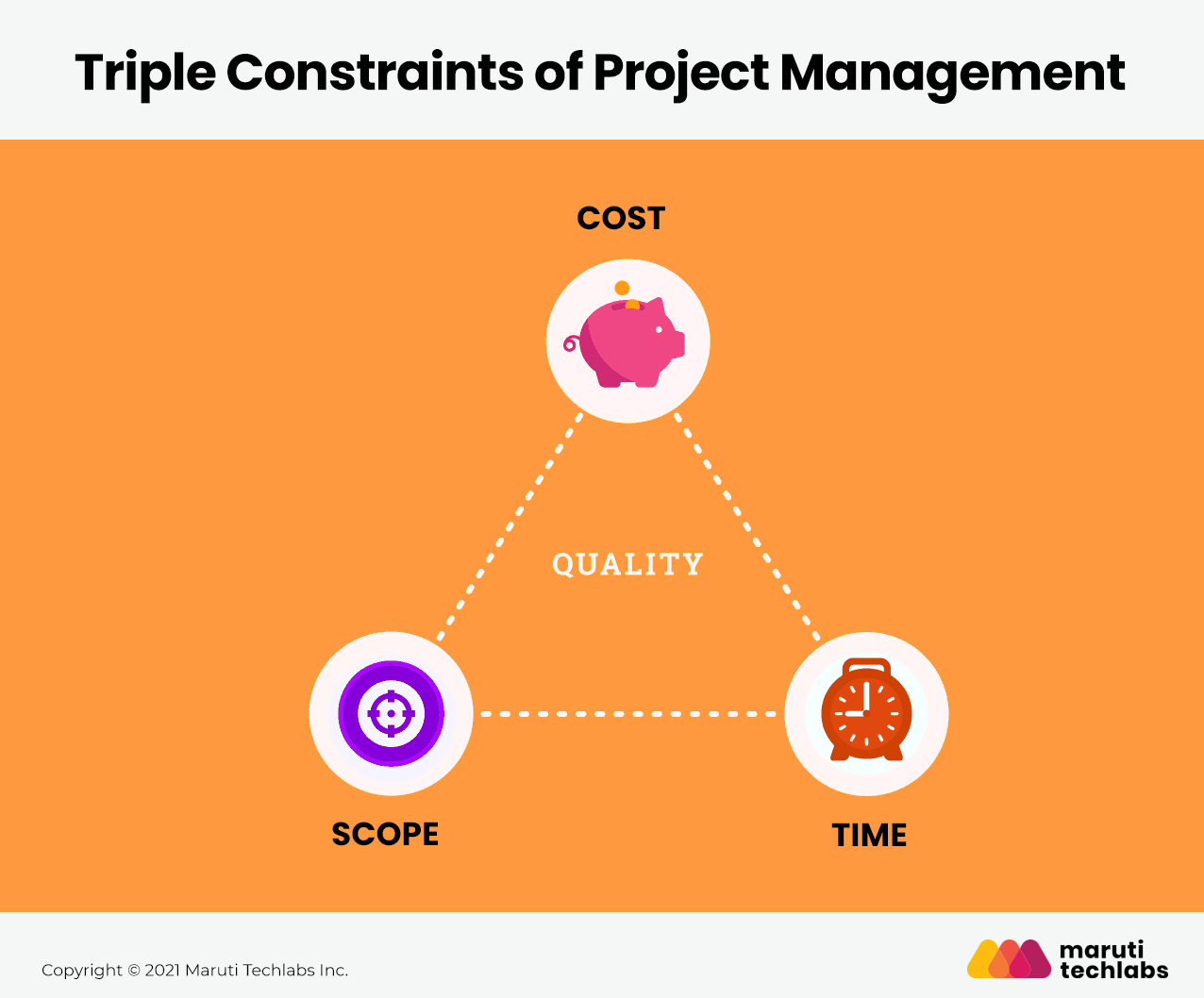
Let us dive deep into how the triple constraints affect the project management process:
Time is the one thing that every project manager has in minimal supply. Time is one of the most precious commodities to a project, and it is something that we can never make more of.
The time constraints refer to the project completion schedule, which includes the deadlines of each phase of the project and the dates of final deliverables. You must do it during the initial and planning phase of the project management life cycle.
The scope of a project involves the work that you will undergo to complete the project. It is an overall view of all work you must do, and it consists of identifying the primary tasks, deliverables, features, and functions required to meet the purpose of the project lifecycle.
Note that the project’s scope is identified during the planning phase using the work breakdown structure. If it is not correctly defined, it may extend during the execution phase due to unforeseen circumstances. This process is generally known as scope creep and might lead to project failure.
When working on any project, there are many costs associated with it. The cost of the project, also labeled as the project’s budget, is a combination of all financial resources of the project.
Project managers are responsible for estimating this controlling cost of the project for delivering it within the approved budget of the stakeholders. Remember that prices comprise the expenses of materials; it also covers labor costs, quality control, vendors, and other factors.
The Triple Constraints of project management assume that the three factors of scope, time, and cost are inseparably linked. The triple constraint describes the balancing act of these three factors. Keeping the triple constraints of a project in mind will effectively help you adapt to the changing condition of your project management process.
As triple constraint is a crucial part of any project, it is essential to note that all three factors of this triangle always influence each other. For instance, if there is a setback in project deliverables, some adjustments must be made in either scope or cost.
Change is a universal process. Keeping the project management process in mind, adapting the triple constraint approach will ensure that this change does not jeopardize the entire project.
The Triple Constraint Triangle is an overarching model with its own theories. However, it is often criticized because it doesn’t account for all of the variables involved in project management.
Many professionals have critiqued this model and often come up with models that reflect the constraints they feel are more important in their industry or field.
Apart from triple triangle constraints, the PMBOK guide now includes the following additional variables in the project management process:
Even though the new variables allow a thorough picture of the entire project management process, the traditional triple constraints model still holds power to conceptualize the relationship between high-level attributes of the project efficiently.
Projects are an essential part of any business model, but they can quickly spiral out of control and drain your resources if not managed correctly. The secret to a successful project is ensuring the right people are on the bus and guiding it in the right direction.
Here are some of the tips recommended for a successful project management process:
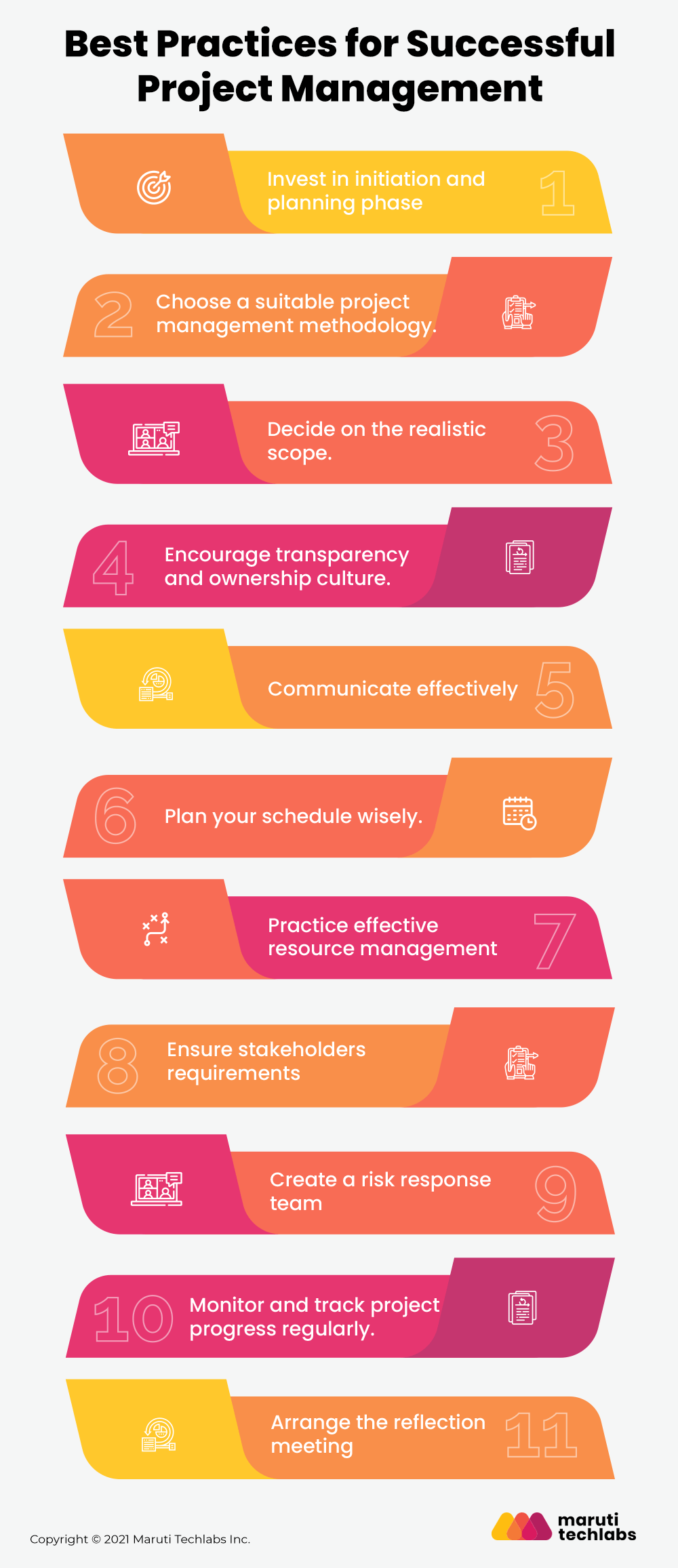
1. Invest in initiation and planning phase
By identifying the project objectives, requirements, and priorities in the early stages of the project life cycle, you can avoid the chances of risks and confusion while executing the project. A project plan also helps you identify the resources, budget, and risks associated with your project.
2. Choose a suitable project management methodology.
Project management methodologies are the set of principles that enable you to manage, plan and execute your project efficiently. Choosing the proper framework guides you through principles and processes used to plan, manage and execute projects.
3. Decide on the realistic scope.
52% of the organizations run into scope creep or unpredicted changes during the project. However, you can effectively define your project scope by including the right people in your project planning stage, such as experienced stakeholders, and avoid a lot of frustration later.
4. Encourage transparency and ownership culture.
With a strong culture of transparency and ownership, the leaders and team members can depend on each other for their work regardless of how stressful your plan gets.
5. Communicate effectively
When working on a project with others, make sure everyone’s on board with the process and respective decisions that affect them. Effective communication is one of the top project management practices because it keeps team members informed about the operations at every stage to avoid misunderstandings.
6. Plan your schedule wisely.
Creating realistic project timelines is an essential part of project management. The goal of your project timeline is to create a schedule that you can deliver on while still being realistic in terms of the amount of work your team will have to complete.
7. Practice effective resource management
Managing your resources means ensuring that you have the right personnel on your team for the job, allocating that personnel correctly to maximize their productivity, and preparing detailed schedules to make sure things run smoothly.
8. Ensure stakeholders requirements
It is mandatory to have a clear understanding and proper communication before starting a project. Get your stakeholders engaged in knowing all goals and objectives before you begin working on it because that’s how you can achieve what you want.
9. Create a risk response team
With the number of things that can go wrong in a project, you should have a backup plan before anything occurs. The risk response team should take all the steps necessary to prevent further damage or loss. This team will have to have authority over all the other groups, as they are the ones who will single-handedly take charge of the situation if something horrible happens.
10. Monitor and track project progress regularly.
Monitoring the progress of each task in your project is essential to keeping things on time and within budget. Monitoring and tracking should be handled regularly rather than waiting for a milestone to arrive. You should identify the critical path and monitor progress on an ongoing basis to maintain control over the project schedule.
11. Arrange the reflection meeting
The wrap-up meeting gives you time to analyze the project while the details of the projects are still fresh in your mind. This way, you’re better able to see the project from different perspectives and identify areas to improve your work management practices.
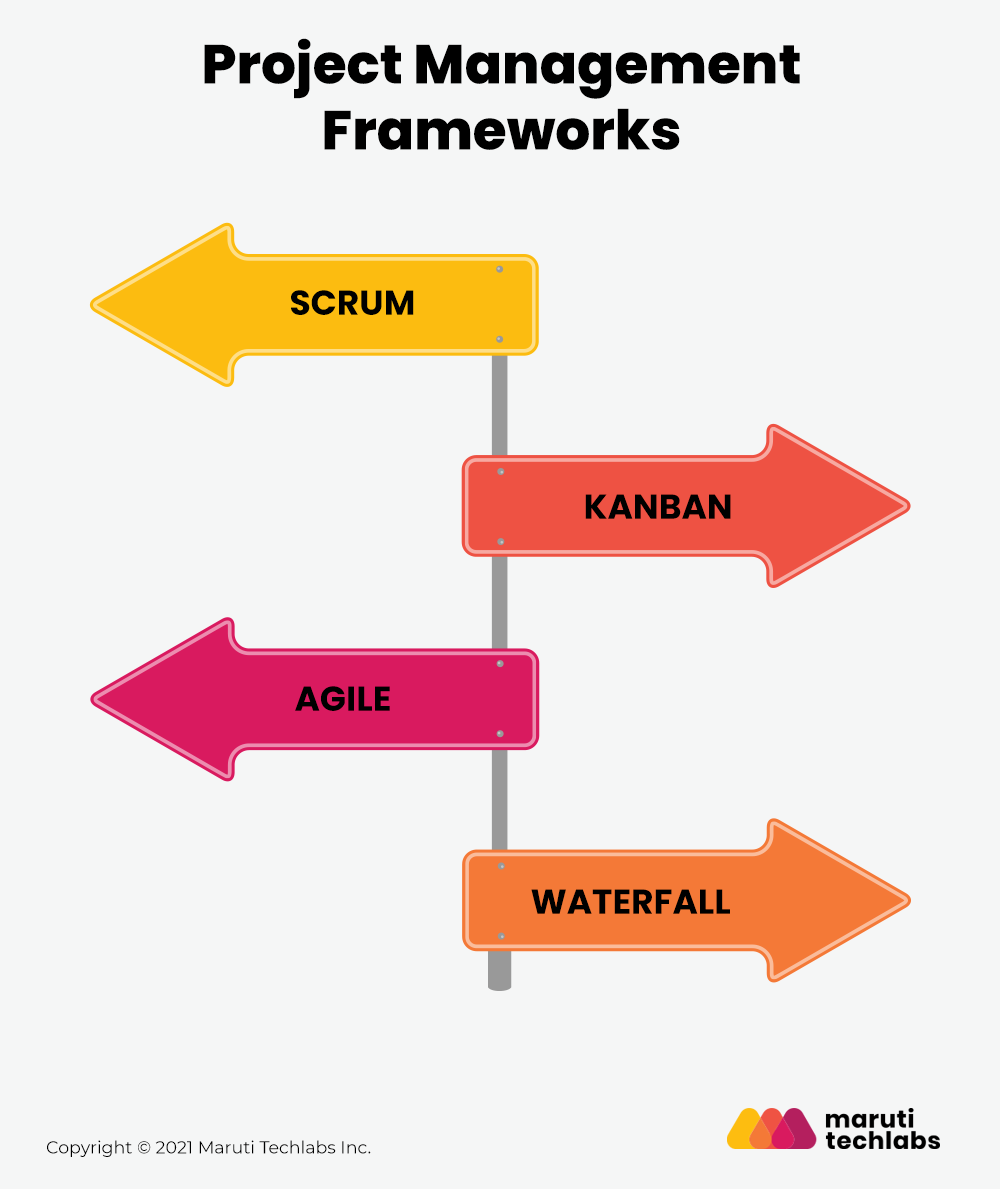
Project management frameworks are formalized processes designed to guide effective project management systems. They provide a common language to discuss the purpose of the project lifecycle and give structure to the project development process.
The choice of framework relies upon the nature of the project and organizational factors such as company culture and the availability of trained project managers. Here are some of the common project management frameworks discussed in detail:
The waterfall model is the most common approach to project management. It is also known as the classical or traditional project management approach. The idea here is that requirements are identified, design is built, tested, and implemented before any work is started. Hence, there are no surprises during deployments since all requirements have been taken into account.
The waterfall methodology is linear. As a result, it’s challenging to incorporate feedback into the process or correct problems that might surface along the way. It can lead to schedule delays, cost overrun, and other undesirable outcomes.
Kanban is an approach to project management that improves workflow by placing tasks on a Kanban board (visual task board), where workflow and progress are clear to all team members.
The card-based structure allows for quick and easy work status tracking and can be used with any project. With the Kanban method, teams cannot estimate how much work they can complete or how long it will take.
Instead, they define the workflow process and the number of cards available within that process. Each card represents a single step in the workflow process, and as more cards fill up the board, the team knows it needs to move to the next step in the process or find more workers to do the job.
Agile teams use kanban boards to create user stories and backlog planning in software development. With the dawn of digital technology in our era, you can use software like Trello Trello to quickly implement project management processes.
Scrum is a framework for sustaining and developing large and complex products. It is a simple but powerful framework for rapidly growing products. It can be used to innovate, design, or plan complex projects of almost any size.
Scrum provides a structure for teams to follow to deliver value continuously. The framework enables teams to optimize the value they release based on honest customer feedback and empirical data from their previously provided commitments.
Scrum often manages the projects based on the “sprint” approach. However, it is the ideal framework for management teams of no more than ten people and is frequently wedded to a two-week cycle along with daily scrum meetings.
Agile is a development methodology used in software projects, but agile principles are applied innovatively to other projects. Agile frameworks mainly focus on projects where speed and flexibility are priorities.
Agile is commonly described as an “iterative” approach because it involves short bursts of work called “sprints.” Teams iterate over their requirements or tasks until they are completed, then move on to the next step. This process is called incremental development.
The idea is that teams only plan the work completed within a given period, allowing frequent reviews and adjustments.
Agile project management is a modern methodology that attempts to streamline software development. It helps companies deliver a product in quick iterations, enabling them to get feedback from their audience and make adjustments as necessary.
Agile project management centers around the word “agility,” which means “mobility nimbleness.” Therefore, the fundamental idea of agile management is to get the work done as quickly as possible and allow an easy change of direction.
Agile project management best practices include five essential elements to go through the building blocks of the agile process:
At Maruti Techlabs, we work closely with you as your go-to product development partner. With over 12+ years of experience in agile-powered product development, we’ve worked with clients large and small across various industries and geographies, helping them make the right decisions about the tech stack, solutions, and processes they adopt and inculcate in their product development journey. Our goal is always to keep your technological vision aligned with both your business priorities and end users’ expectations.

There are various project management tools in software engineering available in the market. Let us focus on some of them in detail here:
A Gantt chart is a graphical representation of tasks in a project, their durations, dependencies, and start/finish dates. Gantt charts are generally used to describe project schedules, but they can also plan non-project-based activities.
The task inside the Gantt chart is listed from the left and populates the timeline by stretching the status bar from the start date to the end date. Also, you can efficiently perform the editing in the Gantt chart by the dragging and dropping method.
The dashboard is one of the most powerful project management tools available. It offers a top-down view of the entire project, which enables you to have a bird’ eye view of what’s going on at any given time.
The dashboard also gives you an at-a-glance overview of your project’s progress against its original plan, current milestones against the initial milestones, or how far along projects are concerning each other.
Some dashboards are built by analyzing the project reports and compiling them into external programs. Most project management tools have the default feature of automatically creating the project dashboard using your project data.
Task lists are popular project management tools that allow you to manage, assign and track tasks across the project to ensure they’re meeting the demands of the project schedule.
Task lists also provide a way for you to prioritize work to maximize productivity. A task management tool enables the team to control and manage their tasks, adding more transparency into the process.
A kanban board consists of columns representing each stage of production and cards depicting the tasks associated with each stage. When a task is scheduled, one or more cards are placed on the appropriate column. The card is moved to the next column when the job is complete.
It is adapted to identify the progress and performance of a successful project. Project reports are used to share the data on key performance indicators of the project, for instance, actual project vs. the baseline costs, workload, etc. Reports are easy to share and the best communication medium for updating stakeholders.
Innovations in technology are changing the way we work. In a world of rapidly evolving business models and a growing demand for flexibility and speed, AI (Artificial Intelligence) is increasingly integrated into project management tools and techniques.
PMI’s Pulse of the Profession survey suggests that 81% of respondents are ready to impact their organization with AI technologies. Apart from AI, a Forbes article display that there are three project management trends that we can expect in the future:
With rapidly growing competition in the market, businesses need to be innovative, be more competitive, and gain a competitive advantage over their rivals. The innovation can be achieved by improving the project management systems that are already established or even by building new ones.
Did you find the video snippet on What prompted the shift to agile methodology? What principle was MarutiTech following before that? to be insightful? We have a ~22 min video where Mitul Makadia gets into the weeds, and we discuss about Implementing & Scaling Agile to streamline Software Development. Take a look –
Project management is a wide-ranging term that encompasses many different roles and responsibilities within the same project. It’s common for businesses to have projects that need to be done, and taking them on can be an intricate process if you don’t know how to manage a project step by step.
Project management is a lot like playing chess. The same rules apply, but the effectiveness of every move differs with every player and every scenario. You cannot learn project management overnight, but with practice and dedication, you can improve over time.
Also read: 8-Step Guide To New Product Development Process (NPD)
Knowing the fundamentals of project management is essential, but knowing how to apply them in different situations is crucial. We hope you enjoyed this comprehensive guide to project management and that you found some valuable insights to manage your projects better, meet your goals and improve your bottom line.
At Maruti Techlabs, we help you capture your ideas during the early stages of your project management process before they get lost or corrupted. With our custom product development services, you can quickly validate your vision, go to market sooner and figure out what parts of your product resonate with your users. This helps you stay lean and agile while allowing you to make the necessary changes in your product before you invest a lot of time and effort into anything that will not scale in the end.
Having worked on multiple challenging projects from more than 16 industries, and having built, launched, and scaled our product WotNot over the last four years – one could say that “we’ve seen the movie.” We have burnt our fingers and scraped our knees. We know what it takes to create MVPs/PoCs that can be used to kick-off discussions with potential investors and acquire your first set of users.
Get in touch with us to prototype your brilliant idea today!


