

Top 15 Low Code Platforms 2025 – Selecting the Best Low Code Platform






Low code is a visual development approach that lets teams build applications faster using drag-and-drop interfaces and reusable components.
It reduces the need for manual coding and enables both technical and non-technical users to collaborate and deliver digital solutions quickly and efficiently.
Low code is becoming central to digital transformation as organizations face rising demand for rapid application delivery. Market growth is driven by the need to modernize legacy systems, accelerate innovation, and address developer shortages.
In 2026, low code platforms are expected to play a key role in enterprise-scale modernization. This article highlights leading low code trends, their benefits, challenges, and ways to choose the right platform.
This is precisely why we made a podcast on the topic. Harsh Makadia, Technology Evangelist at Maruti Techlabs, talks to Bikshita Bhattacharyya about using low code technology for building and shipping products.
He also talks about how he implemented low code technology for his client, the tangible benefits they got from the implementation, and more! Here is a small snippet from that episode. Check it out!
Low code adoption is rising quickly as organizations seek simpler ways to build applications, automate processes, and strengthen digital delivery across all business functions.
Low code usage continues to grow across enterprises as the demand for faster development increases.
Analysts estimate the market will expand significantly by 2026 due to rising investments in automation and application modernization. Businesses of all sizes are adopting low code tools to address talent shortages and shorten delivery cycles.
Low code improves agility by reducing development time and enabling faster experimentation. Teams can iterate quickly, respond to customer needs, and improve workflows without long development cycles.
It boosts productivity by empowering more contributors and fuels innovation by enabling the rapid delivery of new digital experiences across the organization.
Low-code platforms offer a powerful way to accelerate development, reduce costs, and enable cross-functional collaboration while still supporting enterprise-level scalability.
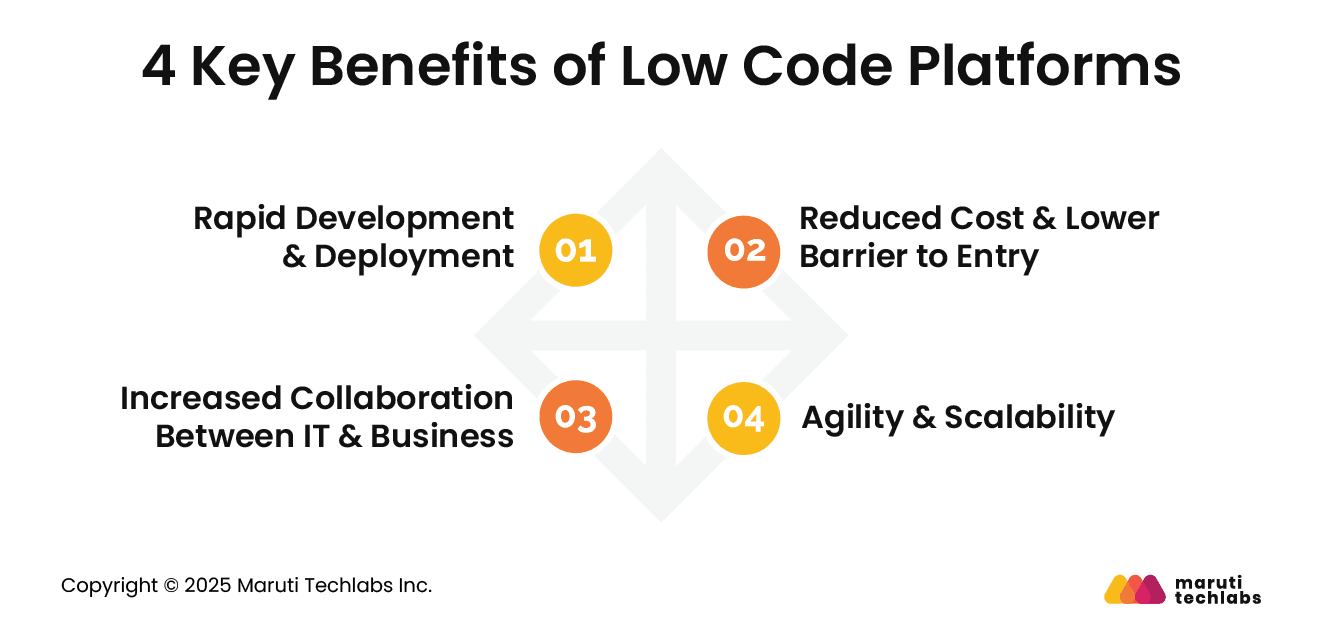
Low-code tools let teams build and launch applications much faster by using visual interfaces, prebuilt logic, and guided workflows. This reduces complexity, shortens development cycles, and helps organizations deliver solutions rapidly.
Faster deployment also allows teams to respond quickly to market changes and evolving customer expectations.
Low code reduces development costs by minimizing manual coding and improving efficiency. Smaller teams can deliver more output with fewer resources, which lowers project budgets.
It also opens application development to non-technical users who can contribute meaningfully without advanced programming knowledge, reducing dependency on specialized developers.
Low code encourages collaboration by providing shared visual tools that both business users and technical teams can use. Requirements become clearer, development cycles become more efficient, and outcomes become more aligned with business needs.
This shared environment strengthens communication, reduces misalignment, and enables faster delivery of impactful solutions.
Low-code platforms support flexible application updates, making it easy to adapt workflows and features as needs change. Many platforms offer enterprise-grade scalability, enabling applications to grow alongside the business.
Organizations can continuously enhance solutions without major rebuilds, ensuring sustained performance and long-term agility.
Low-code platforms help teams create internal tools for operations, finance, HR, and supply chain. These applications streamline tasks, improve visibility, reduce delays, and enable faster decision-making while minimizing reliance on traditional development resources.
Low-code enables the rapid development of customer portals, such as onboarding systems, self-service dashboards, and support interfaces. These portals enhance customer experience, reduce response time, and offer personalized interactions.
They also help companies deliver consistent services across channels while adapting quickly to changing customer needs.
Low-code simplifies automating routine workflows, such as approvals, document processing, and service requests. It reduces manual effort, improves accuracy, and accelerates turnaround time.
Automated processes free teams to focus on strategic work and improve overall operational efficiency across business units.
Organizations can reduce development time by up to half, lower operational costs, and significantly improve delivery speed, resulting in strong returns on digital investments.
Effective low-code development requires structured processes, strong governance, and clear collaboration between business and technical teams.
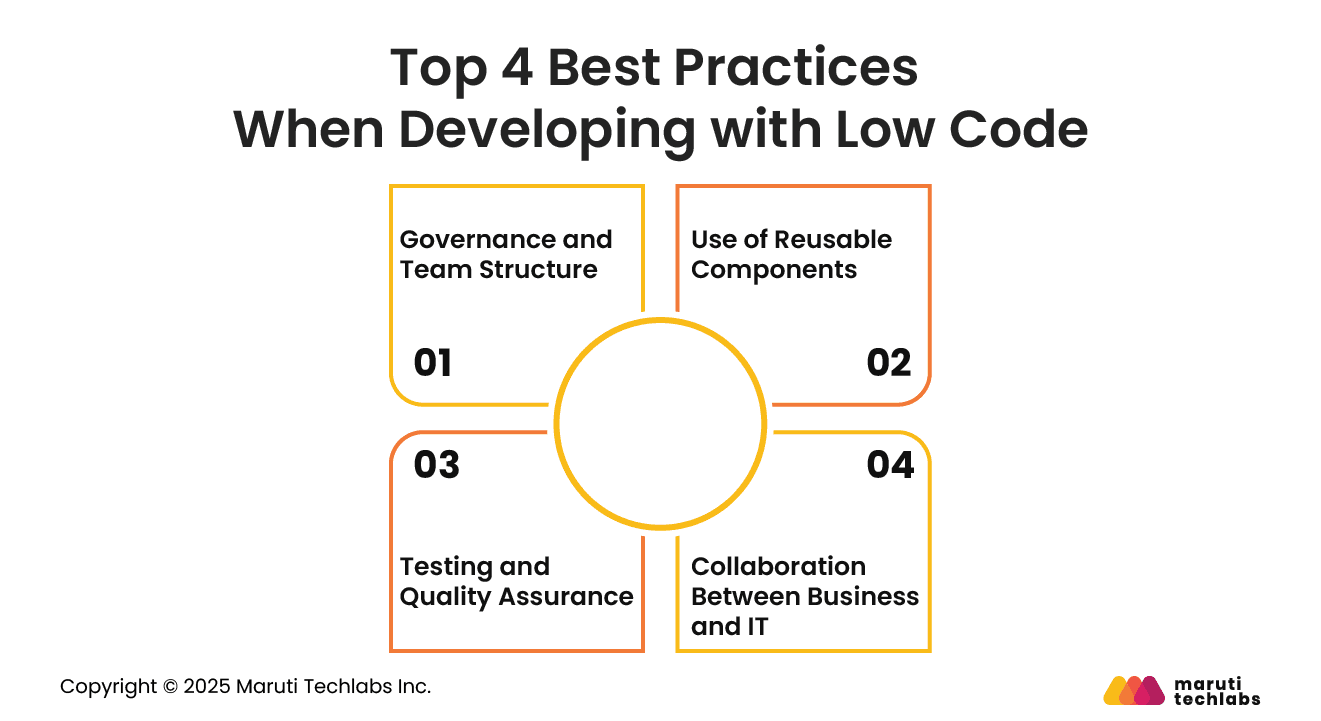
Define roles clearly and establish centralized governance for all low-code projects. Use structured approval flows, quality checks, and shared guidelines to ensure consistency.
Cross-functional teams improve coordination, reduce rework, and maintain compliance. This creates a stable environment for successful low-code development.
Encourage creation of shared components such as forms, workflows, and UI elements. Reusability saves time, improves quality, and ensures consistency across applications.
A component library also helps teams easily scale development and maintain uniform standards in large, complex environments.
Conduct thorough testing of workflows, integrations, and data handling. Validate performance under realistic conditions and ensure compliance with standards.
Automated testing tools accelerate verification and help maintain reliability as applications evolve. Strong quality assurance practices support smooth releases and long-term stability.
Encourage constant interaction between business users and IT teams to refine requirements and validate solutions. Shared workspaces and visual tools reduce misunderstandings.
This collaboration ensures solutions align with goals, improve adoption, and deliver measurable value across departments.
One of the main factors for the rise of the low code development model is faster deliverability and better innovation. They offer an environment where applications can be deployed much faster, and user experience can be continuously revised.
Some of the other reasons for the popularity of the low-code model include –
Low-code platforms require much less engineering efforts, thus automatically lowering down the cost in the long run.
Low-code development platforms make IT teams more productive by speeding up the overall app development process. Further, the robust agility of low-code platforms translates to faster deployable solutions and easily adaptable strategies.
Low-code development platforms enable apps, features, and processes to be built and modified by non-technical users without putting pressure on in-house IT teams to build, code, troubleshoot, or implement a solution.
Quality low code development platforms make it easier for developers and non-developers to build scalable enterprise solutions. In fact, one of the major reasons for the rise of low code platforms is how these help young startups and entrepreneurs build their pilot MVPs without writing any code.
Low code tools enable low code development by reducing the amount of time and manual work needed for app development in the traditional approach.
Almost all low code development platforms are built with a common principle in mind – to make it quick and easy for both developers and non-developers to design and deploy software solutions.
The following features make this possible for low-code development platforms –
If you’re looking to find the best low code tools for your specific organizational needs, here we’re discussing the top 15 low-code platforms along with their features, pros, and cons to help you make an informed decision.
OutSystems is one of the most intuitive low code platforms out there. Packed with features, OutSystems offers customizable app-creation experience and handles the entire software development lifecycle.
Another highlight of Outsystems is that the platform supports integration with any database, external enterprise systems, or custom app via pre-built open-source connectors, APIs, and popular cloud services.
The platform also comes with various pre-built modern UI templates for desktop, tablets, and mobile apps.
![Low Code Platform - [outsystems]](https://cdn.marutitech.com/9ccaa1c3-outsystems.png)
Features:
Pros:
Cons:
Mendix is one of the most well-known low-code development platforms that allow you to build apps with absolutely no coding. It also collaborates with you in real-time.
Mendix enables faster app development with an extensive set of tools for developing, testing, deploying, and iterating.
The platform’s highlight is that it’s a visual development tool that offers re-use of components to speed up the overall app development process.
![Low Code Platform - [mendix]](https://cdn.marutitech.com/d8d41621-mendix.png)
Features:
Pros:
Cons:
Appian is an excellent low-code development platform that features intelligent automation to develop powerful business applications.
Using Appian, you can collaborate seamlessly with your team members. This low code platform is so intuitive that you do not need any coding experience to work with Appian.
Features:
Pros:
Cons:
Quick Base is primarily a cloud-based RAD and database software that is widely used by developers as their favorite low-code tool.
Quick Base stands true to its name – it’s really quick in helping you build a basic form-based app. But, at the same time, it’s not the best low code tool to customize your app’s user-interface.
Features:
Pros:
Cons:
ProcessMaker makes it easy for users to automate processes, connect and extend third party systems to deliver agility to business processes. The best part is dashboards and KPIs that come inbuilt in the platform that enable easy tracking and measurement.
Features:
Pros:
Cons:
One of the fastest-growing low code development platforms, Microsoft Power Apps, allows you to build apps that are fast and features a point-and-click approach to app design.
Built natively on the cloud; it lets the developers extend app capabilities using cloud service. Further, developers can also use custom connectors to connect legacy systems with newly developed apps.
Microsoft Power Apps also enjoys the advantage of being a part of the Azure and Power Platform ecosystem. It provides excellent flexibility of integration with other Microsoft and third-party products.
Features:
Pros:
Cons:
Google App Maker requires some coding knowledge to get around. Its simple design and robust documentation make it a great platform. And needless to say, it effortlessly connects with G Suite APIs.
Features:
Pros:
Cons:
Do you think low code development can be leveraged to ONLY build static websites? Harsh Makadia does a deep dive on how Low Code can help in writing complex business logic, customizations, make API calls, & build mobile friendly applications. Take a look at the video below 👇
Unlike other low-code tools that let you deploy your apps on any public cloud or on-premises, Salesforce Lightning is only for Salesforce CRM users who want to build their own user experiences without writing any code.
Put simply; it is a low code development platform that combines the power of Salesforce with low-code app development. The platform has various tools such as SalesforceDX, App Builder, and Lightning Flow that help speed up software development.
Features:
Pros:
Cons:
A popular name in the low-code app development platform category, Zoho Creator’s drag-and-drop interface makes it super easy to build robust apps featuring forms, dashboards, and sophisticated business workflows.
One of the key highlights of the Zoho Creator is that every app comes natively mobile so that you can customize actions, separate layouts, and gestures for your smart devices.
Features:
Pros:
Cons:
Kissflow is another famous name in the free low code platforms category. It is a cloud-based low code tool and a business process management software. The platform allows users to create a range of automated business applications through a simple, easy-to-use interface.
Features:
Pros:
Cons:
Creatio is a leading low-code development platform that enables enterprises to accelerate their app development process and customize the mobile app in the time it takes to customize the desktop application.
Using the tool, you can configure the page layout in the Creatio mobile version or add a new section via wizard in no time.

Features:
Pros:
Cons:
Quixy is a no-code BPM and application development platform that can be used by any business to build complex enterprise-grade applications.
The platform has a range of pre-built solutions for multiple use cases such as CRM and project & task management.
Features:
Pros:
Cons:
An easy-to-use IDE platform, Visual LANSA allows developers to code just once and deploy everywhere. It is primarily a cross-platform development tool that values the rapid creation of enterprise-grade applications.
The platform speeds up application development by eliminating the need for developers to master varied technical skills that are usually required to produce software processes and applications.
Features:
Pros:
Cons:
WebRatio is another good low code development platform for building web, mobile, and BPA applications. It is mainly an Agile development tool that uses OMG (Object Management Group) and IFML (Interaction Flow Modeling Language) standard visual modeling language.
Features:
Pros:
Cons:
A relatively new low-code app development platform, DWKit is essentially a BPM (business process management) software but offers several advantages to developers.
The platform is a little more complicated compared to other similar solutions and requires robust developer’s skills. DWKit is an ideal tool for companies looking to build products of their own.
Features:
Pros:
Cons:
Did you find the video snippet on How should organization plan to implement Low Code Platform? to be insightful? We have a ~18 min video where Harsh Makadia gets into the weeds, and we discuss how early stage startups can benefit from Low Code Development. Take a look –
Selecting a low code platform requires a precise evaluation of business needs, technical goals, and long-term scalability to ensure successful and sustainable adoption.
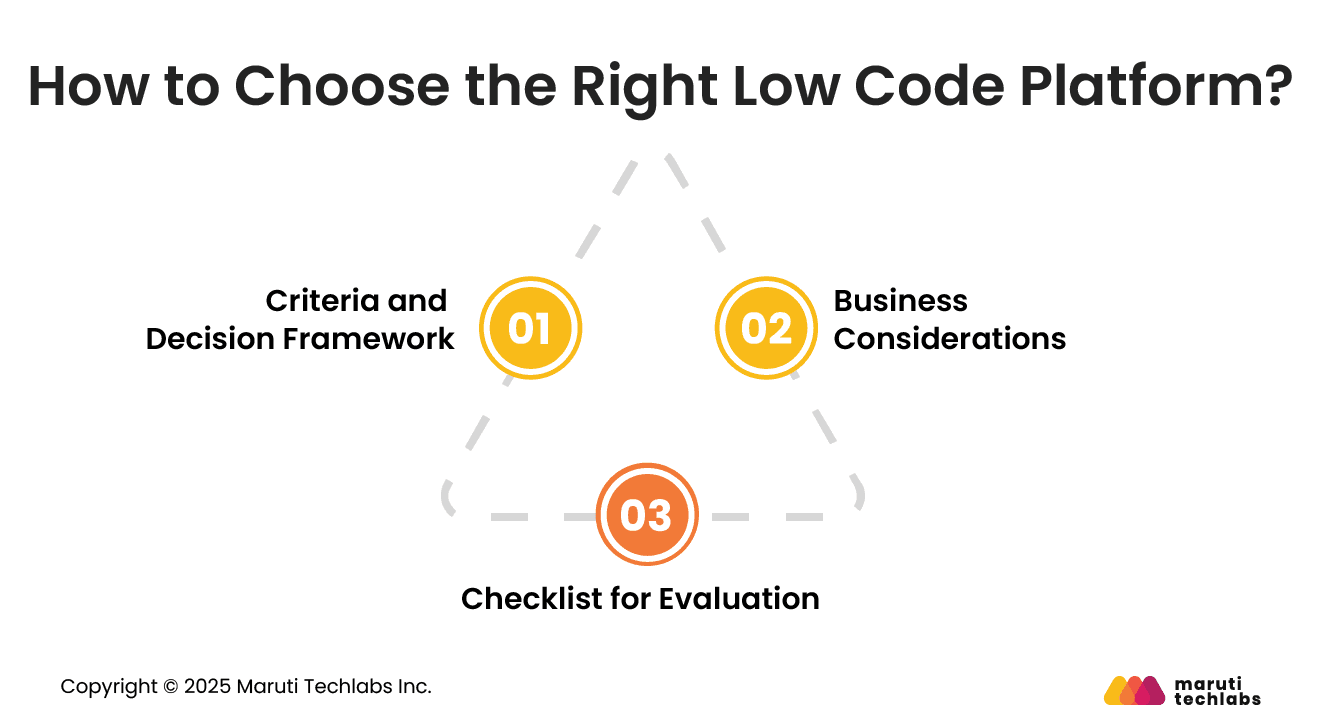
Focus on usability, integration capabilities, security features, governance controls, scalability, and available extensions. Assess how well each platform fits your workflow and team skills.
Consider long term flexibility, vendor reliability, and the platform’s ability to support complex projects. A balanced evaluation ensures an informed and strategic selection.
Smaller teams may prioritize ease of use and speed, while larger enterprises need strong governance, advanced integration, and scalability. Highly regulated industries require robust security and compliance features.
Complex projects demand flexible extension options. Align platform selection with the unique needs, size, and domain specifics of the organization.
Review security, integration options, governance controls, data management features, scalability potential, workflow automation tools, collaboration support, and ease of customization.
Validate performance benchmarks and assess training availability. Ensure the platform aligns with both immediate requirements and future expansion needs to guarantee long-term success.
Low-code offers significant advantages but also presents challenges that organizations must plan for to ensure stability, security, and long-term maintainability.
Low-code can lead to uncontrolled application creation when governance is weak. Without proper oversight, teams may build fragmented solutions that create data inconsistencies.
Clear policies, approval workflows, and centralized monitoring are essential to prevent shadow IT and maintain a strong and secure application environment.
Some platforms limit flexibility by making it difficult to migrate applications or reuse components across systems. This can restrict future choices and create long-term dependency.
Understanding platform openness, export options, and integration capabilities is vital to avoid being unexpectedly locked into a single vendor ecosystem.
Low-code platforms sometimes restrict advanced customization for complex or specialized needs. When specific functionalities require deep coding, teams may face limitations.
Understanding boundaries early helps organizations choose platforms that meet both sophisticated and straightforward requirements while balancing speed with flexibility for long-term use.
Applications built on specific low-code tools may face performance challenges as usage grows. Inefficient workflows or limited back-end flexibility can slow down operations.
Careful evaluation of architecture, scalability features, and real-world performance benchmarks ensures that the platform can support future demand without performance issues.
Low code is evolving rapidly as advancements in automation, AI, and enterprise architecture reshape how applications are built and delivered.
AI-assisted features will enhance automation, generate workflows, recommend components, and optimize designs. Low code platforms will integrate intelligent assistants to speed development and improve decision-making.
AI will also support predictive capabilities, stronger insights, and better personalization across applications.
Citizen developers will play a larger role by contributing directly to solution creation. Low code will empower employees across functions to build simple tools safely under guided governance.
This democratization increases capacity, fosters innovation, and reduces pressure on traditional development teams.
Low code will extend into complex enterprise systems with stronger integration layers, improved security, and advanced performance capabilities.
Businesses will use it to modernize large workflows, orchestrate services, and manage critical operations without sacrificing reliability or scalability.
Various low-code platforms offer different capabilities and approaches to the process of software development. While some platforms come with a shorter learning curve, others focus more on advanced integrating capabilities. While some emphasize collaborative development, other low code platforms enable better customizations.
Therefore, it is crucial to analyze your business needs and map your development journey with the tool you choose. You should also factor in the amount of development work you want to delegate to your citizen developers.
Maruti Techlabs has worked with organizations worldwide to provide end-to-end low code development services. Right from competitor analysis to PoC development to usability testing, our experts do it all!
Book a free consultation with our experts to expedite your app development and better utilise the low code tools available today!
![SL-103020-37400-03[1].jpg](https://cdn.marutitech.com/small_SL_103020_37400_03_1_9ef554f0fb.jpg)

