

Maximizing Software Quality: Types and Tools for Reliability Testing






Ensuring software performance and stability is crucial for delivering a seamless user experience. To achieve this, every aspect of the software must function flawlessly, where reliability testing comes into play.
However, executing reliability testing is complex. It requires a combination of manual and automated approaches, the right tools, and, most importantly, experts skilled in designing performant applications.
In today’s competitive market, businesses can't afford to experiment. They must deliver superior, error-free experiences swiftly, making reliability testing an essential part of the software development lifecycle.
he importance of this process is underscored by a June 2024 survey from Global Market Insights, which projects the software testing market, valued at USD 51.8 billion in 2023, to grow at a CAGR of over 7% between 2024 and 2032.
Let’s explore the benefits, types, methods, and top tools for reliability testing. Read on to gain a comprehensive understanding of how this process works.
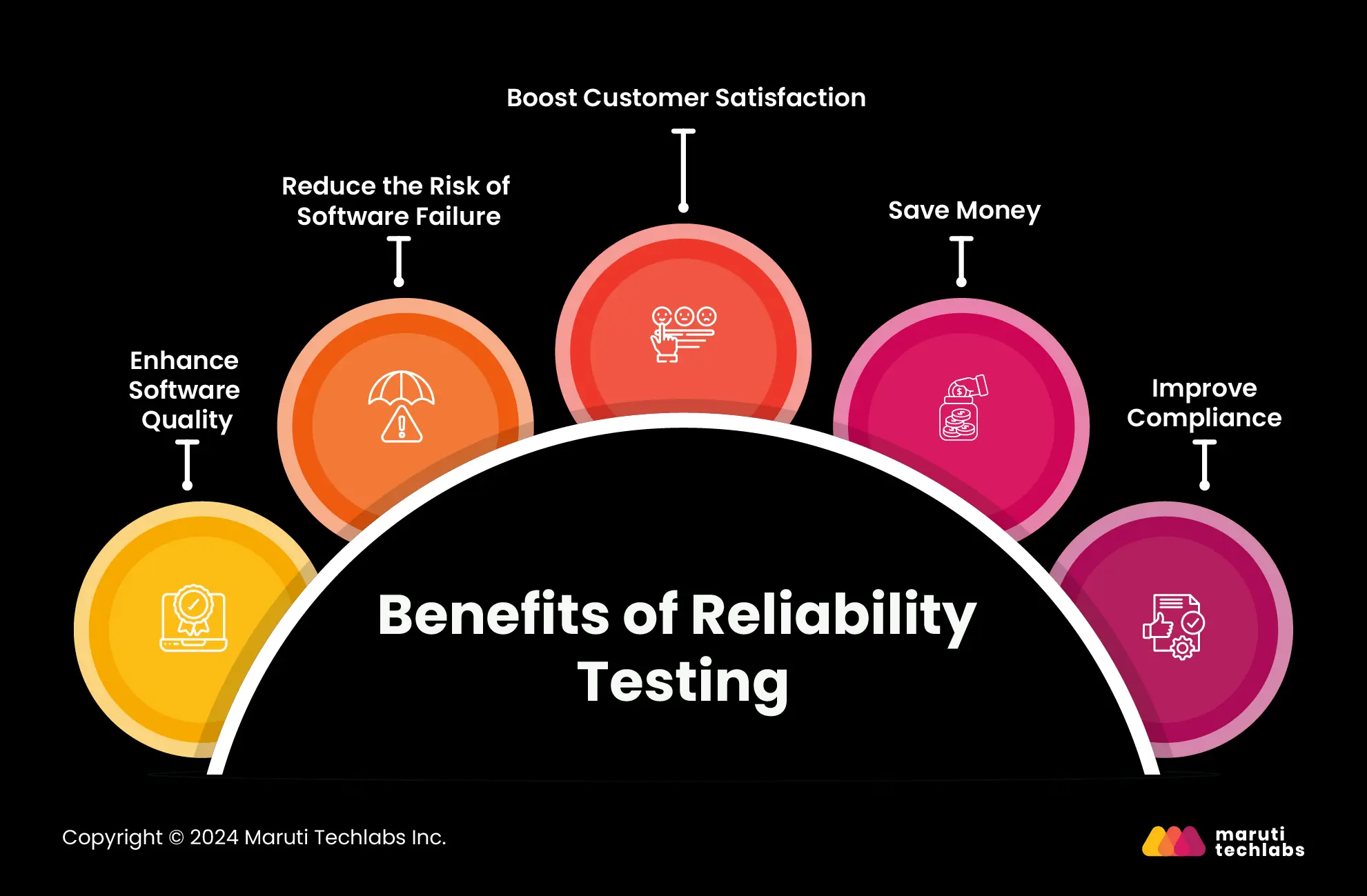
Ensuring your software's dependability can increase customer satisfaction and reduce maintenance costs. Here are the significant benefits reliability testing can bring to your software.
Reliability testing points out defects that might hinder the software's use. This enhances the software's overall quality, increasing its reliability for users.
Software failure can significantly impact an organization's reputation. Reliability testing helps businesses save money while diminishing the risk of software failure in production.
Reliable software would meet user expectations, increasing customer loyalty and satisfaction. It also increase user’s trust in a brand by increasing consistency while reducing breakdowns in a software.
With reliability testing, you can identify and fix bugs early before they reach production, eliminating expensive software fixes.
Some industries may require software testing before deployment. Reliability testing can help you comply with the rules and regulations and avoid fines and penalties.
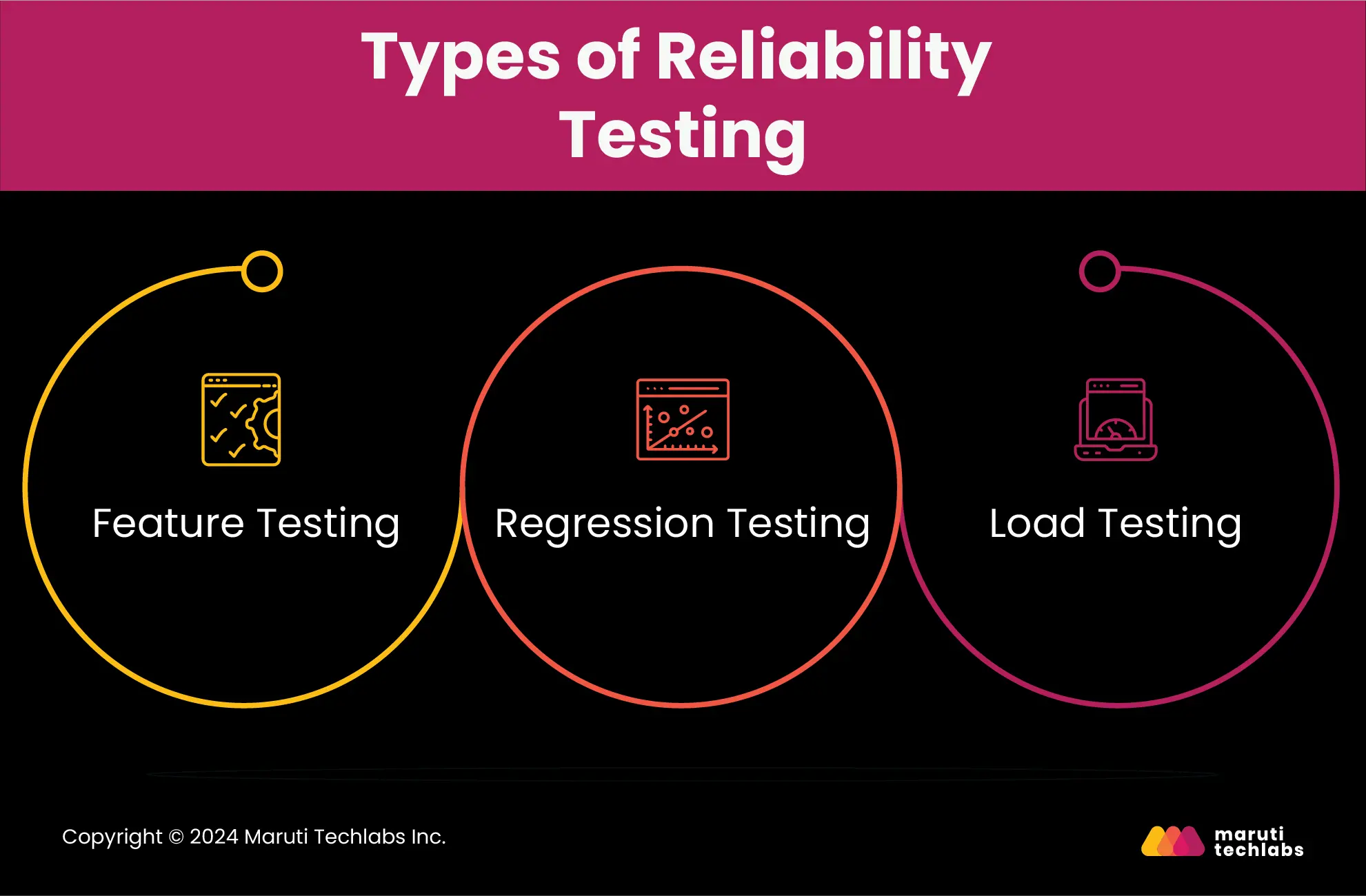
Reliability testing mimics real-world usage and scenarios that help businesses discover software failure rates.
Many different types of tests contribute to the reliability of software. Let’s observe the most common ones.
In this type of testing, all features have to be executed once to verify individual functionality. One must also check if each operation is appropriately executed, ensuring minimal module interaction.
Regression testing assures software consistency by checking whether it’s error-free after adding a new feature or updates to the system. Therefore, it’s suggested that a regression test be performed after every new feature or software update.
Load testing determines an application's sustainability, ensuring its performance doesn’t degrade when placed under a high workload.
Reliability testing is a complex and costly process. Therefore, its execution requires thorough planning and a detailed roadmap. The method also requires specific prerequisites, such as data for the test environment, test schedules, and test points, that must be built or collected before implementation.
Here are some of the notable aspects to consider when conducting reliability testing.
There are a few factors that can create hindrances that you should consider.
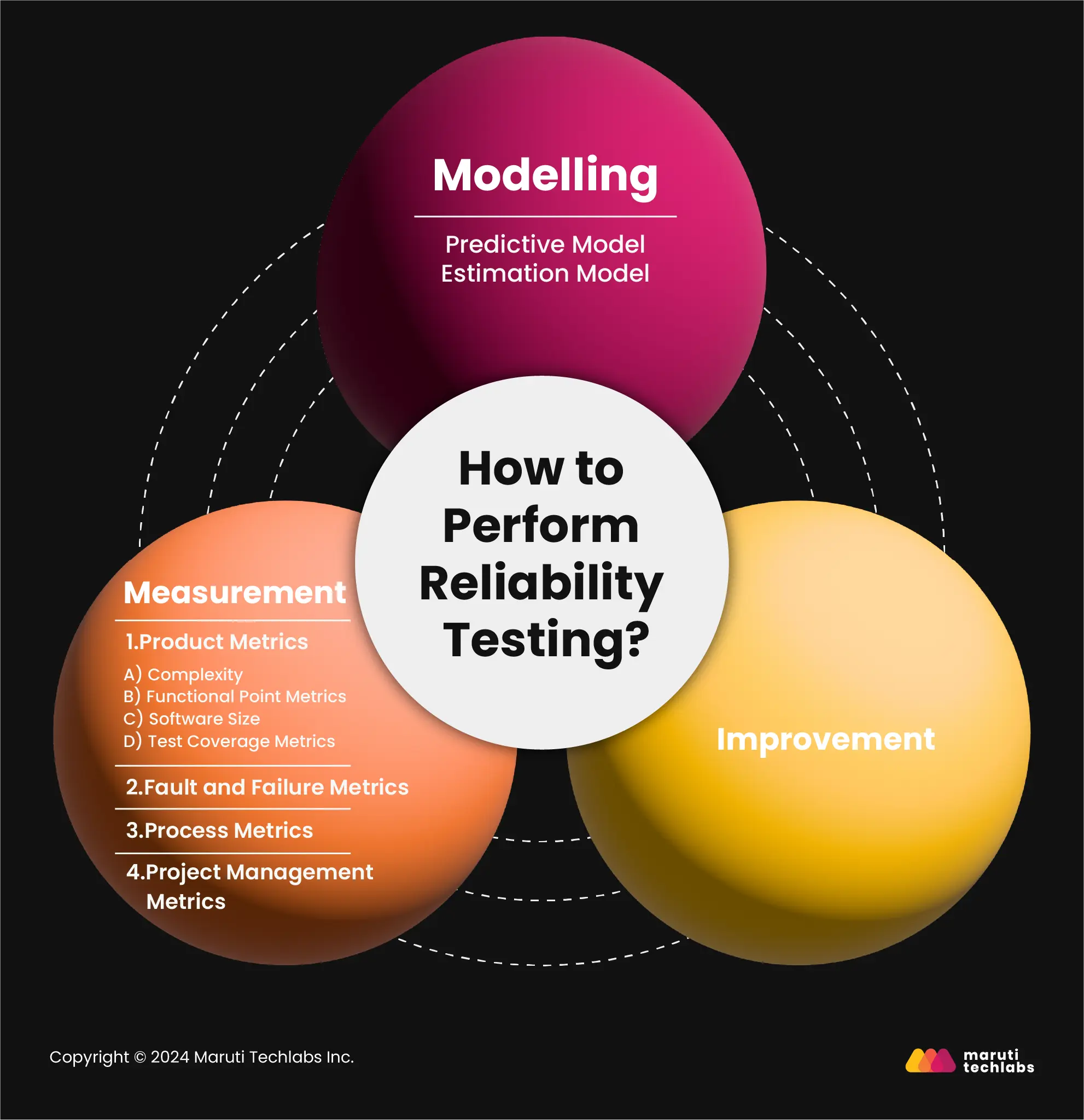
Reliability testing can be categorized into three main steps:
Firstly, we must determine a suitable reliability model for the problem to achieve results that align with your business objectives. However, we would have to experiment with numerous models, as trying only one will not yield the desired results. To approach this, one must be ready to use assumptions and abstractions.
These models can be further divided into two categories.
It’s challenging to learn a software's reliability without conducting tests. There are four categories for measuring software reliability:
Let’s briefly examine the above categories.
The product metrics comprise four different metrics, namely:
A. Complexity
Software's reliability is directly proportional to its complexity. Assessing a program's complexity requires creating graphical representations of the code.
B. Functional Point Metrics
Irrespective of the coding language, this metric is concerned with the functionality offered to the user by taking a count of input, output, master files, and more.
C. Software Size
It measures the software’s size by calculating the lines of code that exclude the comments or non-executable comments while only considering the source code.
D. Test Coverage Metrics
It performs end-to-end tests on the software, offering insights into fault and reliability.
Here are the parameters used for these metrics.
- MTBF (Mean Time Between Failures)
- MTTF (Mean Time To Failure)
- MTTR (Mean Time To Repair)
Quality and process metrics go hand in hand. Therefore, process metrics are constantly monitored to enhance software quality and reliability.
A great project, involves acute project management tactics. Reliable software is an outcome of a planned development cycle, including risk management process, configuration management process, and more.
This is the final stage of the reliability testing process. Software improvements are subject to the issues faced in the development cycle and the complexity of the application. However, these improvements are often compromised due to time and budget constraints. Therefore, keeping a check and ensuring developers prioritize improvements with other aspects of the project is crucial.
Successfully concluding your reliability testing process and obtaining maximum results necessitates intricate planning and management. Let’s observe the essential steps to conduct and gain maximum results from reliability testing.
You must have a vision of what you want your end product to look like. This clarity will help you bridge the gap between your current version of the software and your desired software.
An operational profile amalgamates realistic test scenarios, such as usage patterns and workload conditions, that mimic real-world use. It can be a mirror that reflects how actual customers will interact with your software.
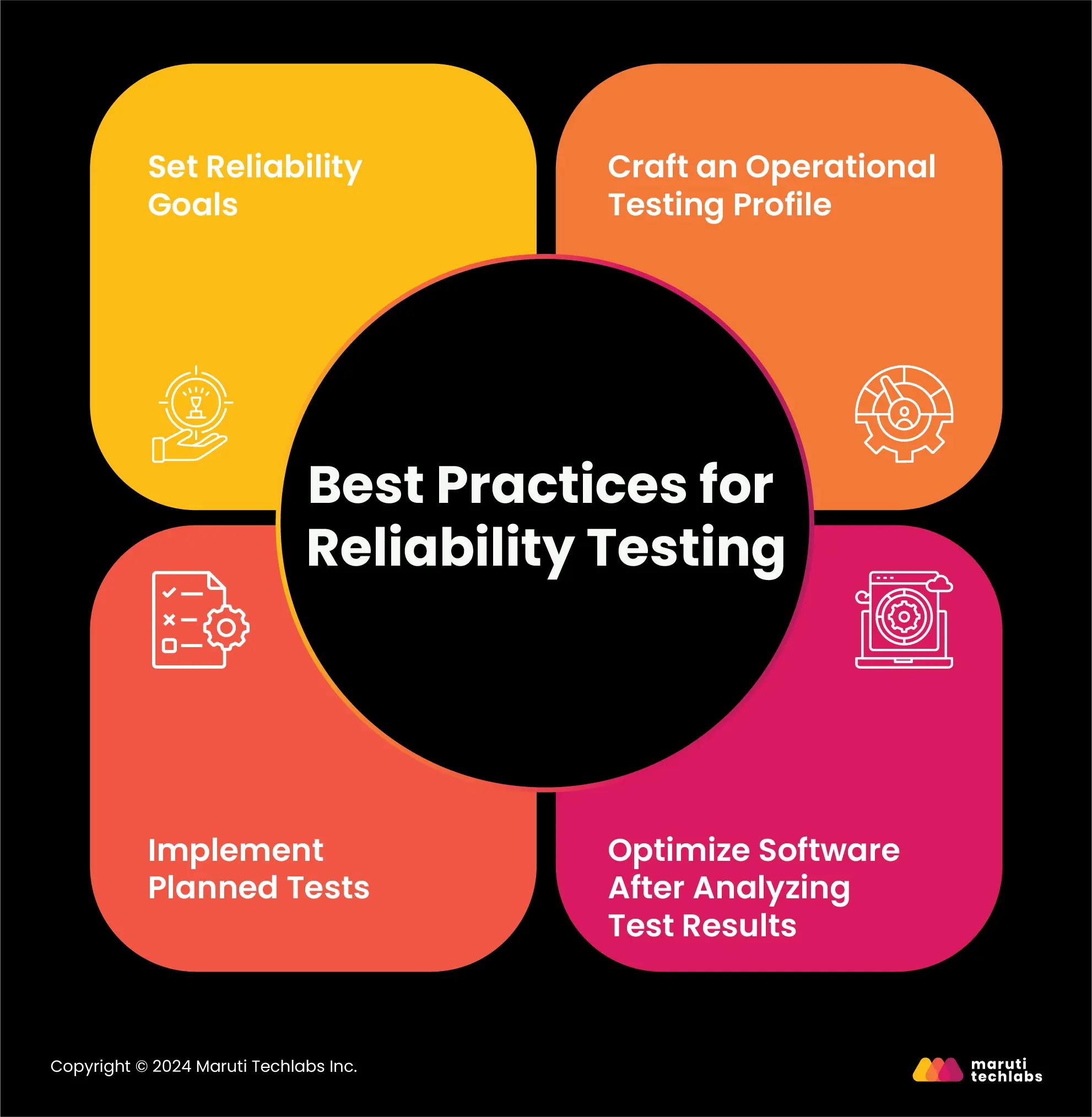
Curate testing scenarios to conduct stress testing, load testing, endurance, and other additional parameters. Plan a chronological execution of these tests while observing your software’s performance, stability, and sturdiness.
Once you conclude all your tests according to the operational profile, it’s time to examine the results and identify areas for improvement. This analysis helps identify weak areas and performance bottlenecks, assisting with architectural enhancements and optimization.
Here are three pillars of reliability testing: Modeling, Measurement, and Improvement.
Various modeling techniques, such as prediction and estimation, can be used to test software's reliability. One can leverage existing software development data to estimate current and future performance and reliability. You can consider factors such as data sources and their importance in the development cycle and the specific time frame and select a suitable model for your software.
Software reliability isn't tangible. However, conducting different tests and observing results and related metrics can clarify how your software would fare under real-time scenarios. To learn this, one can examine metrics like product, process, project management, fault and failure metrics, and mean time between failures (MTBF) to identify areas for improvement.
Improvement strategies are subjective to software issues or features. You can use a tailored approach based on the complexity of your software module, keeping in mind the time and budget constraints.
Here are the top reliability testing software available in the market today.
SOFTREL is a veteran that has been offering reliability testing services since 1991. It offers various services, such as the ‘Software Reliability Toolkit’, ‘Frestimate Software’, and more, to examine software reliability.
Sorel is the most futuristic tool on the market. It offers four types of reliability growth tests: arithmetical Mean, Laplace Test, Kendall Test, and Spearmann Test. It also supports two types of failure data processing: inter-failure data and failure intensity data, and it is a preferred choice for reliability analysis and prediction.
SMERFS, developed in 1982, is an abbreviation for Statistical Modelling and Estimation of Reliability Functions for Software. It offers two versions: SMERFS and SMERFS Cubed. It is primarily used to predict failure and fault rates by examining raw data.
Many new advancements in reliability testing can enhance testing accuracy and efficacy. Here is a list of these promising developments.
Advanced AI and ML algorithms are already employed to predict system and software reliability. For instance, AI-powered tools can examine stress test results and suggest patterns to discover an intricate reliability problem. These tools combine historical data and real-world scenarios to determine potential issues before they become a reality.
Software’s resilience to cyber-attacks has become an essential parameter to test as more systems connect to the Internet. AI tools offer invaluable insights by simulating cyber-attacks and pinpointing vulnerabilities.
The use of IoT devices is exponentially increasing. As these devices are interconnected, ensuring their safety and reliability is essential. Many new practices are available to check these devices' compatibility, interoperability, and data-handling capabilities. For example, IoT devices on mixed networks and environments can be thoroughly tested using cloud-based testing platforms.
The popularity of wearable devices has increased by many folds in the past five years. Therefore, reliability testing is essential to ensure that they can withstand everyday wear and tear. New methods, such as testing wearable devices in temperature, humidity, and vibration chambers, are introduced to check for durability.
Advanced simulation and virtual testing allow testers to test systems in a secure and controlled environment without fear of damaging the production environment. They're also used to test systems with myriad parameters and conditions that would be impossible to curate in a real-world environment.
Automated tests reduce the possibility of human error by consistently and continuously conducting tests. Additionally, applications and systems can also undergo tests under different conditions and for longer durations using automated testing.
Your application or software represents your business’s commitment to enhancing customer access to your products or services.
More and more businesses today are realizing this and have started making reliability testing an evident part of their SDLC. This approach has eliminated the back and forth with changing or upgrading multiple parts of their app code, fostering timely changes and upgrades.
However, reliability testing can be costly compared to other testing paradigms, especially if you have a highly complex application. So, to make this process most productive and cost-efficient, you should have a well-documented test plan executed by experts from an experienced software product development company. Companies investing in software development New York are increasingly adopting this strategy to reduce time to market while ensuring the best ROI for their invested money and resources.
By following the practices mentioned above, organizations can maximize their software potential and offer exquisite services to their customers. If you're still skeptical about conducting reliability testing correctly, it's better to consult a company offering automation, functional, performance, and security testing services.
Reliability and validity refer to how proficiently a method can measure something. Reliability concerns consistency, and reliability concerns whether results can be obtained with similar conditions. Validity represents the accuracy of a measure, stating whether the results represent what the tests were designed to measure.
Reliability analysis states the credibility and consistency of a measurement scale—consistent results are observed upon repeating the process several times.
Reliability in API testing refers to how performant an API is when put under stressful conditions. A reliable API is predictable, well-versed, and offers maximum uptime with low latency.
The four stages of reliability testing include:


