

Your Complete Guide To Rapid Application Development (RAD)






The traditional waterfall model of software development emphasizes on strict planning, but leaves very little room for incorporating client feedback along the way. This often leads to client’s suggestions resulting in restarting the development phase from the beginning. Rapid application development(RAD) makes up for all the shortcomings of the waterfall model.
Rapid application development follows a continuous iteration process that enables developers to respond to customer feedback and requests during the development process. The Rapid Application Development framework enables software developers to develop and deploy quality apps and software quickly.
Want to know more about the Rapid Application Development model? Read on to get answers to all the questions you have about it.
As suggested by the name, RAD is all about rapid development. It is a model that produces prototypes at high velocity. The customer then provides feedback on the prototype. The feedback is used to make the product live up to the customer’s expectations.
James Martin created the Rapid Application Development model to overcome the waterfall model’s pitfalls and make the software development process more adaptive.
The waterfall model focused on detailed planning at the beginning of each project and creating a well-laid out project roadmap. On the other hand, RAD focuses on developing fast prototypes.
RAD enables developers to work on various independent prototypes parallelly. These are all integrated in the end to create a complete software product.
The prototypes are shown to the client for their feedback when they are completed. The client provides their opinion on the prototype. The developers then take this feedback and make the necessary changes to the prototype. The cycle is repeated until the client accepts the prototype.
Since rapid application development is a continuous iterative process that only stops with the client’s satisfaction, it does not have a strict timeline.
While there are numerous steps involved in the Rapid Application Development model, you can broadly group them together into four phases.
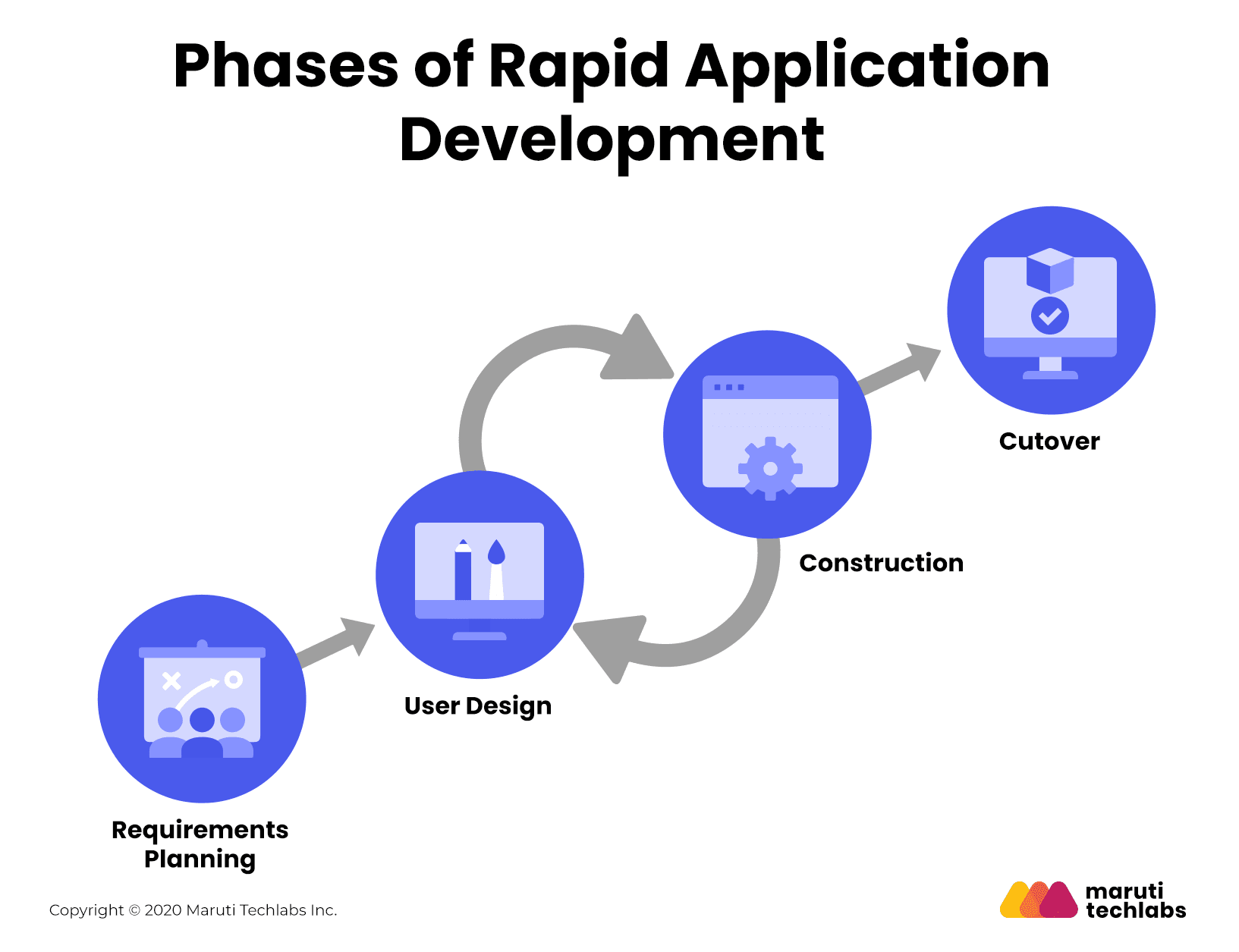 Requirement Planning
Requirement Planning
Every project, irrespective of the framework, has to start with the gathering of requirements. The clients present what they expect the software to do and the features that should be there.
While the requirements gathering phase is common across all software development models, the time spent on the phase differs. Since RAD treats the software as a pliable object, the requirement gathering phase needs to be detailed. It is very much likely that the requirements are going to change along the way.
At the end of this phase, all the stakeholders must reach a consensus on the requirements.
User Design
The next step is where the development starts. Here, the developers begin creating the prototypes. These are then sent to the client for testing and feedback. The developers take the feedback and make the necessary changes.
It is an iterative process that requires heavy involvement from the client’s side. The repeated prototyping and testing will smooth out any bugs in the systems and gaps in understanding the requirements.
The development moves to the next stage only when the client approves of the prototypes.
After the second phase, you have parts of the product but not a complete product. The pieces are put together to create a complete working model in the construction phase.
The client provides feedback and inputs in this phase, too, if needed. In this stage, you construct and verify the system, test it, and prepare for the final transition.
The cutover phase is the final phase in RAD. The working product is ready for deployment. In the cutover stage, you need to work out data conversion and the change from the existing system to the new system, test the product, and train its users.
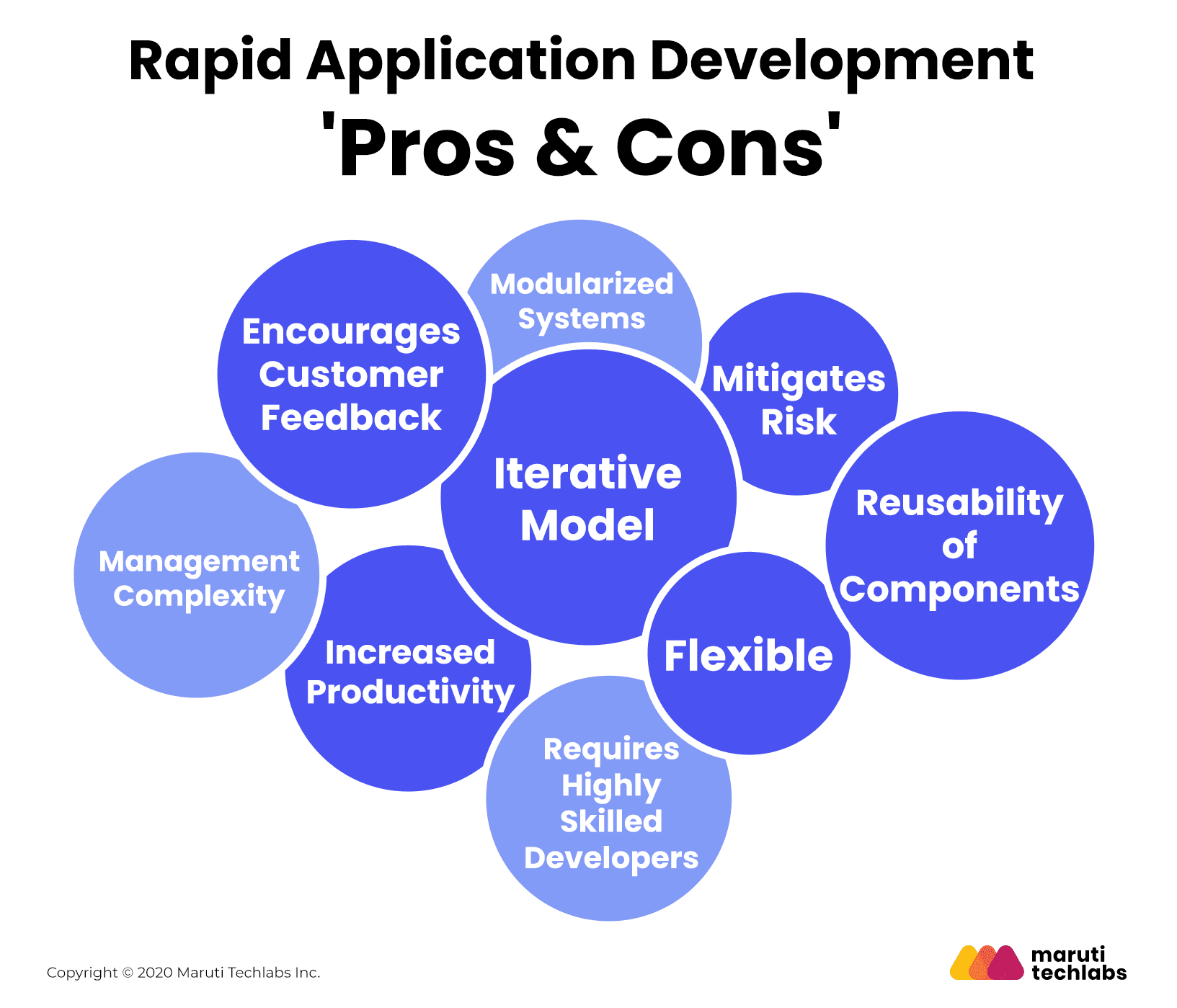
Before adopting any model for software development, you also need to know its advantages and disadvantages. No system is perfect, but the benefits may outweigh the drawbacks in some cases. Here are the Rapid Application Development advantages and disadvantages that you must consider to make an informed decision.
Speed is the primary motto of Rapid Application Development. With rapid prototyping and continuous testing, the software development cycle takes a much shorter time than traditional models.
Since the product is built to the customer’s specifications, the chances of certain features being rejected in the end product are nil. The time and resources invested in the project are not wasted in RAD, making it a cost-effective model.
Since the client provides feedback at every step of development, the result is software that meets the client’s expectations. A happy client leads to happy developers.
There is also a particular joy that developers get during the development process when the client appreciates their work. It motivates them to work harder.
Since the requirements in RAD are not set in stone, it becomes easier to mitigate risks even when they appear after the development has started.
The developers have to foresee the client’s requirements and spend more time understanding the needs to eliminate too many development iterations.
It calls for highly skilled developers with strong modeling skills. The project suffers if the developers are not up to the mark.
While it is easier for a small team to collaborate, constant communication can become complicated when the team is large.
Rapid Application Development builds only those projects/systems that can be modularized. RAD breaks down the software into different modules. The team then develops prototypes parallelly, based on the various modules. Not all software requirements support modularization.
The success of RAD relies on active client participation. The client invests a significant amount of time in testing the product and providing feedback. While it does guarantee a high-quality product, not all clients will be willing to participate enthusiastically in the process.
RAD and Agile may seem quite similar at first glance, but they are not the same because of differences between them. You can think of RAD as a precursor to Agile. RAD came into existence almost a decade before Agile.
Both RAD and Agile aim to deliver working software that meets the client’s expectations by providing continuous delivery and adapting the software as per the clients’ requests. The client is allowed to change the requirements during the development of both RAD and Agile. The similarities between the models end here.
Here are the differences in Rapid Application Development vs. Agile:
RAD is often compared with the waterfall model as it was developed to overcome the challenges posed by the waterfall model. RAD promises faster development, adaptability, client satisfaction, and continuous delivery. On the contrary, the waterfall model is about meticulous planning and sticking to the timeline.
RAD is more suited to the needs of software in the current scenario. However, in specific projects where the requirements can be locked at the beginning and timely delivery is critical, the waterfall model may prove to be the better choice.
To help understand the concept of RAD better, here’s a case study of the RAD model working in real-life.
Consider the case of developing Face. The Face is an intra-organizational communication tool for the Public Relations Department division of a large utility company in the UK. Face was supposed to have a diary, a project management module, and a project management manual.
The team developed the project in an amazingly short short span of three weeks. This was facilitated by the users and the developers working at the same location, which enabled constant communication between them. The developers could show low-tech prototypes to the users, who would then provide feedback on the prototype.
The resultant system was widely accepted and became quite popular within the organization as it met all users’ requirements.
RAD is a radical software development model that can meet the demands of today’s businesses. However, the project needs to meet some conditions to succeed with a RAD model.
If your project meets all these criteria, you should consider choosing the RAD model for software development.
Maruti Techlabs has helped businesses from around the world achieve the rapid application development framework. RAD helps you reach a satisfactory final product faster by factoring in your client’s feedback at each stage of development.
Our experts in rapid prototyping follow Agile, Lean, and DevOps best practices and the perfect execution methodology to create a superior prototype. From understanding your requirements to deploying the final product, we do it all with precision.
To bring your ideas to life, get in touch with us here.
Rapid Application Development (RAD) is a software development methodology that emphasizes fast prototyping and iterative feedback to build and refine applications quickly, with active involvement from users throughout the process.
Unlike traditional models like Waterfall that rely on long upfront planning, RAD focuses on rapid prototype creation, frequent iterations, and continuous user feedback to adapt and improve the product as it evolves.
The RAD framework typically includes:
These phases help teams build, validate, and refine software quickly.
RAD offers faster time‑to‑market, better alignment with user needs, cost efficiency, improved flexibility to handle changes, and higher customer satisfaction through continuous feedback.
RAD can lower overall costs by reducing rework, shortening development cycles, and enabling early issue detection through iterative prototyping.


