

AI Governance: Building Trust And Compliance With Reliable AI






AI governance establishes the rules, accountability, and protections needed to ensure that AI systems are safe, ethical, and aligned with human rights. It helps mitigate risks such as bias, privacy breaches, harmful decisions, and model drift. Without effective governance, organizations risk legal exposure, reputational damage, harm to individuals, and erosion of public trust.
Robust AI governance strengthens an organization’s reputation by demonstrating responsible and ethical practices. It builds confidence among customers, partners, and stakeholders through clear policies, transparency, and accountability. In addition, strong governance ensures compliance with regulatory frameworks, such as the GDPR, the EU AI Act, and ISO 42001, thereby reducing the likelihood of fines or legal penalties.
Effective governance also enhances agility: organizations with governance structures in place can more easily adapt to new laws, respond to regulatory changes, and sustain innovation without being disrupted by compliance challenges.
This article explores the key pillars of AI governance, emerging roles in the field, practical steps for implementation, and the broader value it brings to organizations beyond compliance.
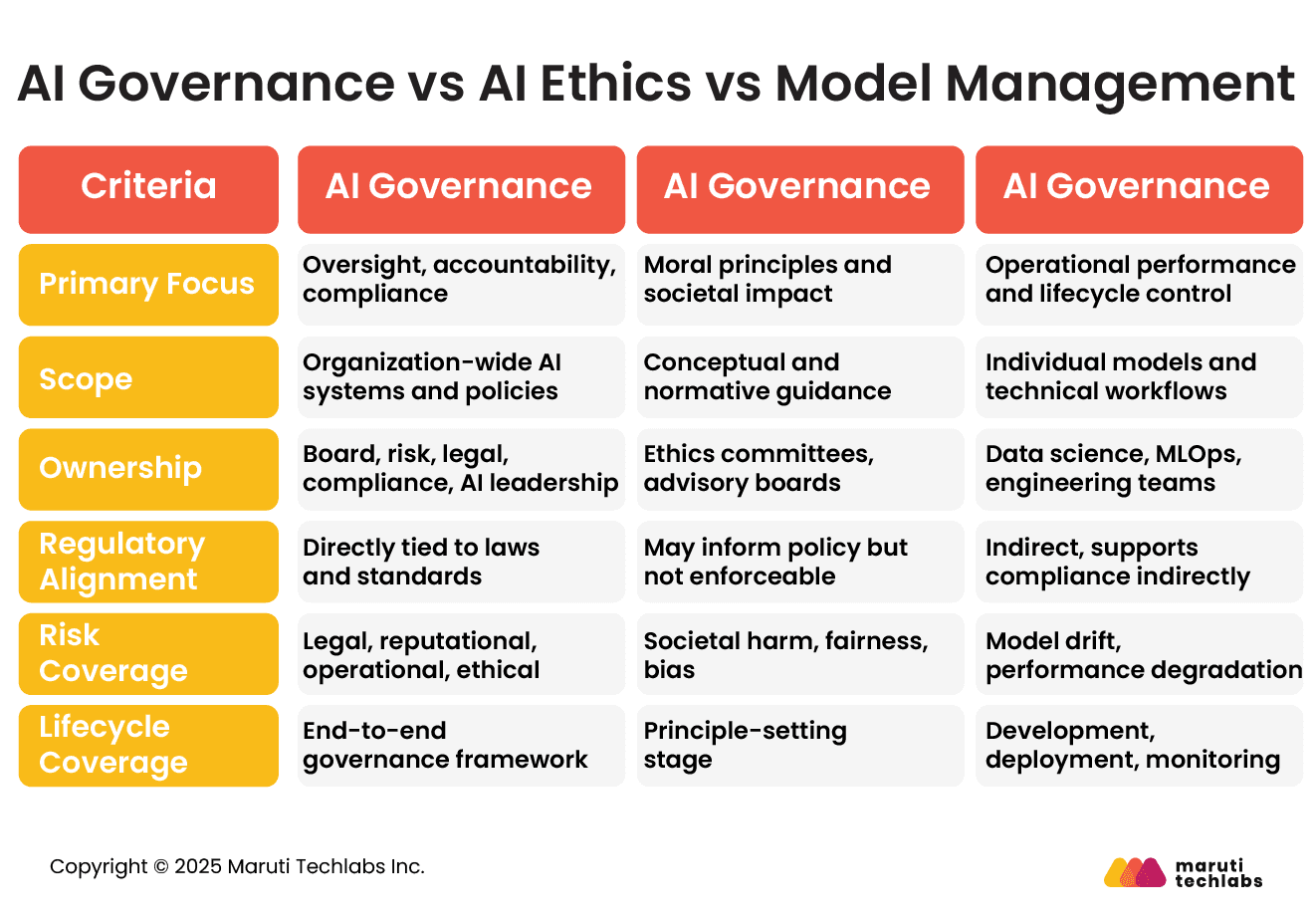
Responsible AI governance is the structured framework of policies, controls, processes, and accountability mechanisms that ensure artificial intelligence systems are designed, deployed, and monitored in a lawful, ethical, transparent, and risk-aware manner.
It operationalizes principles such as fairness, explainability, privacy, safety, and security across the AI lifecycle from data collection and model development to deployment and post-production monitoring.
It aligns technical practices with regulatory requirements such as the EU AI Act and data protection laws like General Data Protection Regulation. Ultimately, responsible AI governance protects stakeholders, mitigates risk, and ensures sustainable, trustworthy AI adoption at scale.
At the heart of AI governance are three essential pillars worth examining. They include:
Verifies the confidentiality and integrity of the data used while safeguarding personal information. This encourages users to share their data for AI applications, fostering trust.
Additionally, it enhances brand reputation and mitigates regulatory risks. A suggested way to maintain privacy is to eliminate Personal Identifiable Information (PII) before feeding it into the model.
Helps avoid bias and discrimination. Most biases stem from the data on which AI models are developed. Leveraging better modeling techniques is a great way to balance these biases.
Bias can also be reduced by improving the explainability of AI decisions. It fosters trust and accountability. Adhering to these principles enables the creation of AI systems that minimize harm, thereby making them more inclusive, trustworthy, and ethical.
Ethics play a crucial role in the application of AI in business contexts. Organizations must consider whether AI is genuinely helping users or manipulating them, and whether people are fully aware that AI is being used.
Accountability ensures that the creators of these AI systems are held accountable for their actions and decisions. This governs the use of AI across different sectors and industries.
AI systems can introduce compounding risks—bias amplification, data leakage, regulatory violations, and operational instability—that escalate rapidly once deployed. Reactive governance responds after harm occurs, often resulting in fines, reputational damage, or system shutdowns.
Proactive governance embeds controls before and during development: risk classification, impact assessments, audit trails, explainability standards, and continuous monitoring. Regulatory frameworks like the EU AI Act increasingly require documented risk management and transparency by design.
In high-stakes sectors such as finance and healthcare, preventative controls reduce legal exposure, improve stakeholder trust, and enable sustainable AI scaling rather than crisis-driven remediation.
As AI adoption accelerates, organizations are creating specialized roles to manage its risks and opportunities.
Here are the new roles that have emerged since the advent of AI.
Building on their expertise in enterprise technology infrastructure, CIOs are shifting towards AI governance oversight.
This is one of the most prominent roles in AI governance. It encompasses responsibilities related to AI strategy, implementation, and risk management.
Responsible for maximizing the value of data assets, the CDAO ensures both quality and governance while fueling AI systems.
This role focuses on executing responsible AI practices within an organization. The role differs from the CAIO position, being more operationally focused and involving senior leadership.
As AI operations scale, they demand specialized individuals to manage their models in production. This role differs from development roles, focusing on the operational aspects of AI lifecycle management.
Organizations today are creating dedicated roles to promote responsible AI practices. This is one such role that addresses regulatory and ethical concerns surrounding AI.
The increased use of AI systems demands roles that can address the unique security challenges that arise from this technology. This includes model theft, adversarial attacks, data poisoning, and other forms of malicious behavior.
Turning strategy into action requires a clear roadmap. Here are a few steps that organizations can follow while executing their AI governance framework.
Begin this journey by identifying high-risk applications, such as predictive hiring and facial recognition. Examine your AI systems closely and be vigilant for potential security risks, biases, and compliance gaps.
Study global regulations like the EU AI Act, OECD AI Principles, NIST AI RMF, and more to develop an AI code of conduct. Examine these governance initiatives by creating an AI ethics committee.
Develop a system that tracks AI decisions in real-time. Monitor compliance violations by conducting regular internal AI audits to ensure adherence to standards.
Conduct extensive and mandatory training sessions on responsible AI use for executives, developers, and data scientists.
Eliminate AI-driven cyber threats by employing stringent data protection measures. Ensure that AI’s decision-making process is transparent and explainable to employees, customers, and regulators.
To ensure safe, consistent, and compliant use of AI across your organization, it's imperative to establish stringent policies and guidelines. The critical areas include:
Define use cases on how different departments or business units can use AI tools, including LLMs. Highlight the importance of copyright/IP concerns, output review, data usage, and restrictions with public AI services.
It’s essential to have a formal review and thorough assessment before integrating third-party AI tools. This includes assessing model transparency, data management, vendor practices, and alignment with internal compliance standards.
Manage the AI model lifecycle by introducing specific and standardized procedures. This includes training validation, data selection, deployment criteria, checking robustness and bias mitigation, and other related tasks.
Leverage renowned frameworks like NIST AI Risk Management Framework (AI RMF) and OWASP AI Security & Privacy Guide (AISVS) to curate engineering best practices and development guidelines. This could include model evaluation, threat modeling, secure coding, and ongoing risk monitoring.
Here, we examine how AI governance has evolved into a vital business asset and how organizations are utilizing it to drive enterprise value.
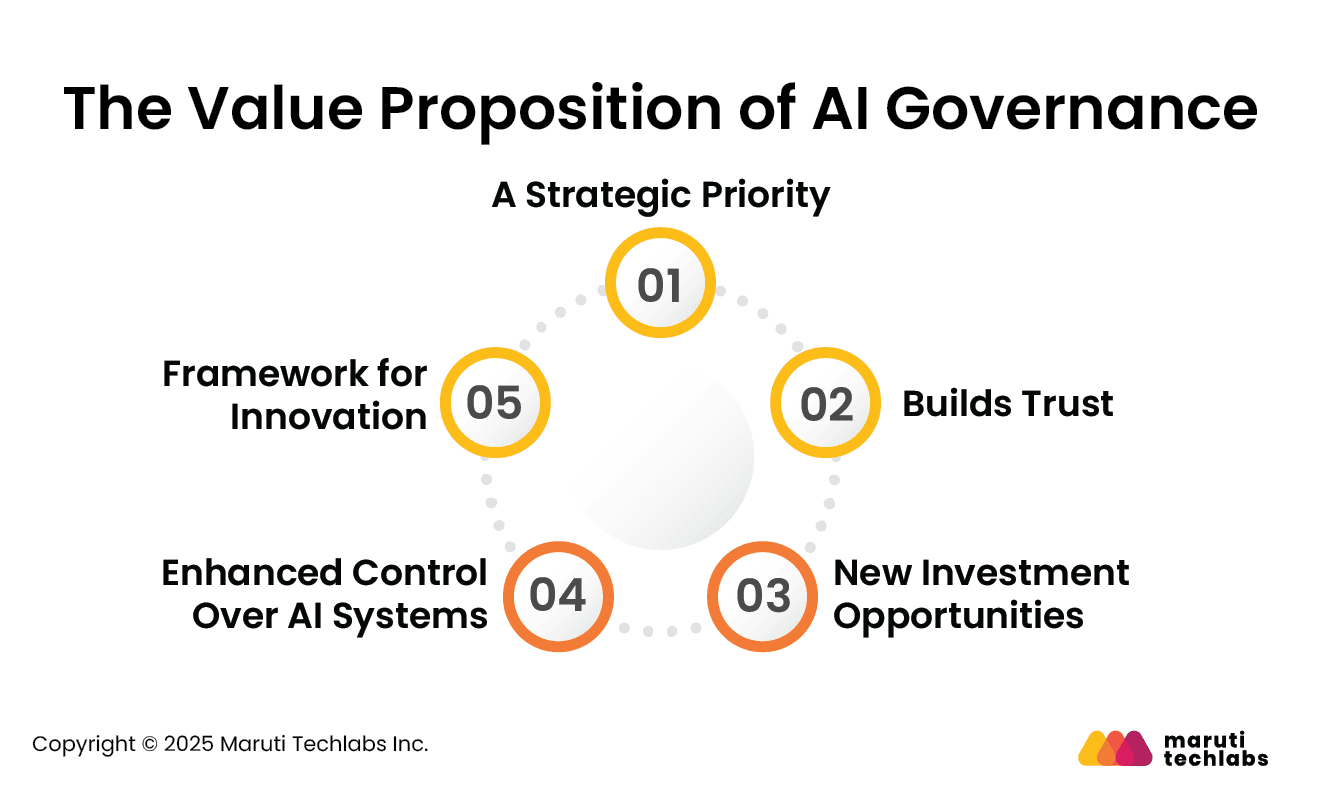
AI governance is now a board-level concern, with regulators demanding oversight and leaders seeking assurance. To address this, CDOs are creating Responsible AI Frameworks that ensure fairness, transparency, and accountability.
Organizations that embed such frameworks empower teams to review projects, align them with ethical standards, manage risks proactively, and provide leadership with clear visibility into AI initiatives.
Customers and regulators increasingly expect proof of responsible AI use. Data leaders address this by aligning AI practices with brand values, maintaining transparency, and setting safeguards to prevent misuse.
Demonstrating accountability in areas such as customer engagement, service delivery, or content creation helps organizations strengthen trust and convert ethical responsibility into business value.
Forward-looking leaders view regulation not as a burden but as an opportunity to strengthen data foundations. Preparing for compliance often unlocks funding for initiatives such as metadata management, documentation, and lineage tracking.
These investments not only reduce duplication and risk but also accelerate AI deployment, enhance decision-making, and enable innovation at scale.
As organizations adopt more third-party AI solutions, maintaining control becomes critical. To mitigate risks such as bias or opaque “black-box” models, governance is increasingly embedded into vendor procurement and evaluation.
Precise requirements for documentation, explainability, and ethical standards ensure external partners align with organizational policies from the outset, giving data teams greater control over the AI ecosystem.
Regulation and innovation can go hand in hand. Governance guardrails provide structure that supports safe experimentation, enabling creativity while minimizing risks.
By treating regulation as a framework for innovation, organizations can build readiness, increase trust, and enable smoother adoption of new AI capabilities across the enterprise.
AI governance is no longer optional. It ensures AI is ethical, transparent, and accountable while aligning with business goals. From embedding governance in procurement to utilizing regulation as a catalyst, leading CDOs are demonstrating that strong guardrails don’t hinder innovation; they enable it.
Effective AI governance strikes a balance between compliance, trust, and performance. It protects reputation, strengthens customer confidence, and equips organizations to adapt to fast-changing regulations. Most importantly, it empowers data leaders to unlock innovation responsibly.
At Maruti Techlabs, we help organizations design and implement AI governance frameworks tailored to their specific business needs.
From AI readiness assessment to responsible AI deployment, our Artificial Intelligence Services ensure your AI systems drive value with trust at the core.
Contact us to begin developing AI systems that your customers can trust.
AI governance entails establishing policies, risk management frameworks, oversight committees, compliance processes, and monitoring mechanisms to ensure AI systems operate responsibly.
It includes model validation, bias testing, documentation, explainability standards, security controls, and regulatory alignment across the entire AI lifecycle, from data ingestion to decommissioning.
AI governance for data privacy ensures that AI systems collect, process, store, and share data lawfully and securely. It enforces consent management, data minimization, anonymization, access controls, and audit logging.
Governance frameworks align AI operations with regulations such as the General Data Protection Regulation and other privacy standards.
AI governance works by integrating structured oversight into AI development and deployment. Organizations define risk tiers, conduct impact assessments, document model decisions, monitor outputs, and implement escalation mechanisms.
Cross-functional teams, including legal, compliance, engineering, and leadership, collaborate to ensure AI systems meet regulatory, ethical, and operational standards continuously.
An example of AI in governance is automated compliance monitoring in financial institutions, where machine learning models detect suspicious transactions and flag regulatory breaches.
Another example is risk-based AI classification frameworks mandated under the EU AI Act, which require documented oversight and continuous risk assessment.


