

QA in CI/CD Pipeline: Best Practices for Continuous Integration and Testing






“A QA pipeline is a structured process within the software development lifecycle that automates and streamlines testing workflows to ensure code quality, reliability, and functionality before deployment. It integrates various testing stages into the CI/CD pipeline to catch bugs early and maintain code health.”
A well-designed QA pipeline includes unit tests, integration tests, UI testing, and performance checks. It improves release confidence, speeds up development cycles, and minimizes the risk of introducing bugs in production.
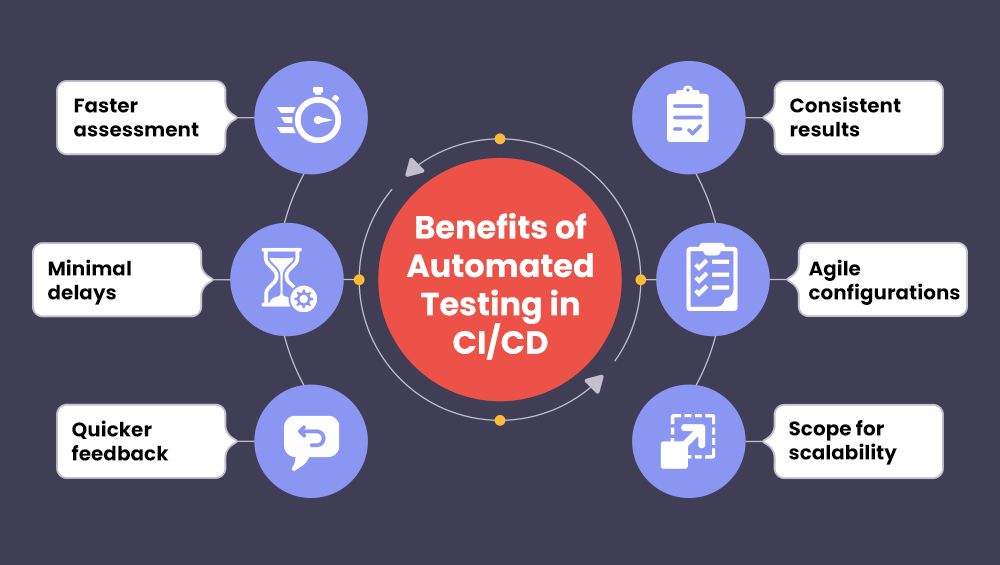
Benefits include faster feedback loops, improved traceability, reduced manual testing efforts, and seamless integration with CI/CD tools such as Jenkins, GitHub Actions, or GitLab CI.
By automating repetitive tasks and enforcing code quality gates, the QA pipeline promotes collaboration between QA engineers and developers, enabling faster and more stable product releases.
QA accelerates delivery and deployment while fixing any recently introduced bugs. Continuous QA fits perfectly in the continuous-everything model and makes everything cheaper and faster.
Most importantly, CI/CD pipeline QA acts as a safety net, which allows the developers to focus primarily on the code, its changes, and the shipping updates, rather than worrying about testing!
Even though the CI/CD pipeline pushes for continuous development, testing, and deployment, it is often plagued with manual testing. One of the greatest issues with manual testing is the delay per iteration, which starts accruing and pushing the deployment back. Slow feedback, slower changes, and painfully slow releases defeat the very purpose of CI/CD as manual testing is unable to keep up with the dynamic requirements.
At the same time, there is a need to run multiple tests depending on the objective of test suites. To conduct these tests, one needs to first identify the test cases and then run them one at a time. Hence, manual testing makes the process sluggish by many folds.
Finally, the test cycles call for separate test environments that teams will have to build manually, upgrade, and tear down. The effort that goes into mimicking the end-user environment may require multiple permutations and combinations that the team will have to identify, build, and update.
The challenges mentioned above can be overcome by onboarding a Chief Technological Officer. Hiring CTO consulting services can help organizations formulate a clear technology strategy aligned with their goals. It allows organizations to navigate the complex landscape of technology and make informed decisions to achieve their business objectives.
Even though manual testing is prevalent, it is evident that it is a failing battle. Following are the clear advantages of CI/CD pipeline automation testing:
While manual testing can be reserved for specific testing types and modules, such as exploratory testing, it is best to automate testing for seamless integration of QA in the CI/CD pipeline.
To modify the CI/CD pipeline, QA professionals can introduce the following actionable measures:
Different browsers (and sometimes the different versions of the same browser) operate on different protocols and engines. Regardless, the performance of the website should remain consistent throughout. Hence, it is crucial to perform cross-browser testing through Selenium.
Given the diverse range of CI/CD tools, it can be confusing to identify the ones that you require. Typically, it should match your overall requirements and support the platforms, frameworks, and technologies that you require.
Naturally, for the perfect CI/CD pipeline automation testing, the developers and testers must work hand-in-hand to achieve the desired results. Through early-stage incorporation, the overall quality of the project will improve rather than posing it as an afterthought. Further, it will decrease the time-to-market, and you will deliver high-quality, tested applications frequently.
With an automated pipeline, one can expect a stable, bug-free build that is ready for deployment. And while it is deployed, developers must gain access to test reports, especially those containing any issues or failures. These reports will shed light on the reasons why it failed the test and the user behavior that led to the load clash. As a result, developers can make changes according to these findings.
Documentation helps maintain the testing quality during automated unit testing, which also improves the quality of solutions. Automated unit tests contribute to self-documentation, where code maintenance plays a crucial role in software development. As a result, developers can benefit from a testing model that develops through self-learning. At the same time, the main documentation helps mitigate any software risk and takes care of maintenance.

A robust QA pipeline includes multiple interconnected components to ensure thorough and efficient testing:
These frameworks (like Selenium, Cypress, or Playwright) automate repetitive test cases for faster and consistent validation. They support unit, integration, and UI testing to maintain code integrity across environments and updates.
Managing realistic and anonymized test data is crucial for validating application logic under real-world conditions. Tools like Mockaroo or synthetic data generators help simulate different use cases without compromising privacy or compliance.
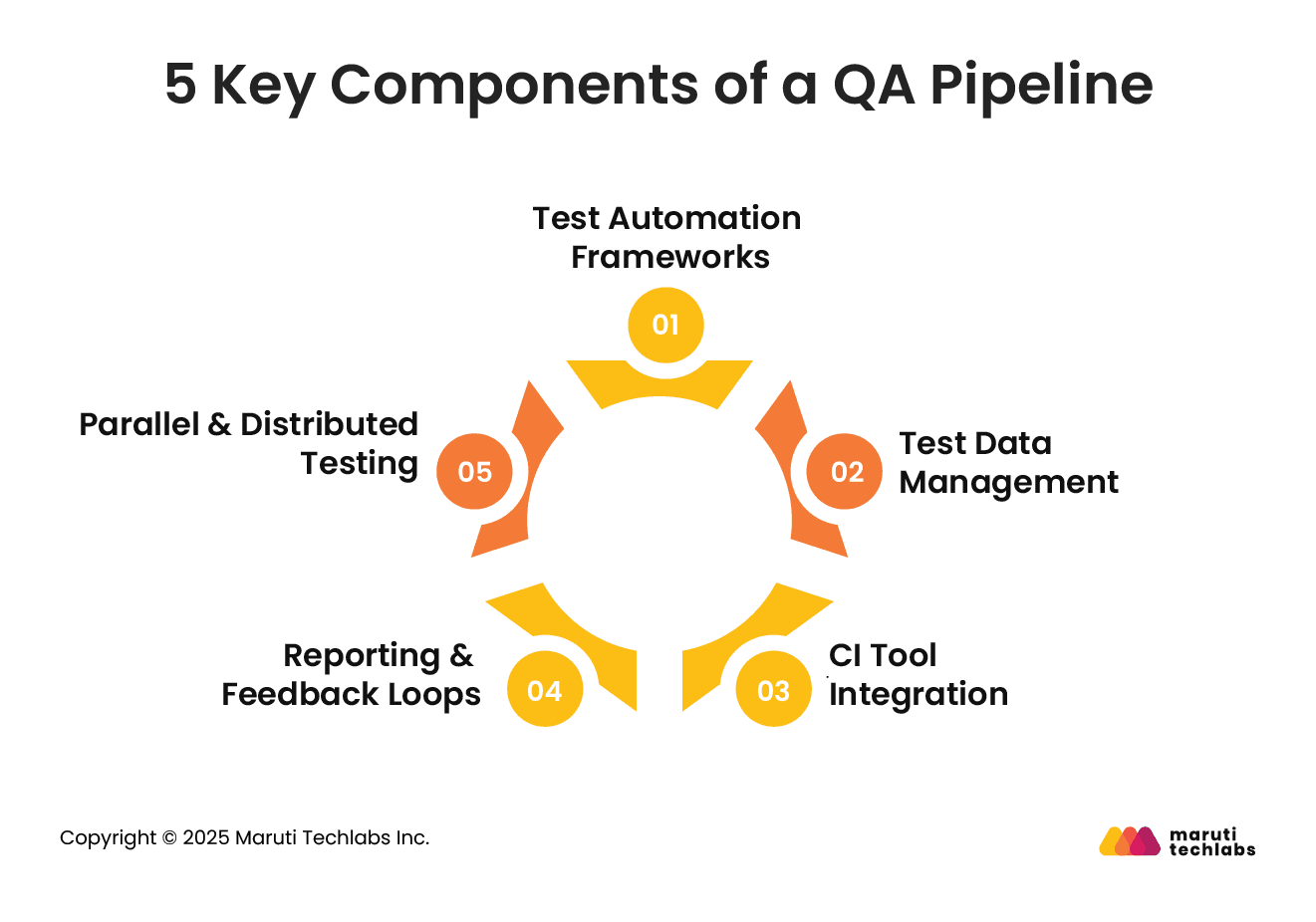
QA pipelines are tightly integrated with CI tools like Jenkins, CircleCI, GitHub Actions, or GitLab CI/CD. These tools automatically trigger tests with every code push, ensuring continuous validation and quick identification of regressions.
Test reports, logs, and dashboards provide visibility into test outcomes. Integrating feedback tools (like Allure Reports or Slack notifications) ensures that developers and QA teams are immediately alerted to failures.
To speed up execution time, tests are run in parallel across multiple environments or machines. This approach significantly reduces testing bottlenecks and accelerates release cycles, especially in large-scale projects.
You can get the best out of the automation testing in CI/CD pipeline through the following measures:
Introducing QA in CI/CD cannot be an overnight change. Hence, make use of a feature-by-feature approach to start with the larger features that need to be broken down into smaller test features. In doing so, development teams can also manage their commits.
On seeing the clear advantages of CI/CD pipeline automation testing, one may want to dive right in and automate everything. However, it is best to first automate those stages and test cases that genuinely ask for it. It is better to assign priorities and work your way through them.
Parallel and automated cross-browser tests increase coverage and reduce test times. Hence, run the tests in parallel and scale the server size to accelerate them.
For perfect and smooth hand-offs, developers must define automatic triggers to deploy the services to the development environment after the code and builds pass all the tests.
Every deployment should be followed by an automatic smoke test. This smoke test will ensure that the code retains its original and core functionality despite the changes. In case the smoke test is positive, the CI/CD pipeline QA must initiate automatic deployment.
Test duplication slows down the regression and automation in the CI/CD pipeline. Therefore, monitor all the test suites to identify similar test scenarios and eliminate all but one.
With continuous QA in CI/CD, the project development cycle can enjoy the following benefits:
Integrating QA into a CI/CD pipeline isn’t without challenges. Below are key issues and actionable solutions:
Unreliable or non-deterministic tests lead to false positives and negatives, as well as slow builds.
Solution: Isolate and tag flaky tests using a stabilization suite that runs separately from core test flows. Continuously monitor and refactor them.
Delays in feedback increase development cycle times.
Solution: Apply the test pyramid strategy—run fast unit and critical integration tests first, followed by longer UI tests. This ensures essential issues are caught early.
Testing in different environments can yield inconsistent results.
Solution: Use containerization tools like Docker to standardize test environments. This ensures parity across dev, staging, and CI/CD environments.
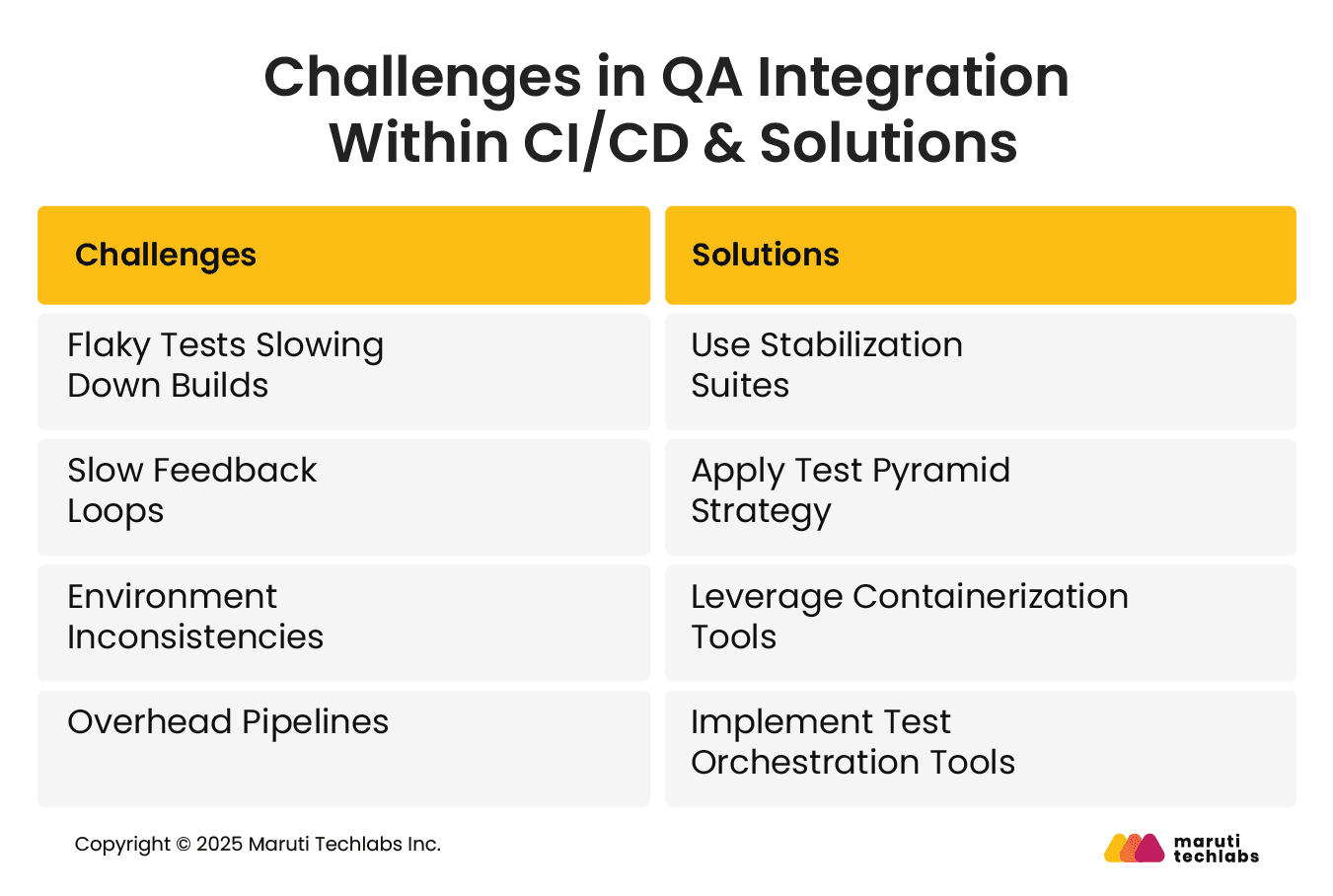
Running all tests on every commit can overwhelm the system.
Solution: Implement test orchestration tools (e.g., TestRail, Launchable) and apply test impact analysis to run only the subset of tests affected by recent code changes.
By addressing these challenges early, teams can maintain a stable, scalable QA pipeline within CI/CD workflows.
Developers use common CI/CD tools to introduce automation in the development, testing, and deployment stages. Some tools are designed specifically for CI, and some are better at managing CD.

Some of the most common CI/CD automation tools used by development teams include:
Teams may even find managed CI/CD test automation tools offered by a wide range of vendors.
Automation testing improves the ability of the CI/CD pipeline to deliver error-free codes without compromising on the quality. And while the automated pipeline is linear, the feedback loop becomes an area of interest as all the crucial metrics will be readily available at this stage. These analytics can help with performance monitoring and enhancement, which will boost the quality of the project.
The close-knit construction of the CI/CD pipeline also highlights the role and importance of every contributor. Further, it demonstrates the effectiveness of their deliverables in maintaining code and project quality. Thus, QA managers should follow a hands-on approach and involve all stakeholders in the test development and environment provisioning strategies. In this manner, businesses can offer a superior product by incorporating quality engineering in software testing.
In a nutshell, the formula is simple, Continuous Integration + Continuous Delivery + Continuous Testing + Continuous Deployment + Continuous Feedback = Continuous Improvement!
Maruti Techlabs offers hassle-free continuous testing services. Our new product development services incorporate 360-degree testing seamlessly in your CI/CD pipeline to streamline and get the most out of your development cycles. Backed by our expertise in CI/CD consulting, we ensure that testing is fully aligned with your automation goals for faster and more reliable releases. For end-to-end QA services, simply drop us a note here and we’ll take it from there.
Continuous integration (CI) in testing is the automated process of running test cases every time new code is pushed. It ensures that code changes don’t break existing features and helps catch bugs early in the development cycle.
Jenkins is one of the most popular CI tools due to its flexibility, vast plugin ecosystem, and strong community support. Alternatives like GitHub Actions and GitLab CI are also widely used for seamless DevOps integration.


