12 Microservices Best Practices To Follow - 2026






If you deep dive into the conventional practices of developing applications, you will find that they were designed as monoliths, bundled into a bunch of code, and installed as a single unit. The practice of handling thousands of lines of code became cumbersome. It created obstacles in the path of architectural changes in large companies.
In contemporary times, digital unicorns are developed and operated in no time. The digital revolution enables this process to occur at a brisk pace. The quantum leap in this field is made possible by flexible, scalable, and robust enterprise architecture that has been dubbed as microservices architecture.
Microservices architecture is a method that structures an application as a collection of services that include the following:
Microservices architecture signifies many small, programmed, and self-contained services that carry out a single business operation. It facilitates speedy, periodic, and dependable delivery of large and complex applications.
Here are few advantages of microservices architecture:
What are the Best Practices under Microservices Architecture?
Here’s a look at 12 of the microservices best practices that you should be following at all costs:
A poor design of the hosting platform of your microservice will never earn you good results despite meeting all the parameters of microservice development. Separate your microservice infrastructure from other components to get fault isolation and better performance.
Pick the correct database, customize the infrastructure that it requires, and keep it exclusive to your microservice. If you use a shared database for all your microservice, then it won’t serve the purpose.
Microservices should be modeled in a style where a class should have only a single reason to alter. Creating bloated services that are subject to changes for numerous business contexts is not an ideal practice.
Prepare your developers who are working in an ongoing environment for the upcoming expectations. Help them understand that the cultural shift is for the long-term benefit of the company.
If you have not handled such a migration in the past, you need to understand that it is not an easy task. Monolithic architectures often involve a web of repositories, deployment, monitoring, and other complex tasks. Changing (or migrating) all of this at once may not be feasible for teams and is bound to leave behind errors and gaps. Moreover, if you have made plans to maneuver shifts all at once, you need to go back to the drawing board.
One of the best ways to handle this is to retain the monolithic structure and develop any additional capability as a microservice. Once you have enough new services in place (and the teams have been sensitized about the new processes), figure out how to break down the old architecture into relevant components and begin migrating them one by one.
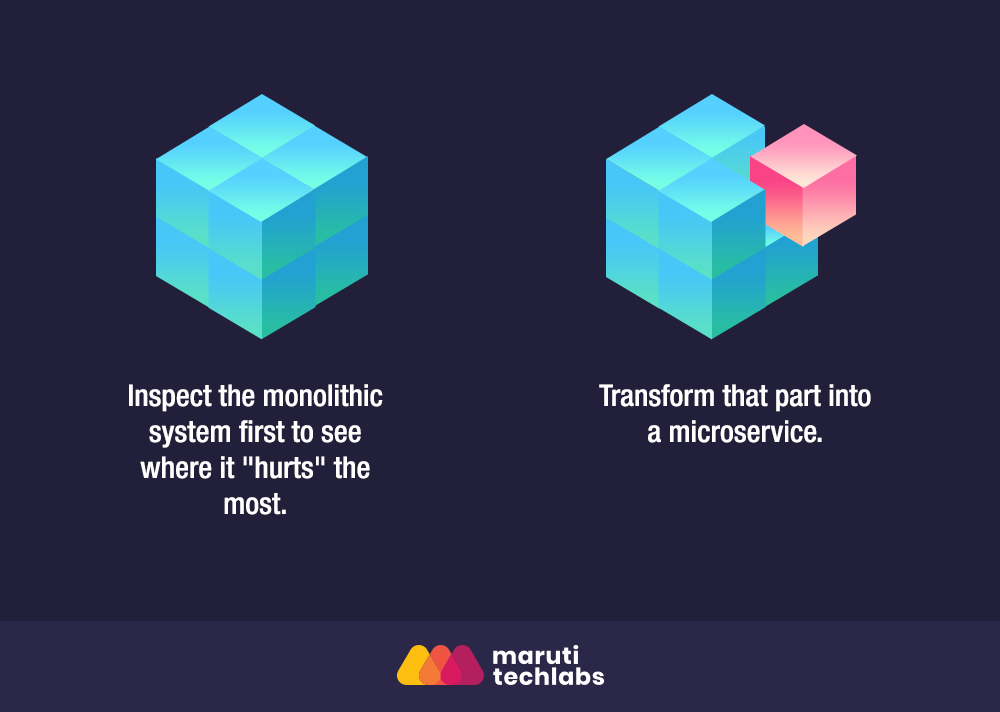
Not having a splitting system right from the beginning of the project can lead to massive hassles in the future. Defining the interactions and processes between different puzzle pieces is one of the critical microservices best practices that should be followed to make the bigger picture clearer, even more so if you are in the migration phase.
Every splitting system is unique to the architecture that is being built. It depends on the methodology you are following and the results you expect at the end.
One tip is to inspect the monolithic structure to understand the gaps it has and components causing the most trouble and then transform this part into a microservice.
Although, this is only possible if you have been monitoring the performance of individual components in the first place. So, if monitoring is not something that you have focused on, it is a great place to begin the cleaning process.

Tools that you can use for the monitoring process include:
Since we now have different processes for different verticals, you are bound to have isolation at the runtime level too. You need to implement some form of distributed computing to pull this off from a pool of possible choices.
Do you need to adopt containerization, event architectures, various HTTP management approaches, service meshes, and circuit breakers? Figure this out before it is too late to backtrack.
While one member in your team may not give importance to the technology or language, another might opine that the product’s life depends on it. Whatever the case, implementing the technology directly and iteratively might make it easier to make changes or even replace it later.
The choice of the language can come down to personal preferences and the comfort level of your team members. But whatever you do, make sure that your team is equipped enough to handle the decision. For instance, choosing an architecture that involves a dozen different programming languages may also translate to a hiring spree, which is often not recommended.
If you are not sure which technology is best for your project, consider the following parameters during the decision-making process:
In one way, Domain-Driven Design is nothing more than Object Oriented Programming applied to business models. It is a type of design principle that uses practical rules and ideas to express an object-oriented model.
In simpler terms, microservices are designed around your business domains. It is used by platforms such as Netflix who use different servers to run their content delivery and related tracking services.
If your primary aim is to deliver a superior customer experience, consider distinguishing between dedicated and on-demand resources. For instance, let’s take an e-commerce platform that builds its microservices and cloud architecture in ways that quickly (and securely) moves workloads between its on-premise and cloud environments. How does this help? Not only does it increase the response time, but it also makes migrating to a cloud-based working environment much more intuitive.
It is relatively common for developers to use open-source microservice tools for security, monitoring, debugging, and logging. However, ensure that they are not over-relied upon in ways that interfere with the performance or safety of the architecture. Depending on your development needs and the types of tools you are using, implement appropriate organizational policies regarding their usage. This can be related to:
The REST (Representational State Transfer) APIs can work wonders for microservices as developers need not install any additional software or libraries while creating a REST API. At the same time, they provide a great deal of flexibility since the data is not tied to any particular method or resource. The result is an ability to handle multiple types of calls, return different data formats, and alter the structure with the correct implementation of hypermedia.
You don’t even need a framework or SDK since HTTP requests are relatively sufficient. Out of the four levels of REST, simply begin at level 0 and make your way up to level 3, as proposed by Leonard Richardson, an expert in the subject of RESTful APIs.
Before changing your system to microservices, it is vital to understand why you need to do it. Analyze your system and study the distinctive features in your system and notice which part of the system troubles you the most. At an early stage, consider a less critical part of the system and evaluate its functions as a microservice.
In addition to these microservices best practices, you also need to make sure that the project manager can handle end-to-end service-oriented architecture migrations and development. Only businesses who understand the nuances of the cultural shift towards microservices will leverage the technology to its full potential.
Many big tech giants and e-commerce sites like Netflix and Amazon have successfully migrated to microservices owing to their easy scalability and agility. However, hiring an agency that offers the best IT talent & staffing solutions can be a smart idea if you do not have an expert in-house team to handle a smooth migration to microservices.
At Maruti Techlabs, we assist you in outlining a high-performance microservices architecture that helps your organization maneuver operational overload and other challenges.
Our Engineering experts have successfully migrated fully-functional apps to microservices architecture and containerized them further. With the help of our application containerization services, your application can have easier traffic routing, selective scaling, faster deployment, and zero downtime.
For comprehensive cloud application development services, drop us a note on hello@marutitech.com, and let’s chat.
1. Why did organizations move away from monolithic architecture?
Monolithic systems became difficult to manage as applications grew larger. Handling thousands of lines of tightly coupled code made changes slow, increased risk, and created barriers to scalability and innovation.
2. Why should each microservice have its own infrastructure?
A dedicated infrastructure ensures better fault isolation and performance. When services are isolated, failures in one component do not cascade across the entire system.
3. Are microservices suitable for every organization?
Not necessarily. Microservices are best suited for complex systems that require scalability and frequent updates. Smaller applications may not benefit from the added operational complexity.
4. How should teams approach migrating from monolithic to microservices architecture?
Migration should be incremental. A practical approach is to retain the monolith initially, build new capabilities as microservices, and gradually break down the existing system into smaller components.