

How to Implement Event-Driven Architecture for Real-Time Apps?






Businesses are challenged to build scalable real-time applications while managing high data loads. Traditional architectures often need to catch up, leading to delays, bottlenecks, and subpar user experiences. Therefore, it’s imperative to adopt event-driven architecture, a design approach that enables systems to respond instantly and seamlessly to real-time events.
With event-driven architecture, your apps can react to triggers like user actions or data updates the moment they occur, unlocking capabilities such as real-time notifications, automated workflows, and dynamic system interactions. This approach isn’t just about speed; it’s about creating more innovative and resilient applications that can be optimized effortlessly.
In this blog, we’ll cover the core principles of event-driven architecture, its role in powering real-time apps, and how you can implement it effectively. Whether you’re a developer tackling system bottlenecks or a strategist planning for growth, this guide offers practical insights to help you stay ahead.
Why are apps like ride-hailing or live chat so fast? The answer often lies in event-driven architecture. But what exactly is it?
At its core, event-driven architecture is a way of designing systems that react to “events”—specific actions or changes in data. An event could be a customer placing an order, a button click, or a sensor recording new data.
Unlike traditional workflows, this approach processes events as they happen, making it perfect for real-time applications where every second matters.
1. Decoupled Systems and Real-Time Functionality
Event-driven architecture allows systems to operate independently yet interact seamlessly through events. It is like a ripple effect: one system generates an event, like updating a dashboard, and another responds instantly by processing it. This decoupling ensures systems are more flexible, scalable, and responsive.
2. Events as Triggers for Action
An event is simply a signal that something has changed. For example, when a customer clicks “Buy Now,” an event is generated. The system quickly captures this event and responds in real time by updating the inventory or commencing the shipping process.
Now, let’s explore the essential components that make this architecture so powerful.
Every event-driven system depends on three key components. These components work together to ensure real-time events are created, transmitted, and acted on.
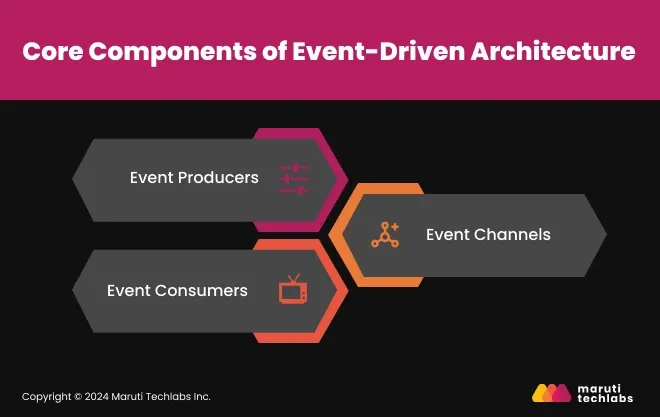
Here’s how they function.
Event producers are systems or devices that generate events whenever something changes. For example, a banking app creates an event when a user makes a transaction. These producers send event data to the system, triggering the next steps—like updating the account balance or sending a notification.
Event channels are the pathways that carry events from producers to consumers. They work independently, meaning they don’t wait for a response to keep transmitting data. Think of them like pipelines in an assembly line—always moving data to the right place. Tools like Apache Kafka or RabbitMQ are commonly used to manage these channels.
Event consumers are systems or components that process events and trigger specific actions. For example, in an e-commerce platform, when a customer places an order, several systems act as event consumers.
Event consumers process the event independently, ensuring tasks are completed efficiently and allowing different system parts to work together smoothly.
Understanding these components highlights why event-driven architecture is so impactful. Let’s explore the benefits it offers.
Delivering reliable, scalable, and responsive services is essential for today’s businesses. Event-driven architecture provides the tools to achieve these goals, helping organizations streamline operations and enhance customer experiences.
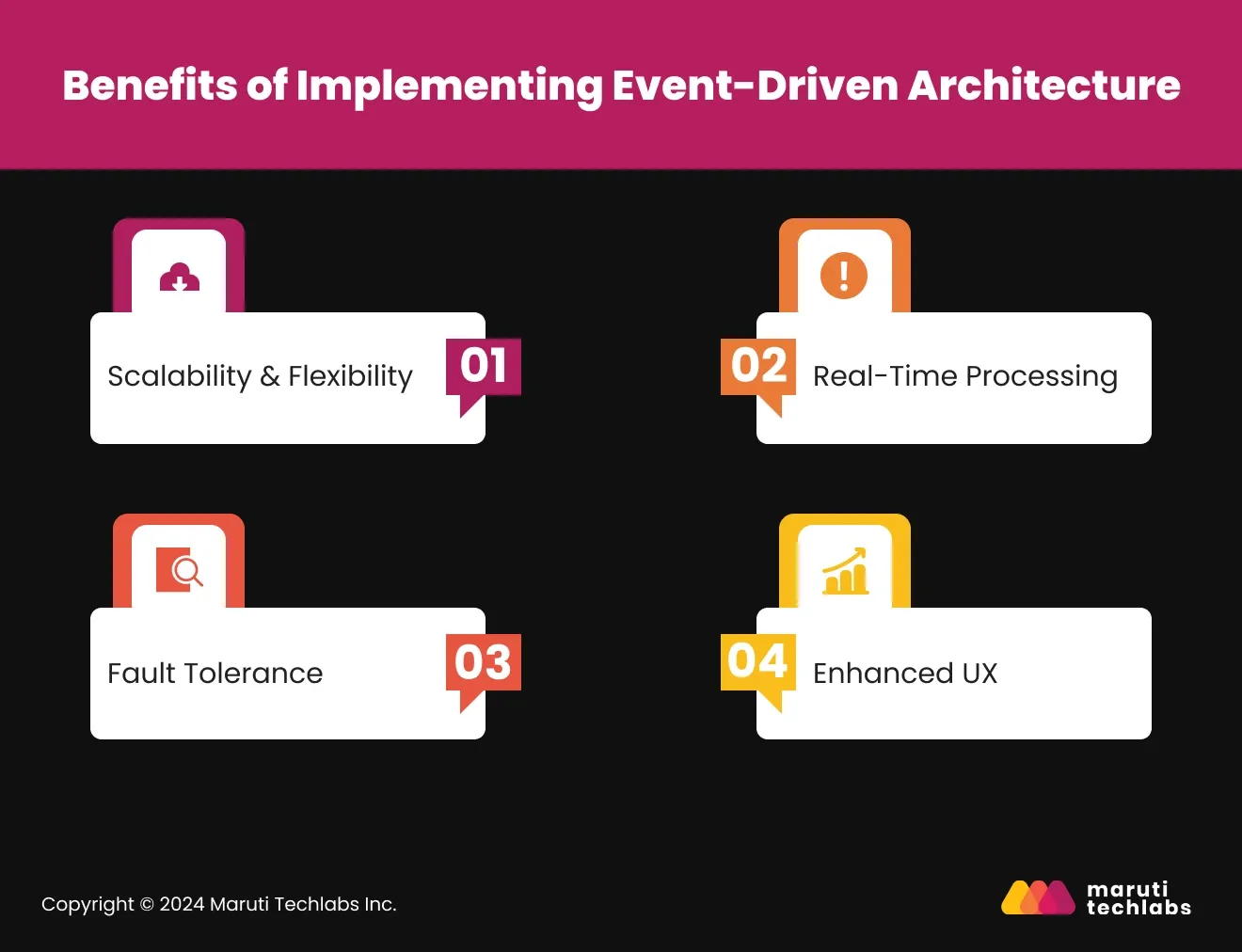
Event-driven systems allow businesses to grow without breaking existing workflows. Instead of scaling entire systems, individual components can be adjusted based on demand. For example, during a flash sale, an e-commerce platform can scale its payment processing system to handle transaction spikes without affecting other components like inventory management.
Businesses can make immediate decisions by reacting to events as they happen. For instance, fraud detection systems in the banking sector can promptly identify and handle any questionable activity. In addition to saving client information, this fosters confidence. This level of accountability reduces potential delays and minimizes hazards.
Event-driven architecture minimizes downtime. If one part of the system fails, others continue working independently. For example, in a healthcare app, even if appointment scheduling is unavailable, patient records and notifications remain accessible, ensuring critical services are uninterrupted.
Consumers always expect instant response as soon as they tap the application. As a result, event-driven systems ensure seamless interactions, whether in the form of payment confirmation or real-time delivery status. This has an added advantage for businesses since consumers are more satisfied and, hence, more loyal.
While these benefits are significant, implementing event-driven architecture has challenges. Here are some critical considerations for businesses.
Though event-driven architecture offers substantial benefits, its implementation comes with several challenges businesses must navigate. Addressing these hurdles is crucial to maintaining system efficiency and ensuring long-term success.
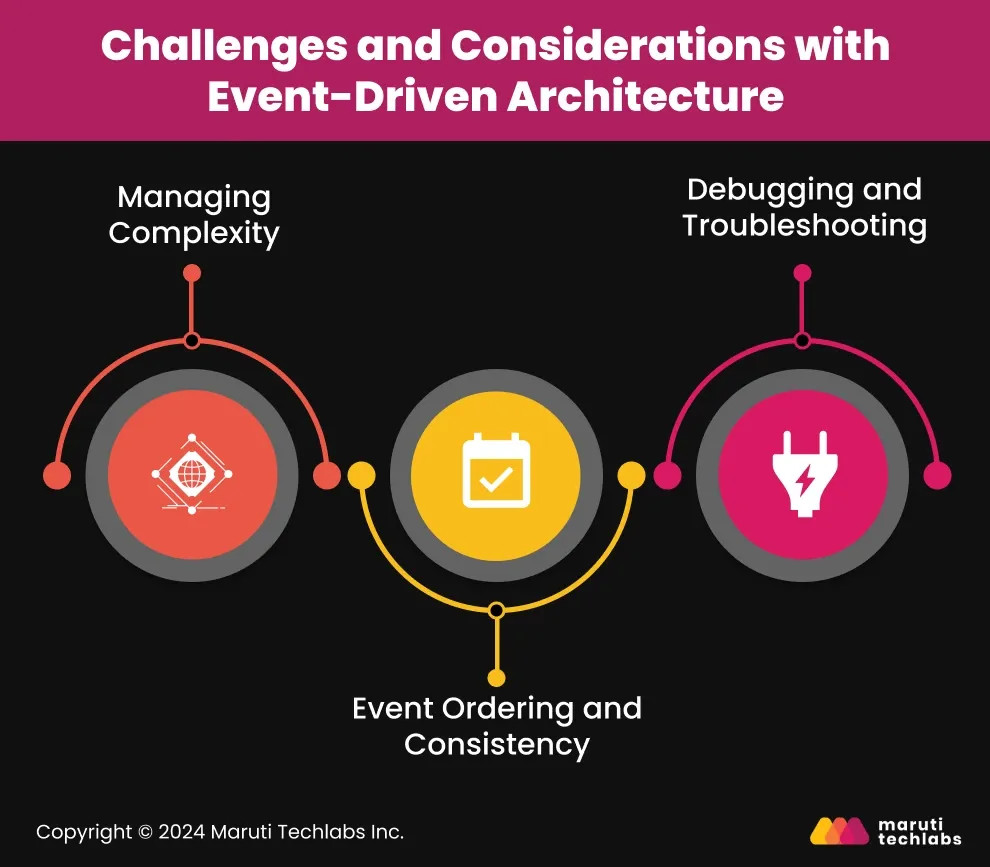
Event-based systems organize components into distinct, isolated sections. As a result, managing these components can be challenging. For instance, if a payment system has to interface with inventory, delivering the appropriate data set to all units becomes problematic at the desired time. Consequently, businesses must create a sound communication control system and exercise monitoring procedures.
The material component is crucial in almost all event-driven systems. If a stock change occurs before order confirmation, you may oversell or sell items you don’t have; this is against inventory management. Tools like Kafka and advanced event-tracking techniques help maintain proper sequencing without disrupting regular operations.
Finding problems in systems that work independently, like asynchronous ones, can be difficult. For example, a missed location update in ride-hailing apps can make it hard to track drivers in real time. Organizations use systems that record and trace each process step to address this issue. These tools help determine where the problem is—whether it’s with the system that creates the event, the one that sends it, or the one that handles it.
Despite these hurdles, many industries successfully implement event-driven architecture to achieve real-time efficiency. Below are some practical use cases that demonstrate its potential.
Event-driven architecture is a proven method for improving real-time applications across industries. Now, we'll explore how it powers modern systems.
The application of event-driven design enhances the user experience and the accuracy of inventory tracking in the e-commerce business. The inventory of the products is easily adjusted each time a customer makes an order to avoid understocking. At the same time, the system also provides suitably targeted product recommendations, thus improving the overall shopping experience in real time.
Event-driven systems play a critical role in IoT devices by handling real-time data. For example, smart thermostats adjust room temperatures based on immediate sensor data, providing a seamless experience for users without relying on traditional manual controls.
In the financial sector, event-driven architecture tracks transactions and updates user profiles instantly. When the system detects unusual activities, such as a large withdrawal, it generates alerts and automatically adjusts user profiles to enhance security. This ensures secure financial transactions and keeps customer data protected.
These use cases show how impactful event-driven architecture is across industries. Now, we will examine how integrating it with other technologies can unlock its full potential.
Here’s how event-driven architecture works alongside microservices, data streaming platforms, and serverless technologies.
While employing microservices, each function is independent; however, events provide a loose coupling between them. For example, in a ride-sharing app, when a user books a ride, the payment service triggers an event. This event notifies the driver and updates the user’s trip history. Additionally, it adjusts the app's recommendations for future rides. Each service responds to the event independently.
When combined with other platforms like Apache Kafka, event-driven architecture is perfect for data flow. Kafka effectively processes input streams containing real-time data while connecting producers and consumers. For instance, a real-time stock trading system can use Kafka to disseminate market data to thousands of traders, and this occurs with extremely low latency and high throughput.
Event-driven architectures integrated with AWS Lambda or Microsoft Azure offer self-scaling capabilities. These systems automatically adjust to meet demand, ensuring consistent performance. For instance, in the middle of the holidays, an e-commerce platform can automatically increase its processing capacity to handle many orders. Cloud services, like AWS or Azure, manage this increased load efficiently, keeping the system fast and stable.
Now that we have a clearer understanding of how event-driven architecture integrates with other technologies, we can examine the steps involved in implementing it for real-time applications.
Implementing event-driven architecture in real-time applications takes careful planning and execution.
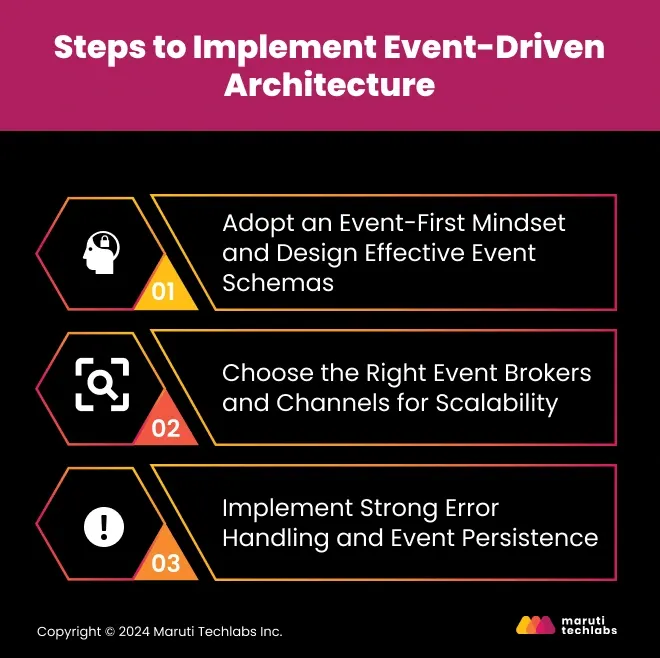
Here’s a breakdown of the key steps to get you started.
In terms of events rather than traditional processes. Design your system to react to events as they happen. Craft event schemas that are clear, structured, and scalable. Imagine building the skeleton of a house: the better your structure, the easier it is to expand as needs grow.
Choose event brokers to handle large amounts of data, or be prepared to change them as your application expands. Apache Kafka or RabbitMQ are designed to scale, handle high-velocity events, and operate like a bridge between services. This choice guarantees that your app will always stay highly responsive, even with high traffic.
A robust system requires a proper error-reporting mechanism. Some events should be handled without interrupting the system; techniques like dead-letter queues can capture failed events. Also, it is recommended that events be preserved for replay or recovery in case of failure to maintain data integrity.
Event-driven architecture allows firms to grow flexibly, respond to new events instantly, and adapt to ever-evolving events. That is why real-time processing suits industries like e-commerce, IoT, and finance, where everything depends on the solution’s speed, accuracy, and flexibility.
By adopting event-driven architecture, your business can tackle the complexities of modern applications. It enables your systems to respond in real time, improving user experience, enhancing performance, and fostering innovation. If you aim to build scalable and reliable systems that meet real-time demands, consider implementing event-driven architecture.
At Maruti Techlabs, we specialize in helping businesses streamline operations and stay ahead by leveraging our expertise with business technology consulting.
Ready to transform your business with event-driven architecture? Get in touch today to optimize your systems for the future.
Event-driven architecture (EDA) lets systems respond to real-time events, such as a customer placing an order or a payment transaction. Reflecting instant responses across systems improves scalability, reduces delays, and boosts user experience.
With EDA, you can scale specific parts of your system independently. For example, during peak times, you can scale your payment processing without affecting inventory, ensuring smooth operations.
EDA is ideal for:
Start by designing systems that respond to events, choose suitable event brokers for scalability, and ensure error handling and data persistence. At Maruti Techlabs, we assist with the entire implementation process to help you get it right.
EDA integrates well with microservices, data streaming platforms like Apache Kafka, and cloud services. It boosts system communication, data flow, and scalability, keeping your business agile and responsive.


