

10 Practical Steps To Minimize TCO in Cloud Computing






The year 2025 forecasts a substantial transition to the cloud. According to Gartner, public cloud spending worldwide is expected to reach $723.4 billion in 2025, up from $595.7 billion in 2024.
As companies invest significantly in cloud computing, understanding the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) becomes increasingly important. The cloud assists companies with financial management and strategic decision-making. Along with benefits like scalability and flexibility, the cloud introduces new complexities with costs that require companies to calculate cloud TCO.
Underestimating the importance of TCO in cloud computing can lead to budget overruns and strategic setbacks. Your well-intended cloud strategy can quickly become a financial burden with fluctuating usage costs, hidden fees, and unexpected hikes.
If you aren’t familiar with the concept of TCO cloud, don’t worry. This blog covers all the essentials of TCO in cloud computing, such as key components, benefits, best practices, and DevOps’ contribution to cloud TCO management.
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) in cloud computing is the complete financial impact of cloud adoption. It encapsulates the total cost over its entire lifecycle, including deployment, operations, and maintenance. TCO offers a holistic view of costs, including both direct and indirect costs.
Learning the TCO in cloud computing is imperative to make informed data-driven decisions if you transition to the cloud. Here’s a breakdown of the most critical elements that can contribute to your overall cloud adoption costs.
This is the primary cost while calculating cloud TCO. It covers computing, storage, and network expenses. Most cloud providers today follow the pay-as-you-go model, which primarily focuses on costs that include:
Cloud providers' offers vary between on-demand, reserved, and spot instances. Businesses must plan carefully and analyze workloads to ensure efficient resource usage and budget optimization.
Software licensing can critically impact a cloud’s TCO. Primary costs include:
Businesses looking to cut costs should purchase their licenses instead of directly opting for license-included options from cloud providers. Opting for cloud-native applications and open-source solutions can further decrease licensing costs. However, it may require cultivating new skills and tools.
One has to bear significant upfront costs when migrating to the cloud. These include:
These costs can differ with the migration strategy and complexity of the existing infrastructure.
Transitioning to the cloud requires cultivating new skills for IT staff members. These costs include:
Inadequate training can benefit in the long run but demands an upfront investment.
Everyday cloud management costs can have a significant impact on TCO.
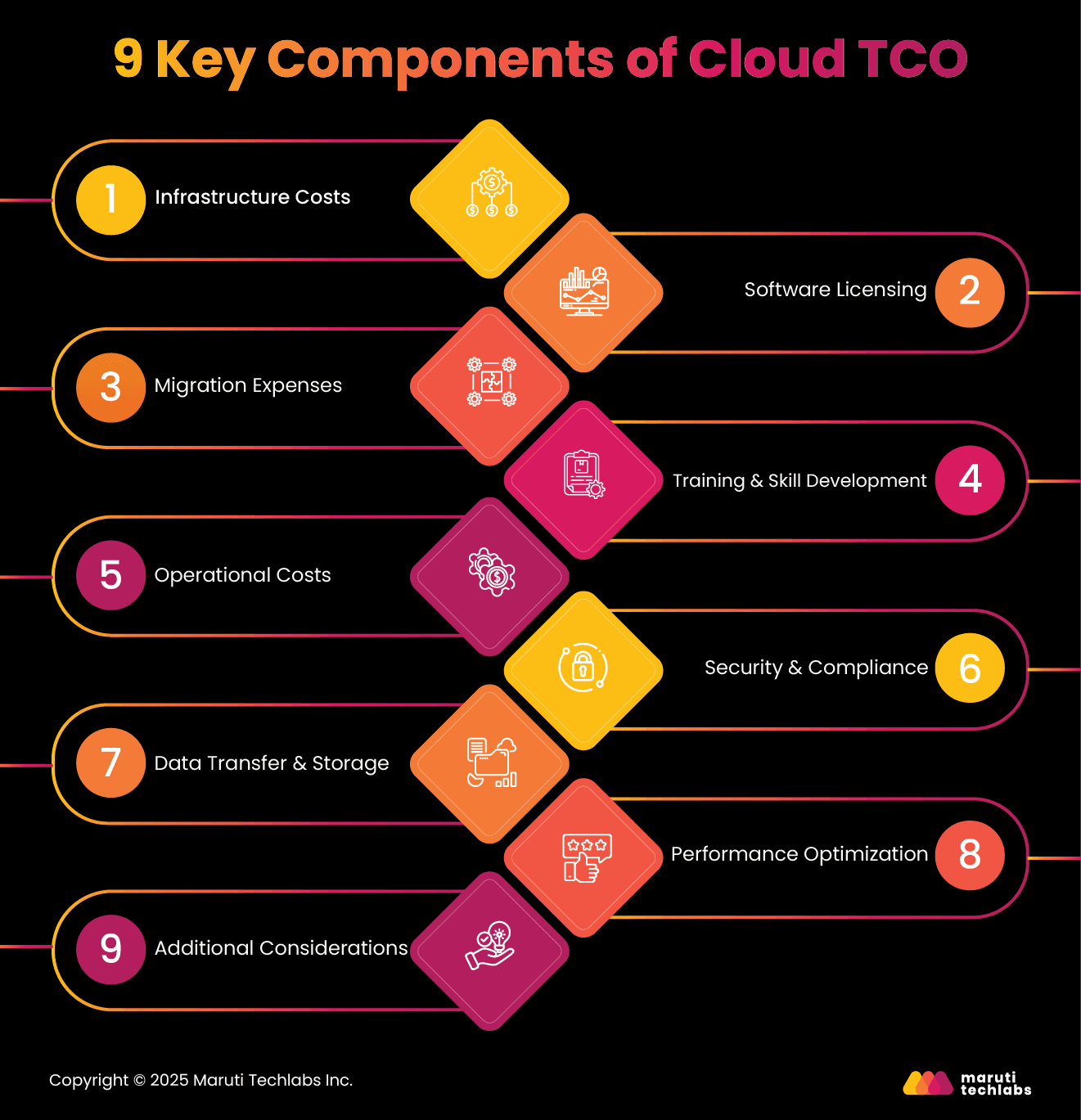
Security and compliance are the most essential aspects of the cloud and affect TCO.
Cloud providers may offer numerous security features. However, certain organizations need additional third-party security compliance.
Expenses related to data are often overlooked.
Ensuring your cloud services offer expected performance also contributes to TCO.
Learning TCO in cloud computing offers evident benefits with cost management. Here are the top 3 advantages of calculating TCO.
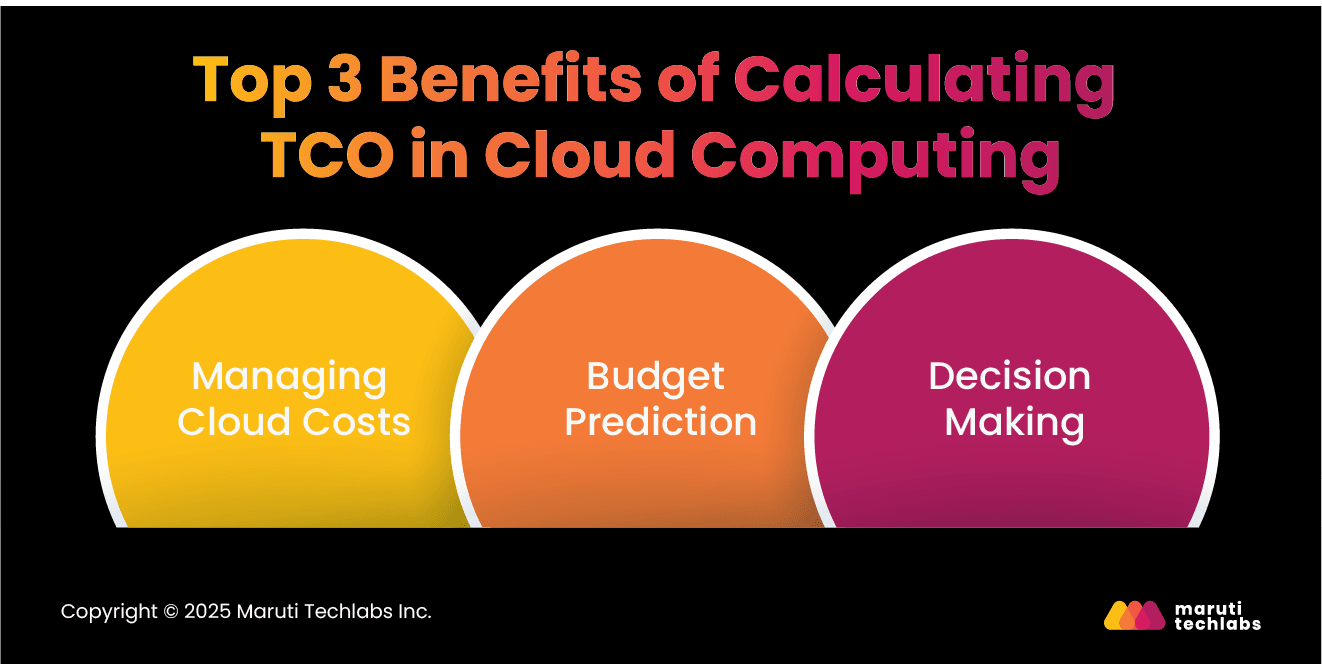
TCO in cloud computing is fundamental to cost management. It allows companies to:
Optimizing cloud costs allows companies to exercise control better and derive maximum value from cloud investments.
Understanding TCO plays a significant role in budget forecasting. It helps organizations:
TCO analysis significantly improves decisions related to cloud adoption and management. It enables businesses to:
TCO in cloud computing empowers companies to make strategic cloud investments by offering a complete financial picture.
Investing in key software development practices of DevOps like CI/CD and Everything as Code (EaC) can be highly beneficial for any organization. CI/CD facilitates continuous updates to the code while EaC, your infrastructure, is created in a repeatable and automated manner that adheres to security requirements.
They introduce consistency and a seamless process, saving time and costs. Implementing CI/CD and EaC demands alignment across the organization, but they offer faster deployments and predictable and scalable infrastructure.
The absence of these DevOps practices presents challenges like inefficiencies, technical debt, and security gaps. Manual processes hinder releases, making it difficult to grab new opportunities.
Companies that do not embrace DevOps face the continuous struggle of high operational costs and uncertainty in development timelines. These inefficiencies compromise an organization's competitive edge and limit its ability to innovate and grow.
Now that you know DevOps' contribution, let’s understand how it generates higher revenue.
CI/CD pipelines offer teams immediate feedback loops with frequent, predictable deployments, accelerating feature rollouts. Faster deployments introduce new functionality, subsequently creating more revenue opportunities.
For instance, a startup may begin with monthly deployments, but as it gains traction, it may have to switch to weekly, daily, or even on-demand deployments.
These quick rollouts, whether for internal applications or external products with subscribers, always generate more revenue.
A team must establish infrastructure, permissions, access, APIs, and integrations for every product or application. If the pipelines aren’t developed using EaC, the configuration is not documented, making it cumbersome to scale or repeat services.
Leveraging EaC for writing pipelines allows teams to reproduce pipelines quickly, unlike configuring each application for different environments. In addition, organizations can also try new methods to optimize, automate, and enhance other parts of the CI/CD pipeline.
Teams configuring CI/CD pipelines without EaC makes issue resolution difficult in future instances. These pipelines are created manually with no traceability.
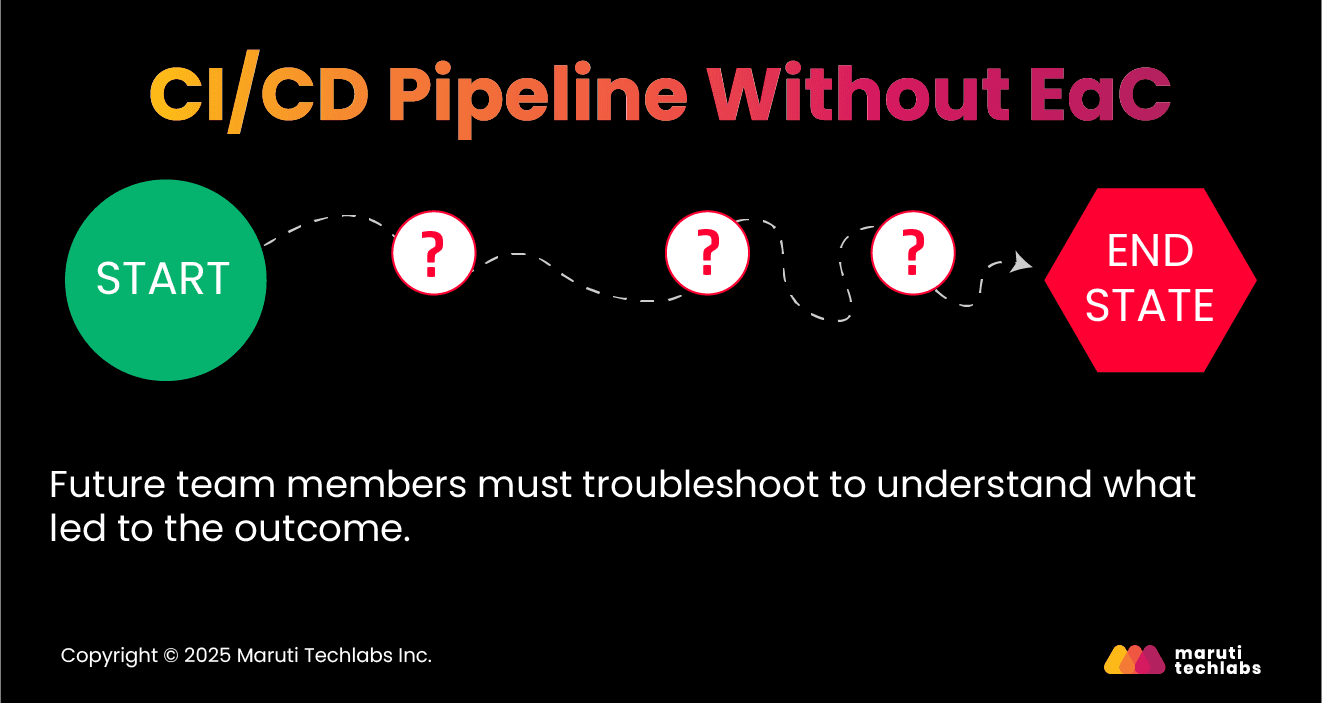
Subsequently, days, weeks, or months later, the team members who did the work will have no idea how the end state was achieved, making it exhausting for future teams to detect and resolve issues.
CI/CD pipelines developed using EaC offer complete visibility into configurations, making it easy to track how the final state was achieved. Teams can quickly discover and fix issues if a test doesn’t work as expected. The absence of EaC makes debugging a lengthy process requiring manually retracing steps, resulting in inefficiencies.
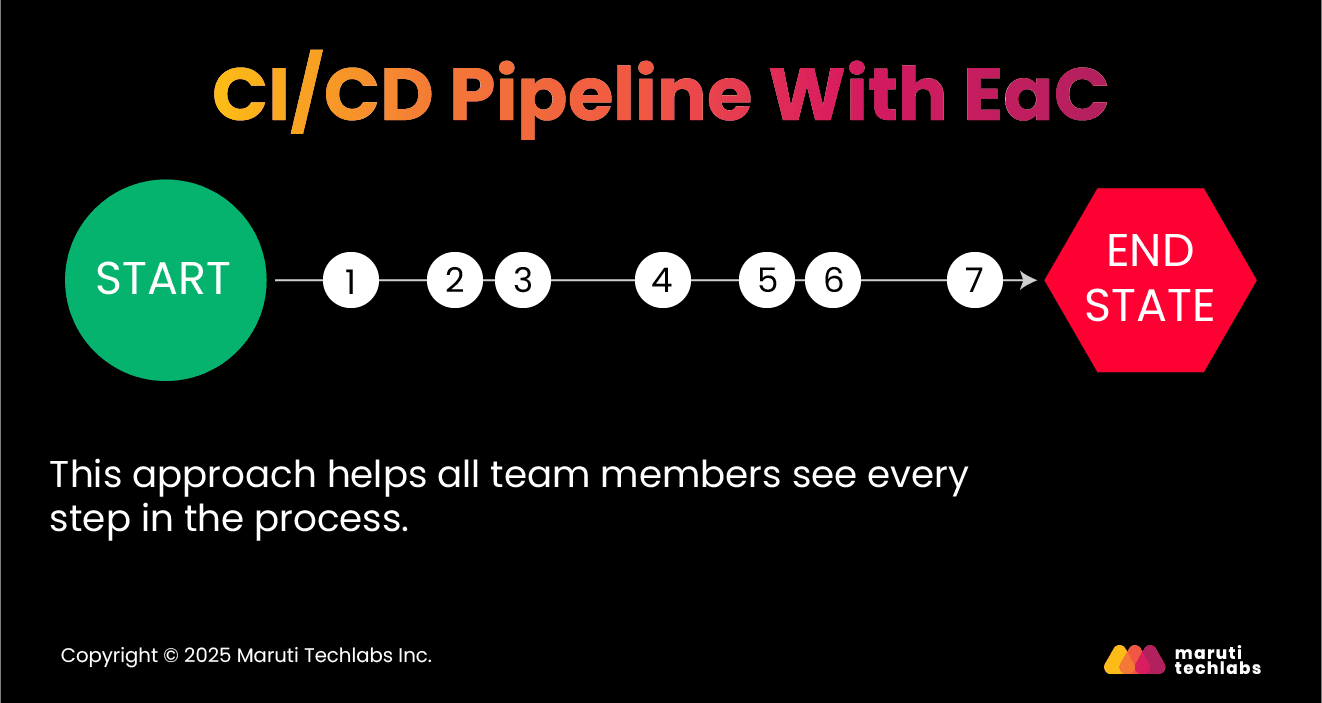
Hence, CI/CD and EaC can significantly lower operational expenses and cloud TCO in the long run by improving scalability, security, and efficiency.
With companies worldwide adopting cloud services, lowering cloud TCO is a top priority. However, this doesn’t mean compromising performance or business requirements.
Here are some proven practices you can follow to reduce your cloud TCO.
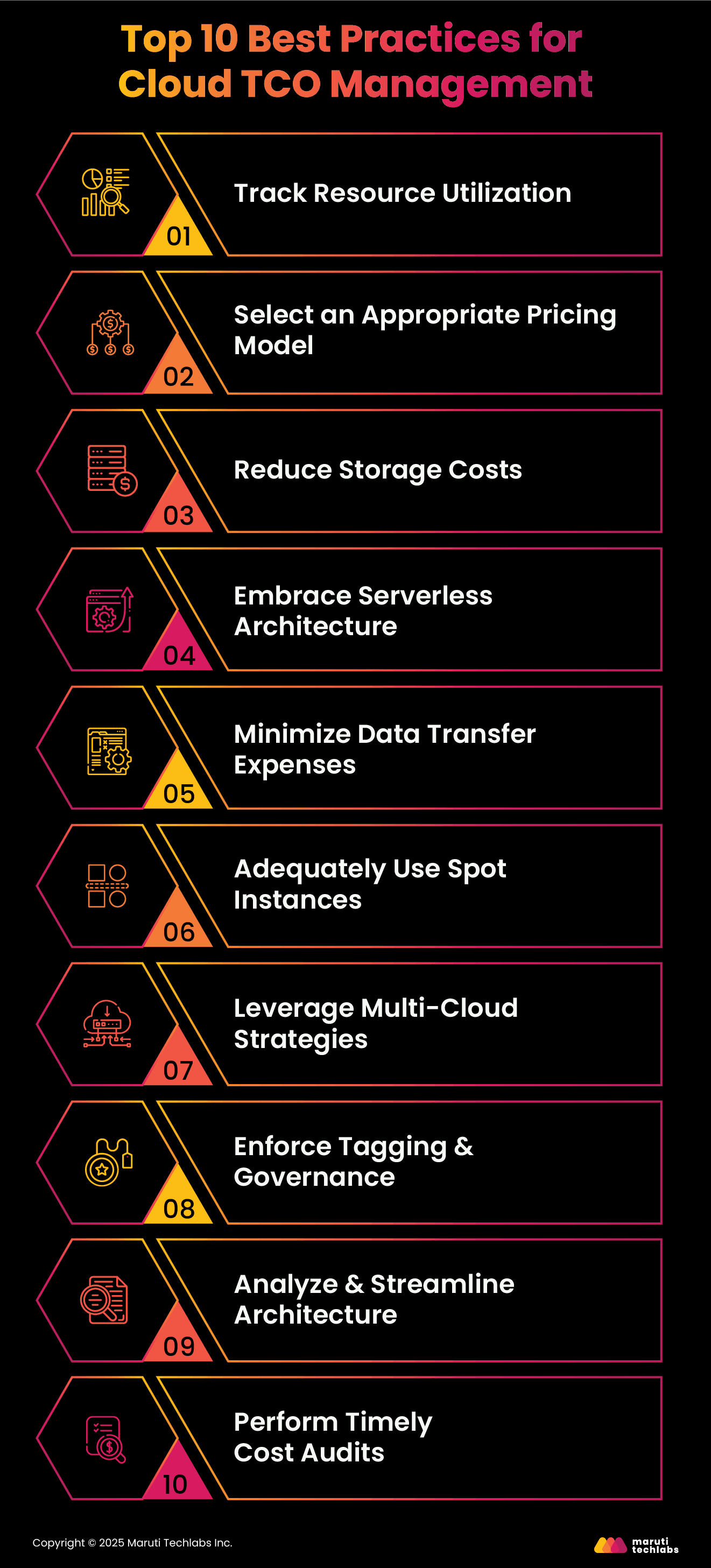
As the cloud ecosystem continues to advance and evolve, so will the strategies for learning TCO in cloud computing. Understanding TCO in cloud computing offers several advantages, such as better budget planning and allocation, forecasting future cloud expenses, cost comparison amongst cloud providers, the financial viability of cloud investments, and more.
An important thing to remember with cloud is that it’s a journey that observes a continuous learning curve. However, the abovementioned best practices can help organizations stay ahead of the curve.
With our 14+ years of experience, we at Maruti Techlabs can help you understand your TCO with cloud services. Leveraging our cloud application development services and DevOps Services can cover all the variables associated with calculating cloud costs and optimizing your software development cycle. Additionally, our cloud security services ensure your infrastructure remains secure as you optimize for cost and performance.
Get in touch with us today to garner a complete understanding of your cloud’s TCO.
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) in Cloud Discovery provides a comprehensive view of the expenses associated with cloud adoption.
TCO in cloud computing comprehensively evaluates all expenses linked to deploying, running, and managing cloud services throughout their lifecycle. It includes direct costs, such as subscription fees, and indirect costs, like training and ongoing maintenance.
Key parts of TCO include direct costs (subscription fees, data transfer, storage, and computing) and indirect costs (management, training, downtime, support, and integration). Knowing these costs helps businesses accurately assess and manage their cloud expenses.
Businesses can reduce cloud TCO by adjusting resource sizes, using reserved instances for steady workloads, enabling auto-scaling, utilizing cost management tools, and regularly tracking and optimizing cloud usage.
Automation 360 Cloud offers up to 50% lower TCO than monolithic platforms by reducing infrastructure costs, minimizing maintenance, enabling scalability, and improving efficiency through automation and cloud-native architecture.


