

Zero Trust Security: The Smartest Way to Protect Patient Data






The modern healthcare landscape is experiencing rising risks surrounding patient data as digital transformation accelerates.
The healthcare industry continues to face the costliest data breaches of any sector. In 2025, the average cost of a healthcare data breach reached $7.42 million, significantly higher than the global all-industry average of $4.44 million. Patient health records are considered dramatically more valuable to attackers than financial data, making the industry a prime target for cybercrime.
At the same time, healthcare organizations are adopting digital technologies, including AI-powered tools, telemedicine platforms, cloud services, and interconnected systems, to improve patient care and operational efficiency.
While these innovations offer significant benefits, they also create new security gaps, particularly in interoperability, identity management, and secure data exchange across distributed networks.
This blog will explore the evolving threat landscape, the importance of architectures such as Zero Trust for protecting sensitive healthcare data, and best practices for secure EMR integrations.
Cybercriminals today are using sophisticated techniques to compromise security. Here are 4 security threats that continue to pose serious risks to healthcare data.
Cybercriminals target healthcare organizations and encrypt patient records, demanding hefty ransom for decryption keys. Additionally, phishing attacks disguised as regular communications can trick anyone into sharing confidential information or compromising access. These attacks can impede hospital operations and incur data loss.
AI is extensively used not only for cyberprotection but to devise intelligent attack strategies. AI-based social engineering attacks are becoming more prevalent, making it difficult to spot fraudulent activity with conventional security measures.
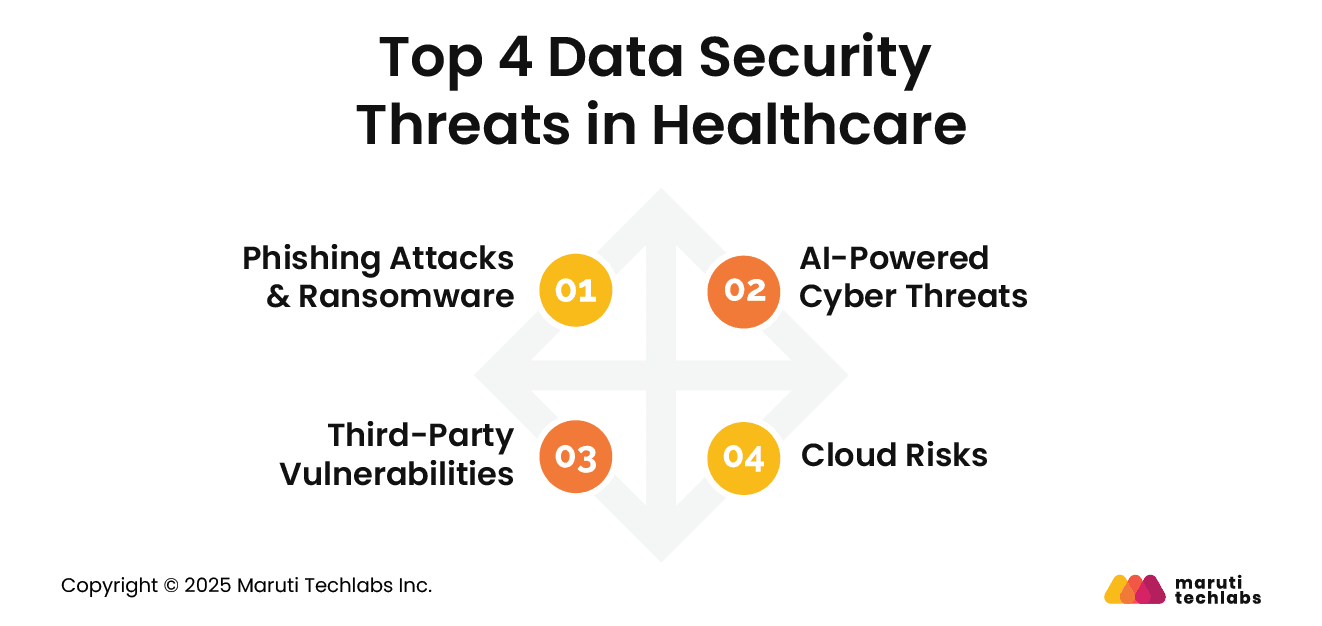
Healthcare companies use third-party applications for cloud storage, software, and medical record management. If these third-party vendors haven’t invested enough in implementing stringent security, it doubles the risk of breaches.
Cloud adoption has been booming for years, and organizations are transitioning to the cloud for improved scalability and anytime, anywhere access. But improper encryption, misconfigured settings, and unauthorized access can create security gaps that attackers exploit.
APIs, if not implemented with adequate security, can expose vulnerabilities that lead to data leaks, compliance violations, and unauthorized access. Here are some of the top risks healthcare organizations face and how to mitigate them.
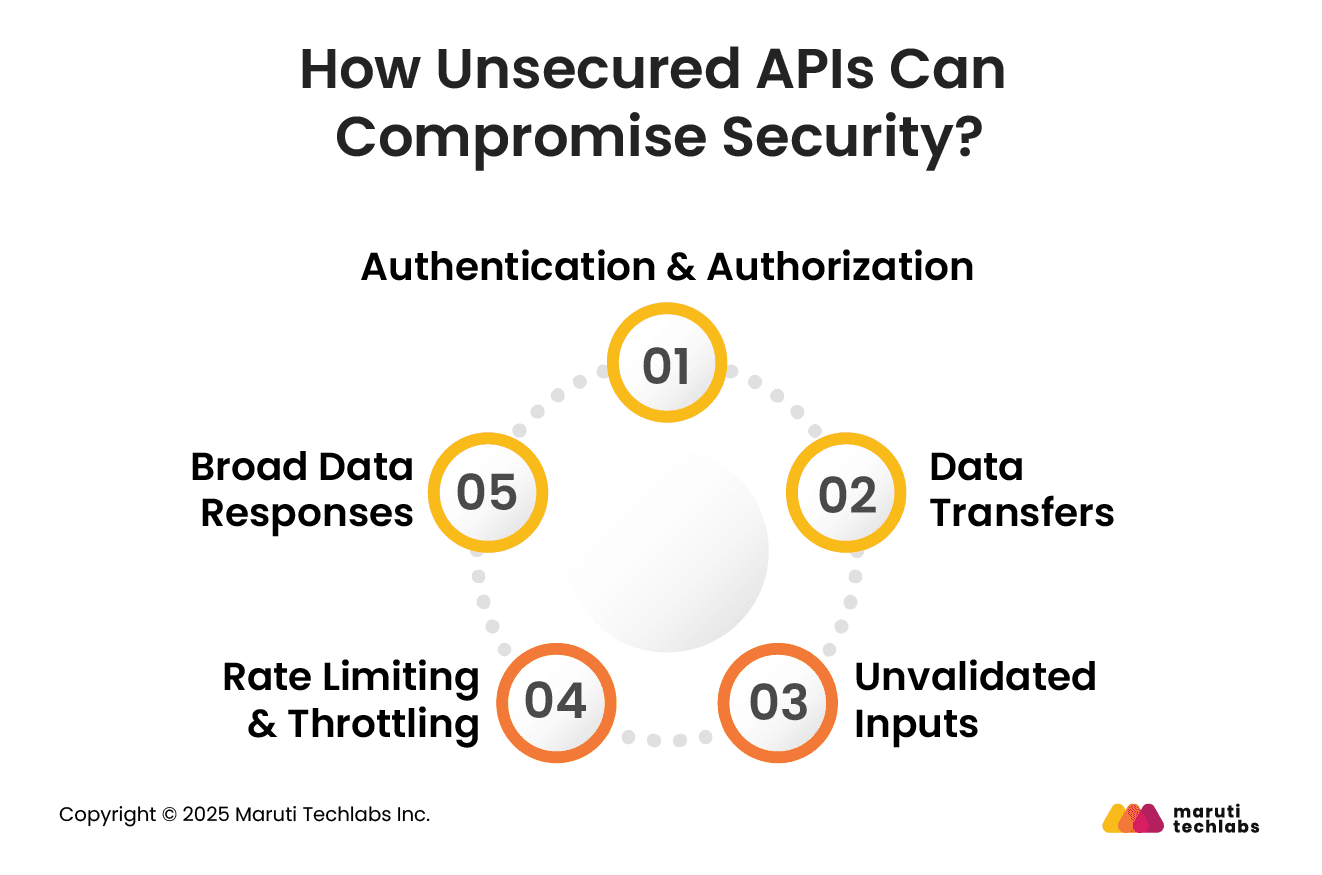
APIs without strong authentication and authorization in place are primary targets for attackers. It’s a gold mine, especially in the healthcare sector, where sensitive data such as medical records and insurance details can be misused.
Expert Tip: Limit access to essential users and systems by implementing multi-factor authentication (MFA) and role-based access controls (RBAC). A simple but effective way to manage access.
If unencrypted healthcare data is transmitted, it can be intercepted. Patient data transfer without adequate encryption can compromise their most private information.
Expert Tip: Leverage HTTPS/TLS to enforce encryption during transit and at rest. Inadequate encryption not only poses risks but is a direct violation of HIPAA and other regulations.
Did you know that unvalidated input data can compromise your systems? Systems with unvalidated input data are prone to injection attacks, such as SQL injection and XML External Entity (XXE). This can severely compromise system integrity.
Expert Tip: Implement stringent input validation to ensure all input data is clean. Ensure your APIs only allow valid, known data types to prevent injection attacks.
Imagine the result if an attacker bombarded your API with requests? APIs are particularly vulnerable to brute-force and denial-of-service (DoS) attacks. This can disrupt service for regular users by overloading the system.
Expert Tip: Ensure user availability and prevent abuse by setting rate limits and throttling rules.
Do you know what data your API responses are sending? In some cases, APIs send larger data sets than they should be sharing. This can expose confidential data.
Expert Tip: Configure APIs to share only essential data. Limit your APIs so they don't share information that isn’t required.
Zero Trust shifts security from perimeter-based defenses to continuous verification, ensuring no user or system is trusted by default. Here’s why zero-trust architecture has proved crucial for industries like healthcare.
Patient health records (PHRs) are more valuable on the dark web than credit card information. They make healthcare organizations prime targets for ransomware, identity theft, and large-scale data breaches.
Telehealth and remote work require something more than the traditional network perimeters. It demands continuous user verification, device validation, and secure access across distributed clinical and administrative environments.

To comply with HIPAA, GDPR, and HITECH, organizations need stringent data access controls, auditability, and least-privilege enforcement to reduce compliance risk, penalties, and reputational damage.
If not adequately secured, hospitals' connected devices can be exploited. They expand the attack surface and increase the need for granular access control and continuous monitoring.
Securing patient data is a critical responsibility shared by all healthcare organizations. With so much confidential data that can be misused in myriad ways, there is a high demand for protection.
Here are seven practices that can help you tighten your security posture.
Access to patient records isn’t a necessity for all your staff members. Therefore, it should only be shared with individuals who actually need it.
Encryption is about securing your data within an unreadable code. Even if stolen, it can’t be understood without a decryption key. It’s important to encrypt the data when at rest or in transit.
Cyberattacks, viruses, or system failures can result in complete data loss. Losing all your patient data can be the worst nightmare for a clinic or healthcare organization.
A viable solution is to store daily backups at an independent location.
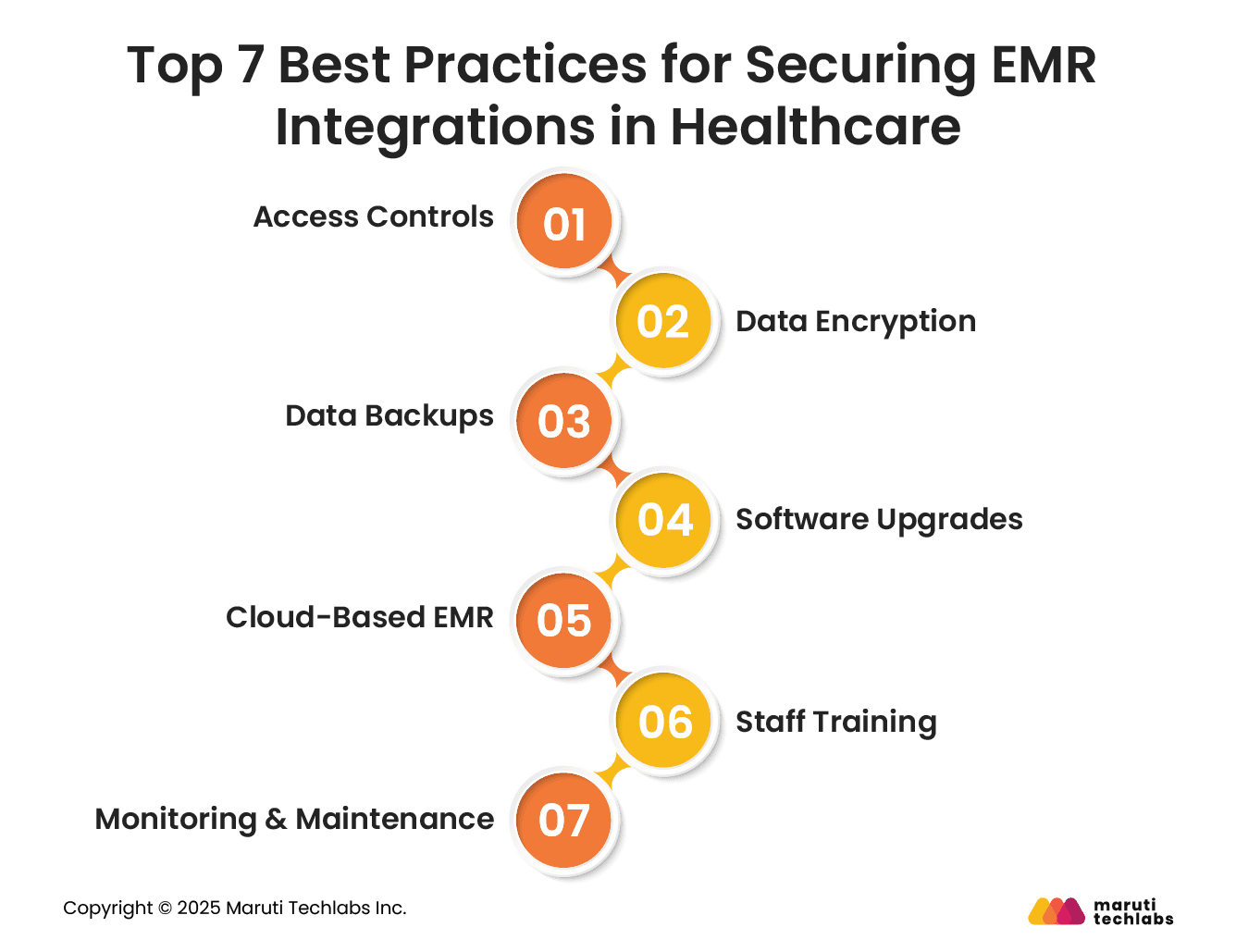
EMR software, if not kept up to date, can pose security risks. With advancements in the types of attacks cybercriminals use, it's necessary to patch vulnerabilities, add protective layers, and keep your systems up to date.
Cloud platforms are more secure than traditional on-prem EMR systems. This is because:
Data breaches aren’t always a result of security mishaps; they can also happen due to human oversight. This includes sharing passwords, clicking compromised links, or leaving systems unattended.
To maintain complete data security, an EMR system should maintain detailed visibility into user activity. Logging activities can help detect suspicious behavior before it becomes hazardous. This can be done using real-time alerts, audit logs, and user activity tracking.
To meet HIPAA requirements, healthcare systems must be designed with security, access control, and resilience built in from the ground up. Let’s observe the foundational requirements of a HIPAA-compliant architecture.
Using AI mechanisms for data privacy, patient data must always be protected throughout the system.
Various users should be granted access with appropriate encryption and access control.
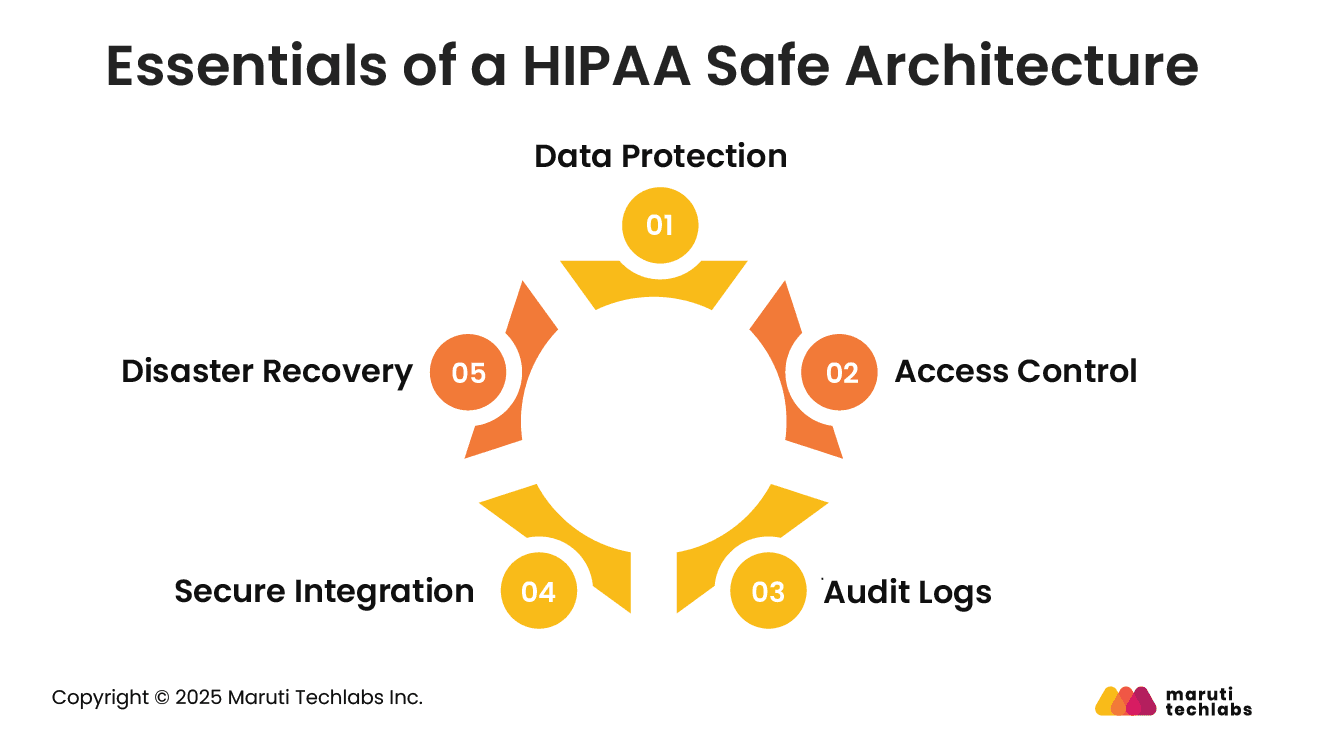
One of the primary HIPAA requirements is logging all interactions with patients. This includes who accessed a particular dataset, when, what they accessed, where they accessed it, and what they did with it.
The logs should also be untampered with. They should be in the system for at least 6 years, searchable for audits, and monitorable for suspicious activities.
Healthcare software can’t function without external integrations. It connects with Electronic Health Records (EHRs), imaging systems, insurance services, telemedicine platforms, IoT-equipped medical devices, patient monitoring systems, and more.
All integrations must adhere to the same level of security as your primary systems. One weak link can unleash a security breach that can compromise everything.
HIPAA demands that patient data should be accessible even in emergencies. This requires your software to have timely auto-backups, data stored in different locations, an optimal recovery process, and backup access methods in case of system failure.
This is important because, in the case of ransomware, your systems must be robust enough to recover without paying the criminals. In addition, during natural disasters, patient care should remain unaffected.
Healthcare data security has become a high-stakes priority as cyber threats grow more advanced and attack surfaces continue to expand. From ransomware and AI-driven attacks to unsecured APIs, cloud misconfigurations, and vulnerable integrations, the risks span people, processes, and technology.
At the same time, regulatory mandates like HIPAA and GDPR leave little room for error. Adopting Zero Trust principles, strengthening API security, and building a HIPAA-safe architecture are no longer optional; they are foundational to protecting patient trust and ensuring continuity of care.
A proactive, layered security approach enables healthcare organizations to safeguard sensitive data while supporting modern care models such as telehealth and cloud-based systems.
If you’re planning to strengthen your healthcare ecosystem’s security posture, consult Maruti Techlabs’ AI Strategy & Readiness Services to assess risks, align AI initiatives with compliance requirements, and design secure, scalable healthcare systems.
Connect with us today and discover how we can help you build a secure, intelligent, and accessible healthcare ecosystem.
Data security in healthcare refers to protecting patient information from unauthorized access, breaches, and misuse. It includes safeguarding electronic health records (EHRs), medical histories, billing data, and personal identifiers using encryption, access controls, monitoring, and compliance frameworks such as HIPAA.
Patient data can be secured by implementing role-based access controls, multi-factor authentication, encryption at rest and in transit, regular system updates, secure backups, staff training, and continuous monitoring. Adopting Zero Trust principles and ensuring HIPAA compliance further strengthens protection.
Small clinics benefit from platforms like Microsoft Azure Health Data Services, AWS HealthLake, Google Cloud Healthcare API, Drata for compliance, and Vanta for security automation. These platforms offer scalable security, built-in compliance, encryption, and centralized access management.


