

How to Develop Production-Ready RAG Systems: 7 Best Practices






Retrieval augmented generation (RAG) has become essential for building trustworthy AI systems. Large language models are powerful, but they often produce outdated or incorrect answers when relying only on fixed training data.
RAG solves this by bringing in relevant, fresh information from reliable sources, thereby improving accuracy, grounding responses, and reducing hallucinations. This makes it ideal for enterprise use cases that require precision, like customer support, research, compliance, and decision support.
As organisations scale AI adoption, RAG ensures models can continue learning from new events, documents, and insights without retraining, making it a practical, future-ready approach.
This blog provides readers with a clear, step-by-step roadmap for building production-ready RAG systems, along with future trends and best practices to help teams design accurate, scalable, and continuously improving solutions.
Retrieval Augmented Generation is a framework that allows generative AI models to retrieve information from reliable and specific data sources in real-time, enhancing their accuracy.
LLMs are neural networks. They’re measured by the parameters they contain. The parameters are a collection of patterns that represent how humans use words to form sentences.
This parameterized knowledge enables LLMs to respond to general prompts. However, it doesn’t help users who want to retrieve any specific type of information. RAG fills this gap for LLMs. It enhances LLM performance by accessing external, real-time, and verified data and generating context-aware responses.
To understand how RAG helps LLMs, let’s examine a common challenge that businesses face today.
Imagine you work for an electronics company that sells devices such as refrigerators, washing machines, smartphones, and laptops. You plan to create a customer support chatbot that helps answer frequently asked customer queries related to product specifications, warranty, and other topics.
You decided to leverage GPT-3 or GPT-4 to build your chatbot. However, the following limitations of LLMs result in an inefficient customer experience.
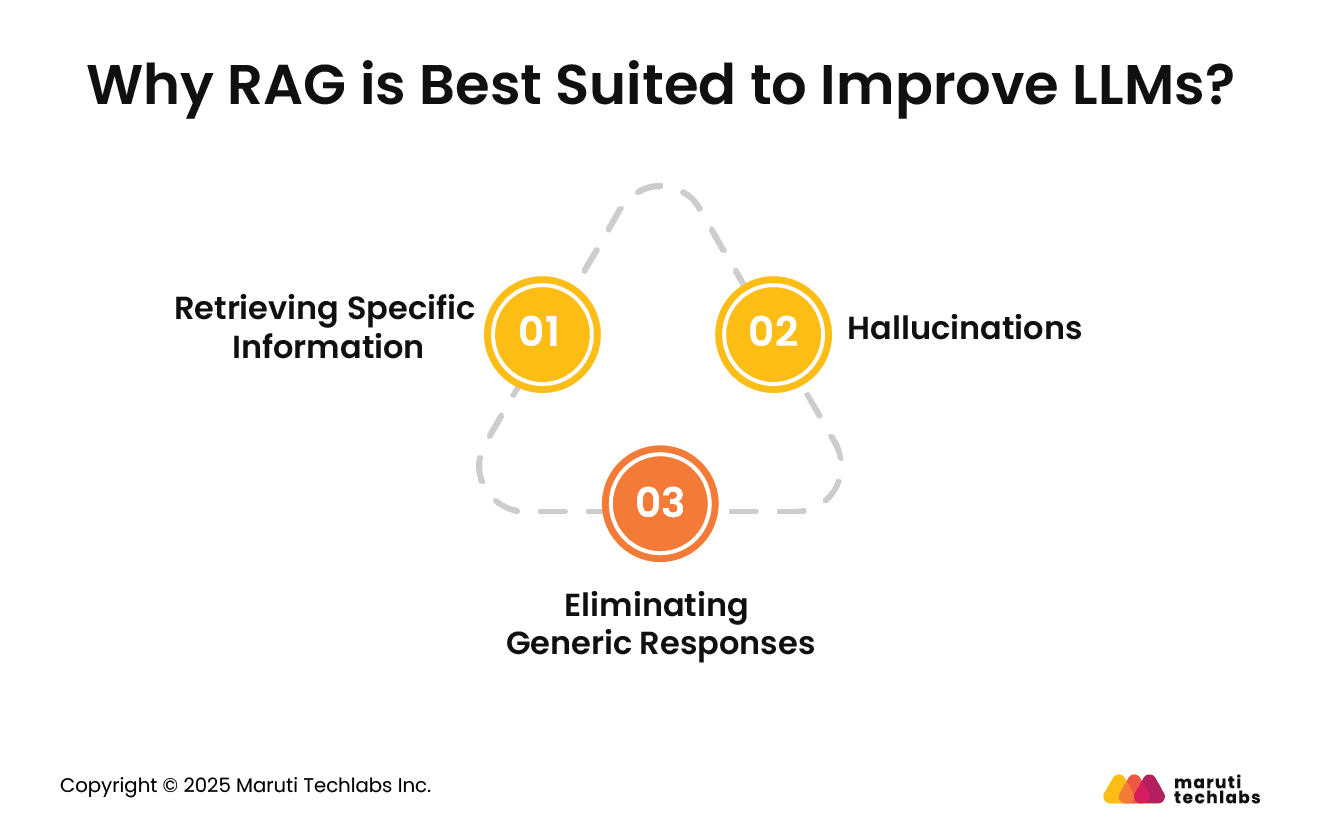
LLMs offer results based on their training data. A conventional LLM wouldn’t be able to answer the questions specific to the electronics you sell.
This is because the LLM wasn’t trained on data related to your products. Additionally, these LLMs have a cutoff date, which limits them to offering responses that are no longer current.
LLM can generate confident false responses known as “Hallucinations.” They also, at times, offer inaccurate responses that are entirely related to your query based on imagined facts.
Language models often provide generic responses that lack contextual relevance. This approach wouldn't be practical for a customer support platform where personalized responses are crucial.
RAG acts as a savior by blending the expertise of your LLMs with the specific product-related data from your database and user manuals. It provides accurate and reliable responses that align with your business needs.
Let’s understand how RAG functions in 8 simple steps.
As a user submits a query using the RAG interface, the prompt, whether straightforward or complex, commences the entire pipeline.
The query is shared with the embedding model, which transforms it into a high-dimensional vector that captures its semantic meaning for retrieval.
The embedded query vectors are shared with the retrieval engine.
The retrieval engine looks for a vector index of the database of embedded chunks from source documents to discover the most semantically relevant chunks. This is where the “search” process occurs, based on meaning rather than keywords.
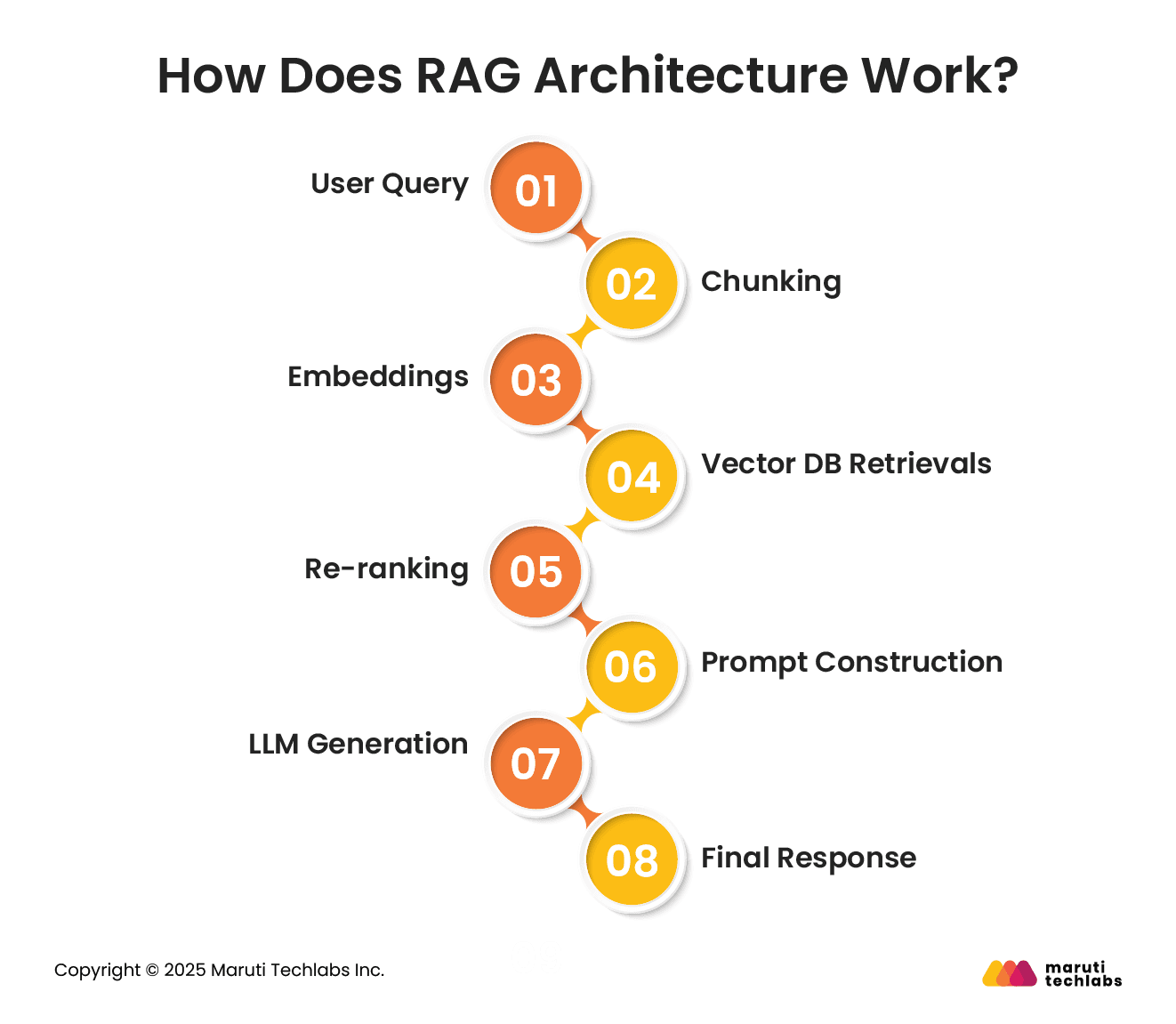
The system pinpoints the most contextually relevant passages from the vector index and shares them back with the RAG pipeline.
The retrieved chunks and original user query are merged to create a single context block.
The context block is shared with the LLM to develop a natural language response combining the original query and the retrieved content.
The RAG interface sends the final up-to-date reference-backed response to the user.
Although RAG offers an effective strategy for optimizing LLMs, its real-time performance can vary due to factors such as latency, scalability, maintenance, and knowledge accuracy. An efficient RAG requires a balance between system complexity, long-term adaptability, and computational efficiency.
Here are the top 3 reasons to consider before implementing RAG.
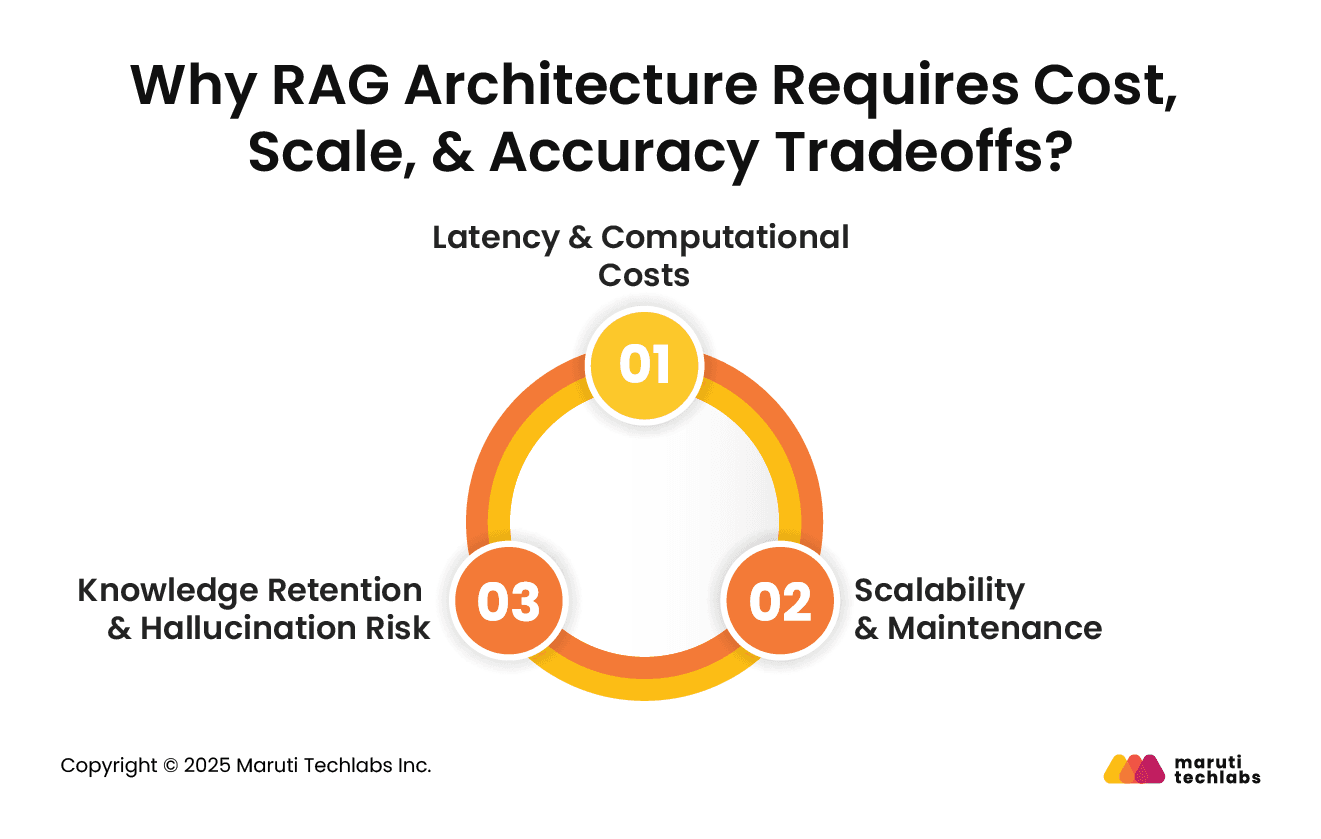
The computational requirements of RAG impact both training and inference efficiency. While it is cheaper to train, RAG introduces real-time retrieval delays that can slow down inference, leading to 30–50% longer response times.
The ease offered by updates and maintenance should be a primary consideration for evolving AI models. RAG is easier to maintain due to its ability to stay updated from external sources.
RAG offers many challenges when we talk about knowledge accuracy and hallucination risks. While they provide the convenience of automatic and timely knowledge updates, they're only as good as the authenticity of their retrieval source. Unreliable data sources or poor indexing can result in hallucinated responses.
Building a strong RAG system needs a structured approach that connects business requirements, data foundations, and model behaviour.
These steps guide teams through the full lifecycle from planning to monitoring so the system stays accurate, explainable, and easy to maintain.
Start by clarifying the problem your RAG system will solve. Identify the target users, expected outcomes, required accuracy level, and the type of decisions it will support.
A clear use case helps shape the depth of retrieval, data requirements, performance goals, and guardrails, ensuring the system aligns with real business value.
Decide what information the RAG system should rely on. Choose documents, knowledge bases, transcripts, reports, or web sources that offer trustworthy and updated knowledge.
Clean, tag, and structure the corpus so it is easy to search. A high-quality corpus directly improves response accuracy and reduces noise.
Choose how the system will find the correct information. Decide between keyword search, vector search, or hybrid methods based on query style and corpus size.
Tune chunking, metadata, and ranking strategies to improve retrieval precision. Strong retrieval design ensures the model sees the most useful context every time.
Create clear instructions that guide the model in using the retrieved content. Structure prompts with context, task, style, and output rules.
Include grounding reminders to ensure the model stays on the provided information. Well-designed prompts help combine knowledge and reasoning to yield stable, consistent answers.
Evaluate how the system performs under real conditions. Test accuracy, relevance, latency, and the quality of final responses using real user questions.
Add edge cases, missing data scenarios, and stress tests. Use both human and automated evaluation to confirm that the system behaves reliably before deployment.
Track how the system performs over time. Watch for drops in accuracy, retrieval failures, outdated content, slow responses, or user dissatisfaction.
Build dashboards for query patterns and feedback loops. Continuous monitoring enables quick issue detection and helps teams maintain consistent performance in changing environments.
RAG systems improve with steady refinement. Update data sources, tune prompts, adjust retrieval settings, and enhance evaluation methods as user needs evolve.
Use feedback to strengthen weak areas. Regular iteration keeps the system aligned with new knowledge, new behaviours, and expanding business goals.
To implement RAG effectively and successfully, it is essential to follow a systematic approach. Here’s how you can do this following 7 simple steps.
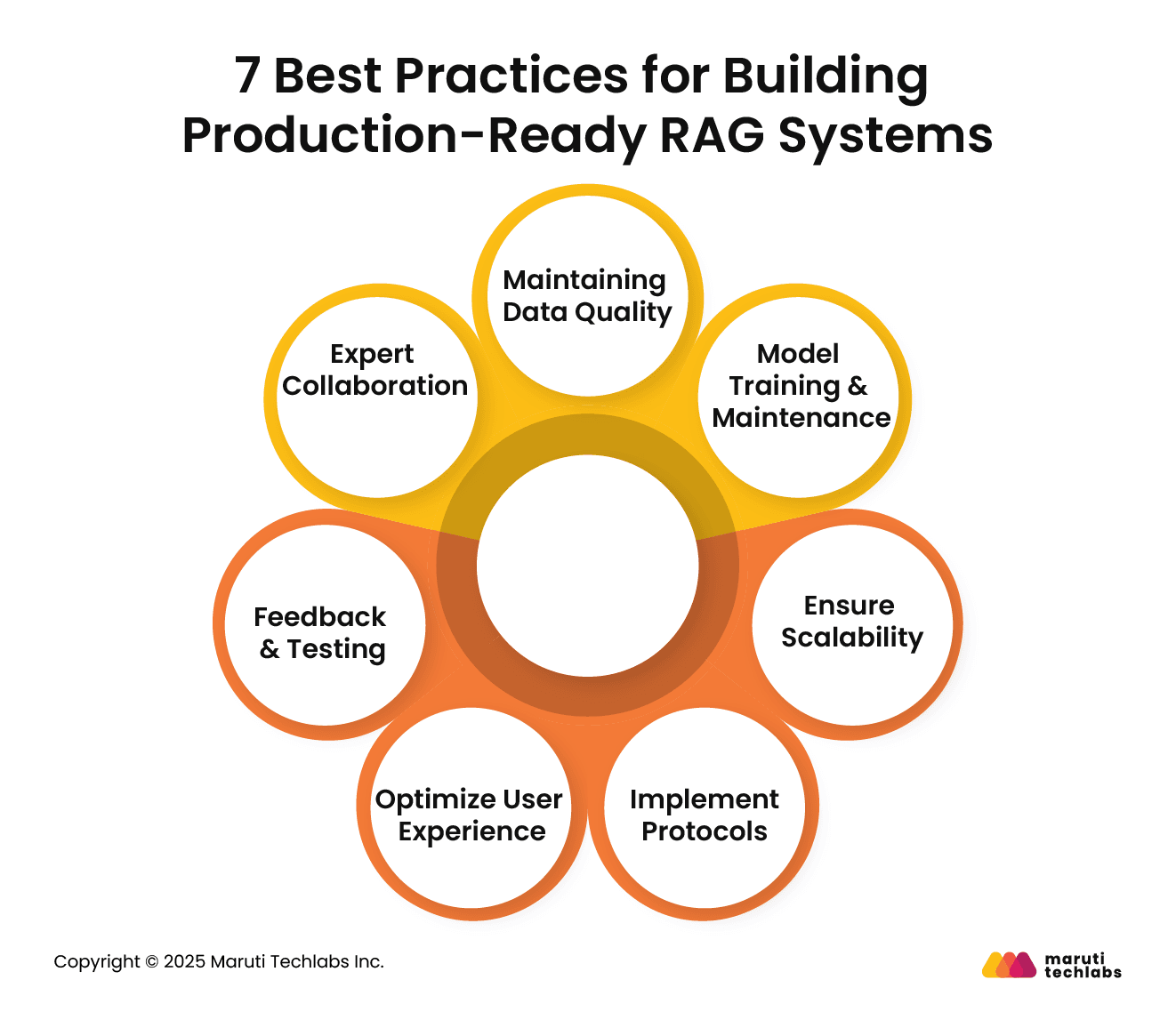
To ensure updated information is fed to the RAG model, follow the practice of continuously updating the data sources. Try to include various sources of information, such as reputable journals, credible databases, case studies, white papers, and other relevant materials, to provide authentic and reliable information.
Keep your model updated with evolving language use and information by retraining the model on a timely basis. Set up an ecosystem with tools and processes to monitor the model’s output. This would help keep tabs on accuracy, relevance, and biases in responses.
Consider factors such as user load and increased data volume, and design a scalable RAG system from the outset. Manage intensive data processing by investing in appropriate on-premise resources, computational infrastructure, and cloud-based solutions.
Adhere to data compliance laws, introducing stringent protocols for data privacy and security. Conduct regular audits to stay informed about the latest developments in AI ethics and regulations.
Enhance system accessibility by creating easy-to-navigate UIs using intuitive designs. Ensure AI's responses are clear, concise, and understandable.
Conduct thorough testing of your RAG system, replicating real-time scenarios. Establish processes that allow you to incorporate user feedback into future updates.
Seek guidance from subject matter AI experts and Data Analytics Consultants who are adept at what they do to create futuristic and scalable systems.
Encourage acute involvement from your technical and non-technical teams.
This holistic approach offers you a blend of outsourced Artificial Intelligence Service providers and your company’s domain-specific knowledge teams.
RAG continues to grow as research explores new ways to improve search, context understanding, and reasoning.
These trends show where the field is heading and what enterprises will expect when building next-generation knowledge-grounded AI systems.
New retrieval methods focus on faster search, better relevance, and improved ranking. Approaches such as adaptive retrieval, dense-sparse hybrid systems, and retrieval that learns from user behaviour are becoming increasingly common.
Research explores models that automatically update retrieval rules, enabling systems to deliver more accurate, context-aware results.
Embedding research is moving toward models that capture deeper meaning, domain expertise, and long-range context. Smaller specialised embedding models trained on enterprise data improve relevance and reduce noise.
Research directions include contrastive training, task-aware embeddings, and techniques that preserve relationships between long documents and complex knowledge.
Enterprises want RAG systems that reflect new information instantly. Real-time ingestion enables continuous updates from documents, transactions, conversations, and events without heavy processing.
Research explores streaming indexes, incremental vector update,s and methods that keep retrieval fresh without slowing performance, making knowledge always current and reliable.
Future RAG systems will handle text, images, audio, and structured data together. This allows a richer understanding of products, support cases, medical scans, designs, and more.
Research is moving toward unified retrieval across multiple formats, enabling models to combine signals and deliver well-rounded answers that match complex real-world tasks.
Enterprises increasingly need RAG systems that meet strict accuracy guarantees, auditability, data residency, and domain adaptation.
They want automated evaluation pipelines, predictable latency, multilingual support, unified retrieval across departments, and tools that reduce manual tuning.
Governance, cost efficiency, and real-time updates are becoming central requirements as adoption scales.
RAG bridges the crucial gap between general-purpose Large Language Models (LLMs) and domain-focused enterprise applications. By offering AI outputs in a curated, contextually relevant knowledge base, RAG ensures that responses are not just rational but also accurate, explainable, and tailored to business needs.
This hybrid approach enables businesses to maintain data security, minimize hallucinations, and ensure regulatory compliance while achieving greater operational efficiency.
Leading organizations are already exploring fine-tuned RAG pipelines integrated with tools and domain-specific strategies to enhance productivity and innovation. As adoption accelerates, we foresee a move toward more customizable, multimodal, and real-time RAG applications.
At Maruti Techlabs, we specialize in designing, developing, and deploying scalable RAG-based solutions tailored to your unique business challenges. Whether you're looking to enhance customer experience, automate internal operations, or unlock hidden insights from your data, our team can guide you through the journey.
Connect with us today and commence your AI adoption journey.
Not sure if your business is ready? Try our AI Readiness Calculator to evaluate where you stand and how to move forward.
RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) is a technique that enhances generative AI by retrieving relevant external information in real time, allowing large language models to generate more accurate, context-aware, and up-to-date responses.
RAG architecture comprises a retriever that retrieves relevant documents from a knowledge base and a generator (typically an LLM) that utilizes this retrieved content to produce coherent, informed, and contextually grounded responses.
Generative AI uses LLMs to create content. RAG combines LLMs with retrieval systems, enabling them to go beyond static training data by incorporating real-time, external knowledge into generated outputs for improved accuracy.
RAG uses structured and unstructured data, including documents, databases, PDFs, websites, knowledge bases, and other domain-specific content, to retrieve relevant context for enhanced response generation.


