

9 Essential Steps for Successful Healthcare Mobile App Development






Healthcare mobile applications have changed the way patients and healthcare practitioners connect. With healthcare apps, it has now become convenient for users to address management and scheduling tasks, medical history, and many other needs. The increasing demand for digital healthcare services means there is immense potential in the market for healthcare apps.
According to Mordor Intelligence, analysts project the global healthcare IT market to reach $728.63 billion by 2029, growing at a compound annual growth rate of 15.24% between 2024 and 2029. However, an app that caters to this vital industry should be built with strategic placement, compliance, and user experience in perspective.
The following guide will present the basic steps in app development for healthcare, covering everything from conducting market research to post-launch updates.
detection, personalized treatment planning, and proactive care management.
Predictive analytics enables clinicians to anticipate risks, optimize interventions, and monitor patient progress more effectively.
These intelligent capabilities create more responsive systems that improve clinical outcomes and reduce long-term health complications across diverse populations.
Telemedicine platforms deliver virtual consultations, secure chats and video interactions that expand patient access. Remote monitoring tools track vitals, chronic conditions, and post-treatment recovery through connected devices.
Together, they reduce hospital visits, strengthen care continuity, and enable clinicians to intervene quickly when anomalies appear, improving patient satisfaction and overall health system efficiency.
Healthcare apps increasingly integrate data from wearables that continuously track metrics such as heart rate, activity, sleep quality, and oxygen levels.
These insights support preventive care, real-time monitoring, and personalized recommendations.
Seamless integration with mobile devices and clinical dashboards enhances diagnostic accuracy and helps patients stay engaged in managing their health.
Interoperability ensures smooth data exchange among systems such as electronic health records, labs, and pharmacy platforms. Standards such as FHIR and HL7 streamline integration by offering unified structures for clinical information.
Robust interoperability enables complete patient histories, reduces administrative duplication, and supports coordinated care across different healthcare providers and facilities.
AR and VR technologies are improving rehabilitation, surgical training, and patient education through immersive experiences.
These tools simplify complex medical concepts and support therapy in safe virtual environments.
When paired with accessibility guidelines, they offer inclusive interactions for users with diverse physical or cognitive needs, making healthcare applications more supportive and empowering.
Patients need simple and supportive experiences focused on care access, reminders, education, and self-management.
Clinicians require accurate data, efficient workflows, and reliable decision support.
Administrators need insights to schedule, allocate resources, and ensure compliance. Clear persona definitions guide feature decisions that address the specific goals and frustrations of each stakeholder group in healthcare.
Chronic disease management may require symptom logging, wearable sync, and medication alerts.
Clinicians may need dashboards, lab integrations, and messaging. Administrators may need reporting, audit trails, and scheduling tools.
Mapping each use case to features ensures applications are purposeful, aligned with workflows, and capable of delivering meaningful outcomes for all healthcare participants.
It’s crucial to differentiate between health and medical apps regarding healthcare mobile applications. While both focused on health, these categories serve vastly different purposes and user groups.
Health apps generally target users interested in staying fit or healthy. They cater to a general audience—people who want to cultivate healthy habits and monitor aspects of their personal well-being.
Although health apps may offer expert-backed health advice, their information often does not come from clinical sources and is typically intended for preventive health care or lifestyle management.
Most health applications are user-friendly and designed to engage users and motivate them toward wellness goals. They are also often HIPAA-compliant, thus protecting user data.
Examples of popular health app categories include:
| Category | Description | Examples |
| Fitness and Workout Apps | Enables users to set fitness goals, track workouts, and monitor physical activity. Includes features like guided workouts and activity logs. | Nike Training Club, MyFitnessPal |
| Meditation and Mental Health Apps | Provides a convenient way to manage stress and emotional balance, making mental health care more accessible. | Calm, Headspace, BetterHelp |
| Nutrition Apps | Track daily food intake, calorie consumption, and water intake. Provide personalized diet plans based on age, weight, and health goals. | MyFitnessPal, Lose It!, Yazio |
| Sleep Tracking Apps | Analyze sleep patterns, monitor sleep duration, and provide suggestions for better rest. Offer insights into sleep cycles and quality. | Sleep Cycle, Pillow, Fitbit |
| Wellness Apps | Broad in scope, covering weight management, hydration tracking, smoking cessation, and lifestyle guidance for overall well-being. | Noom, WaterMinder, Smoke Free |
Health apps are great for proactive self-care and preventive measures, helping individuals maintain a healthy lifestyle without constant professional oversight.
On the other hand, medical apps are more specialized tools for healthcare professionals and patients to actively manage a diagnosed medical condition. Such apps are often used in clinical settings.
In handling patient data, medical apps must comply with strict medical standards and regulatory requirements like GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) or HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act).
Medical applications are often more functional, including seamless integration with Electronic Health Records (EHR) and advanced diagnostic tools to support healthcare providers in delivering care. These apps can directly assist in diagnosing, treating, and managing specific medical conditions.
Examples of medical apps include:
| Category | Description | Examples |
| Telemedicine Apps | Facilitate remote consultation with health experts via video calls and messaging, which is especially useful when on-site visits are impossible. | Teladoc, Amwell, Doctor on Demand |
| Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM) Apps | Allow healthcare providers to monitor patients' vital signs and health data remotely. Beneficial for managing chronic conditions and post-operative care. | HealthTap, Vivify Health, MyChart |
| Chronic Disease Management Apps | Help patients manage chronic conditions like diabetes or hypertension, offering medication reminders, symptom trackers, and educational resources. | Glucose Buddy, MySugr, Omada Health |
| Electronic Medical Record (EMR) Apps | Provide mobile access to medical records, test results, and treatment plans. Updates patient information and assists in decision-making to streamline clinical workflows. | Epic, Cerner, Allscripts |
| Emergency Care Apps | Offer resources in critical situations, providing nearest emergency facilities, basic first aid instructions, and quick reference guides for healthcare providers. | Pulsara, ERres, Red Cross First Aid App |
While health apps focus on general well-being and help individuals stay healthy, medical apps are designed for more severe healthcare management, directly involving medical professionals in patient care. Medical apps typically require higher security and compliance measures because they handle sensitive patient data and are often integrated into clinical workflows.
Recognizing this difference is essential when choosing the type of app to develop or utilize, as the features and requirements for each can vary significantly.
Let’s look at the key steps to build a successful healthcare mobile app that meets industry standards and is effective, efficient, and user-friendly.
Protection of sensitive health data requires encryption, continuous monitoring, and secure storage.
Strong access policies, regular audits, and threat detection reduce vulnerabilities. Structured data lifecycle management ensures appropriate retention and deletion practices.
Together, these measures create a secure environment that minimizes breaches and protects patient trust at every stage of the digital journey.
Compliance with healthcare regulations, such as HIPAA, requires strict management of patient information, robust access controls, and robust audit capabilities.
Documentation, risk assessments, and consistent policy enforcement are essential. Precise adherence to regulation frameworks ensures that applications meet legal standards, protect sensitive information, and maintain operational integrity within highly controlled healthcare environments.
Effective consent flows give users transparency and control over how their data is used. Strong authentication prevents unauthorized access, while audit logs track actions across systems.
These capabilities ensure accountability, support investigations, and meet compliance requirements. Together, they reinforce responsible data management and build confidence among patients, providers, and regulators.
Building a healthcare app is a multifaceted process that demands precision, a deep understanding of user needs, and rigorous compliance with industry standards. In a sector as critical and rapidly evolving as healthcare, seamless functionality, security, and user trust are paramount.
A well-planned healthcare app can revolutionize patient care, enhance operational efficiency, and deliver substantial value to users and providers. The following steps will guide you through developing a healthcare app that is compliant, functional, user-centric, and sustainable for long-term success.
Market research is the starting point of any app development for a healthcare project. The industry's highly regulated and competitive nature makes it even more critical. Market analysis provides insights into user needs, competitor offerings, and potential gaps in the market.
Market research helps identify precisely what your users need and where the problems lie so that you can provide solutions that add value to your app. Otherwise, without such information, you might create a solution that misses the mark on all sides or, worse still, does not meet the industry standards set by the industry.
Key Focus Areas in Market Research:
| Purpose | Key Consideration |
| Who is your target audience? | Identify whether your app targets patients, healthcare providers (e.g., doctors, nurses), or administrative personnel. Consider their age, tech literacy, and pain points. |
| What market trends are shaping the industry? | Analyze current trends like telemedicine, AI-driven diagnostics, and patient-centered care. Determine how emerging technologies can enhance your app's offerings. |
| Who are your competitors? | Research both direct competitors (apps serving similar needs) and indirect competitors (alternatives like web platforms or physical health services). Examine their features, pricing, user reviews, and regulatory compliance. |
| What regulations must the app comply with? | Identify necessary certifications (e.g., HIPAA for U.S. apps, GDPR for European users). Investigate data privacy laws, medical device classification, and approval processes (FDA or CE marking). |
With the foundation of market research laid, the next priority is understanding your target users.
Understanding users is very important for app development in healthcare. User research ensures that your app addresses real needs, improves usability, and provides value, making it an essential step in your app's success.
Healthcare professionals may need quick access to patient data or efficient scheduling systems, while patients might prioritize features like appointment reminders, teleconsultations, or medication management.
Hence, you can study and observe the variations between different user groups. This allows you to design specific feature requirements that cater to the needs of each user category.
The next step would be deciding the type of healthcare app that best aligns with their needs. Let’s explore the options.
Choosing the type of healthcare app you want to develop is more than a pivotal decision. It's a guiding light that will steer the design and functionality of your app development for healthcare in the right direction.
These applications are typically used in hospitals or clinics and include features like patient data management, telemedicine services, diagnostic tools, and appointment scheduling. Developers must integrate the app with Electronic Health Records (EHR) systems and ensure it complies with medical standards.
These apps focus on patient engagement and healthcare management. Features might include tracking vitals, managing chronic conditions, accessing medical records, or booking appointments. Patient apps must be user-friendly and cater to individuals with varying levels of technological proficiency.
A hybrid approach combines features for both healthcare professionals and patients. These apps allow seamless communication between both parties, including teleconsultation, patient monitoring, and record-sharing capabilities.
Let’s now shift gears to create a user-friendly experience.
Design is crucial to any successful app but has added significance in healthcare. During app development for healthcare, it is necessary to follow fundamental design principles that are visually appealing, intuitive, and accessible.
Must-Have Features for Healthcare Apps
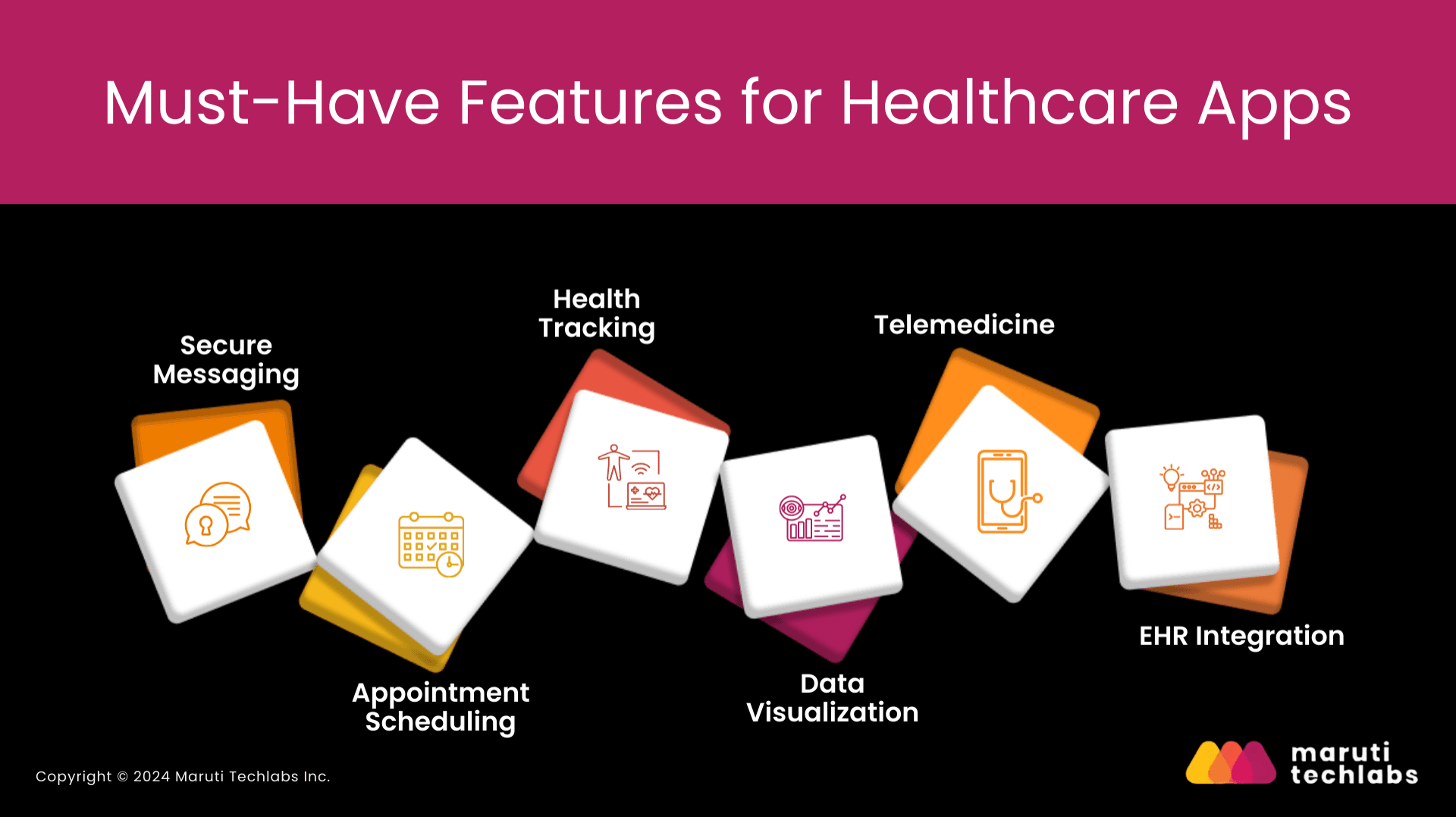
Having established the significance of the user experience, it is time to turn to critical security considerations.
Security and regulatory compliance are the backbone of app development for healthcare. Sensitive patient data, including medical histories and lab results, must be safeguarded at all costs. Non-compliance can lead to significant penalties and a breakdown of user trust.
Apps that handle Protected Health Information (PHI) must comply with HIPAA in the U.S. or GDPR in Europe. This includes securing data in transit and at rest through encryption, user authentication, and access controls.
Organizations must regularly conduct security audits and vulnerability testing and use secure coding practices to safeguard against cyber threats. Implementing multi-factor authentication and monitoring access logs can further enhance security.
HIPAA Compliance Checklist
| Cybersecurity Measures |
| Secure Data Storage (Encryption) | Encrypt sensitive data in transit and at rest to ensure protection from unauthorized access using robust encryption methods. |
| Regular Security Audits and Updates | Regularly check your system for vulnerabilities and update your software to avoid security threats. |
| Strict User Authentication | Enforce solid and unique user credentials, with password complexity requirements and regular password changes to enhance system security. |
| Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) | Implement MFA, requiring additional authentication steps such as one-time passwords or biometrics like fingerprints and face-id to further protect against unauthorized access. |
| Regular Compliance Checks | Conduct periodic compliance assessments to verify adherence to HIPAA guidelines and ensure that security measures are current. |
| Access Control and Activity Monitoring | Implement access control to restrict data to authorized users and continuously monitor logs and user activities to detect and respond to anomalies. |
Picking the right technology for your app development for healthcare is very important. It determines how fast you can develop the app, its performance, and whether it will meet your business goals.
Here are the top technologies for healthcare app development:
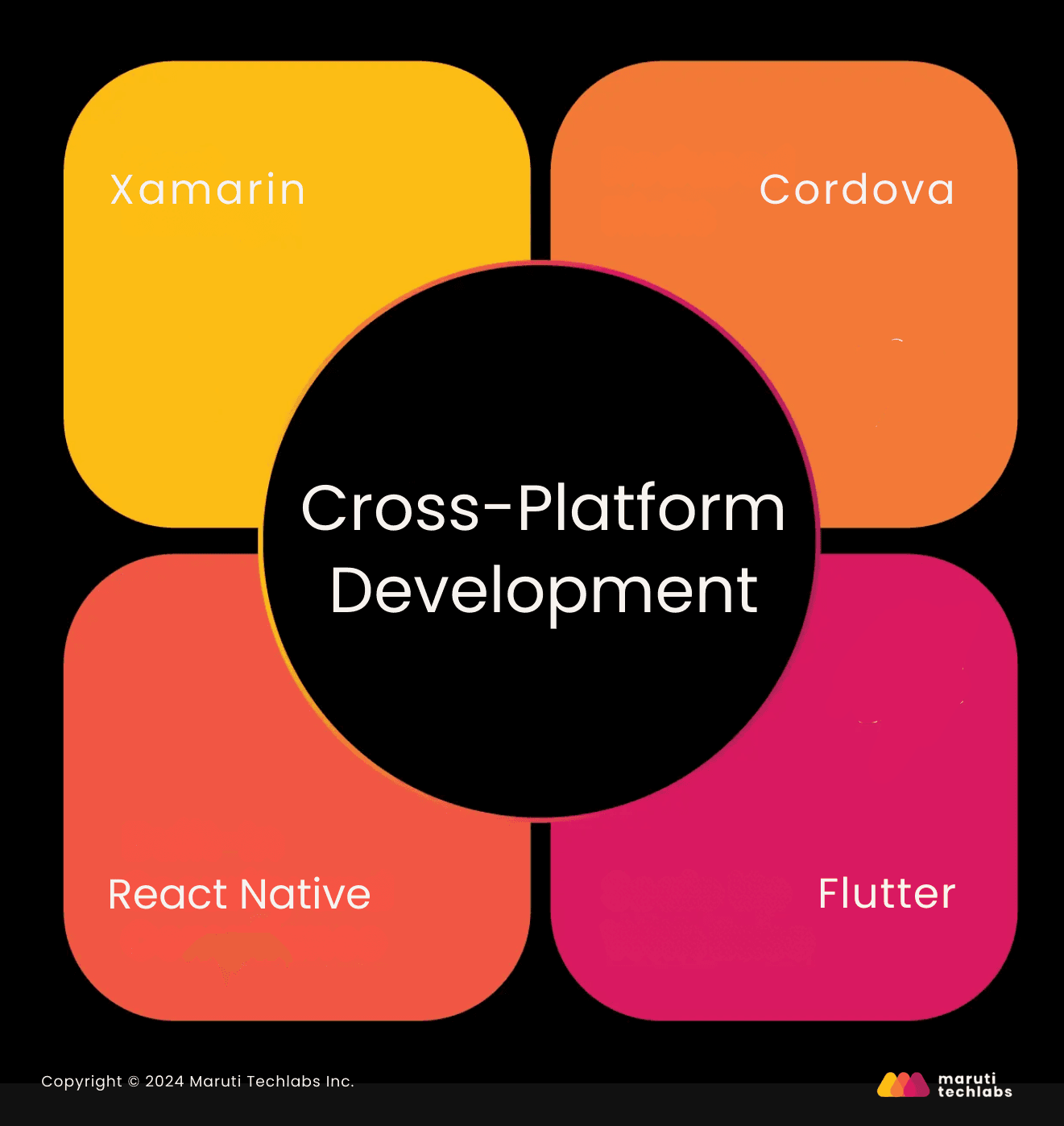
For apps that require a seamless, native experience on iOS or Android:
Choosing the right tech stack can significantly reduce your time to market while ensuring your app is fast, secure, and scalable
Creating a Minimum Viable Product allows you to assess the core functionality of your app without significant upfront investment. An MVP should include just the core functionality needed to attract early enthusiasts and gain insights for future enhancements.
An MVP's primary objective is to market your app while quickly maintaining its core value proposition. By focusing on essential features, you can introduce the app to users early in development and collect actionable insights. The iterative process polishes the app with every test and keeps it at par with expectations and industry standards, only deepening all advanced functionalities.
The next critical phase is rigorous testing to ensure the app performs flawlessly and meets all necessary standards.
Testing is a vital phase in healthcare app development. Given the sensitive nature of the data and the high stakes in healthcare, thorough testing ensures the app functions as intended and is safe for users.
The next step is launching your app successfully and what lies beyond the initial release.
Once rigorous testing has ensured the app’s functionality and security, it's time to launch—a critical phase in app development for healthcare that can significantly impact its success. A strategic and well-executed launch is essential. Then, engage healthcare networks, social media, and email marketing campaigns targeting the first wave of users.
However, the launch is just the beginning. In addition to launching, steady upgradation and maintenance are of equal importance, addressing the possible bugs that may arise with changes, feature introductions, and continued compliance with healthcare's dynamic requirements.
Healthcare apps must be inclusive by offering simple navigation, readable text, intuitive workflows, and adaptable interfaces. Inclusive design ensures that people with varying abilities can access information easily.
This approach promotes equal participation, reduces frustration, and supports better health outcomes by making the digital experience accessible to the broadest possible audience.
Engaging real patients, clinicians, and administrators in usability testing reveals workflow gaps, accessibility issues, and issues with feature clarity. Their feedback ensures that the app works in real-life settings, not just controlled environments.
Consistent testing improves adoption, reduces errors, and leads to designs that genuinely support users in their daily healthcare activities.
Adhering to accessibility standards ensures visual, auditory, and motor accommodations are built into the app. Localization adapts content for different languages and cultural contexts.
These practices create inclusive digital experiences that meet global expectations and ensure users from diverse regions and backgrounds can access the information they need without barriers.
Healthcare applications must process high volumes and continuous data streams from medical devices and clinical systems. Efficient pipelines, scalable storage, and structured validation ensure reliability.
Real-time processing supports critical decisions while maintaining accuracy and consistency. A strong data strategy prevents bottlenecks and enhances the quality of clinical insights.
Reliable offline support lets users access essential features even without stable connectivity. Smart caching, local storage, and conflict resolution ensure smooth transitions when the device reconnects.
These capabilities enhance clinicians' usability in remote settings and ensure uninterrupted access to critical patient information during emergencies or while on the move.
Clear visual dashboards help clinicians understand patient trends, spot anomalies and make informed decisions quickly. Visualizations simplify complex information and support proactive interventions.
Analytics tools uncover patterns, highlight risks, and provide performance insights. Together, they strengthen clinical confidence and empower users to interpret large health datasets effectively.
Continuous monitoring and strong maintenance practices ensure healthcare applications remain reliable, compliant, and able to support evolving user needs across clinical and administrative workflows.
Reliable support includes bug fixes, performance tuning, and regular feature improvements. Healthcare systems evolve quickly, and applications must adapt to new requirements, clinical standards, and user feedback.
Proactive updates and quick resolutions ensure consistent performance and reduce disruptions for both patients and care teams who depend on the platform daily.
Integrated analytics track usage patterns and highlight performance issues. Error reporting systems identify failures early, enabling rapid resolution. Structured feedback channels give users space to share frustrations and requests.
Together, these insights guide improvements, strengthen reliability, and ensure the application continues to meet the expectations of diverse healthcare stakeholders.
Structured versioning helps maintain compatibility while safely releasing new features. Regular updates ensure compliance with evolving standards, enhance security, and improve the user experience.
Controlled deployment processes reduce risk and ensure a smooth transition for all users. This discipline supports long-term system stability and sustainable growth for the healthcare application.
Healthcare app development brings unique challenges that require careful planning, strong governance, and ongoing evaluation to ensure safety, reliability, and compliance across all environments.
Healthcare apps handle highly sensitive information, increasing the risk of breaches. Weak encryption, insecure APIs, or accidental data misuse can compromise patient trust.
A privacy-first design, strong access controls, and consistent monitoring help protect data, uphold confidentiality, and maintain compliance with strict healthcare regulations and expectations.
Integrating with electronic health records, devices, and legacy systems can be difficult due to inconsistent formats and slow interfaces. Complex workflows require accurate mappings and extensive testing.
A structured integration plan and adherence to standards improve reliability and help ensure information flows smoothly across different healthcare environments.
Even well-designed apps may face adoption challenges if users find workflows confusing or burdensome. Straightforward onboarding, personalized guidance, and continuous training improve confidence.
Engaging users early in design and testing ensures the app aligns with real practices, reduces resistance, and supports sustained use in clinical and administrative settings.
Changing healthcare regulations create compliance challenges. Incorrect data handling, missing documentation, or inadequate controls may result in penalties.
Strong compliance frameworks, frequent audits, and transparent processes help organizations remain aligned with regulations and protect long-term operational integrity across regions with varying healthcare standards.
AI assistants will provide real-time support through symptom guidance, medication reminders, and personalized health insights. Clinicians will benefit from automated charting and decision assistance.
These intelligent tools will reduce administrative burdens, improve patient engagement, and enhance care coordination across digital platforms in both clinical and remote environments.
AR and VR will deepen medical education through immersive simulations that enhance understanding of anatomy, procedures, and patient communication. Patients will benefit from guided therapy, pain distraction, and more straightforward explanations.
These technologies support more engaging learning experiences and improve outcomes by making complex concepts easier to grasp.
Blockchain will support secure, tamper-resistant health records that give patients greater control over data sharing. Decentralized platforms reduce fragmentation and improve transparency across providers.
These capabilities strengthen trust, streamline consent, and support interoperable care networks that operate with integrity and long-term reliability across digital systems.
App development for healthcare is not a one-time effort. By following the steps outlined in this guide—from conducting thorough market research and understanding user needs to ensuring security compliance and post-launch updates—you’re setting the foundation for long-term success.
Taking a strategic approach to healthcare app development can have a profound impact on patients and healthcare workers by improving results and streamlining procedures.
It is imperative that you consistently improve the functionality, security, and user experience of your app to remain competitive in the rapidly evolving healthcare sector. Working together with a reputable tech company like Maruti Techlabs will assist you in overcoming these obstacles and realizing your dream healthcare app.
If you’re looking for mobile app development services in Dallas, Maruti Techlabs offers tailored solutions built specifically for the healthcare industry—ensuring compliance, security, and user-centric design.
Get in touch with Maruti Techlabs today to explore innovative solutions for mobile app development for healthcare needs and take your digital transformation journey to the next level!
Choosing a robust tech stack and architecture from the outset is essential to ensure scalability.
Healthcare apps can significantly enhance patient engagement by providing intuitive, user-centered, personalized health management features. Features such as appointment reminders, medication trackers, and real-time health monitoring tools empower patients to take an active role in their care. Integrating telemedicine options, secure messaging, and educational content can create continuous, convenient interactions between patients and healthcare providers.
Additionally, gamification elements like setting health goals, tracking progress, and offering rewards or feedback for reaching milestones can motivate patients to stay engaged with their health journeys.
Some of the common challenges include ensuring regulatory compliance, safeguarding patient-sensitive data, integrating with existing healthcare systems (such as EHR), and maintaining high-security standards. Balancing user-friendliness with complex functionalities required by healthcare professionals can be challenging.
Regular updates are necessary to resolve bugs, improve security, and add new features in response to user feedback. Staying updated with healthcare regulations and technological innovations is essential to keeping your app compliant and competitive.
Due to the sensitive nature of health information, data privacy is paramount in healthcare app development. Implementing robust encryption methods, secure data storage, and strict access controls is essential to protect patient data from unauthorized access and breaches.


