

Navigating Challenges and Solutions While Implementing AI in Insurance






Artificial Intelligence (AI) has become integral for recognizing and optimizing internal and customer-centric operations in various industries. The insurance industry, often considered conservative in adopting new technologies, is slowly embracing AI solutions such as Generative AI. AI solutions for insurance sketch a world of opportunities by streamlining processes using automation.
A survey conducted by Sprout.AI revealed that 59% of insurers in the UK and the US have already implemented generative AI technologies, such as ChatGPT. Generative AI works wonders for the insurance sector by fundamentally reshaping processes such as underwriting and risk assessment to claims processing and customer service.
You can see a future where AI becomes so ubiquitous that companies no longer market themselves as ‘AI companies’ because they’ve all become AI companies.
-Barron's
Cathy Gao
Partner, Sapphire Ventures
Generative AI, evident from the name, suggests that it generates content. It’s designed to learn from input data, allowing it to produce original content, such as text, images, and even music.
Models such as GPT 3.5 and GPT 4 can potentially improve insurance operations in four key ways:
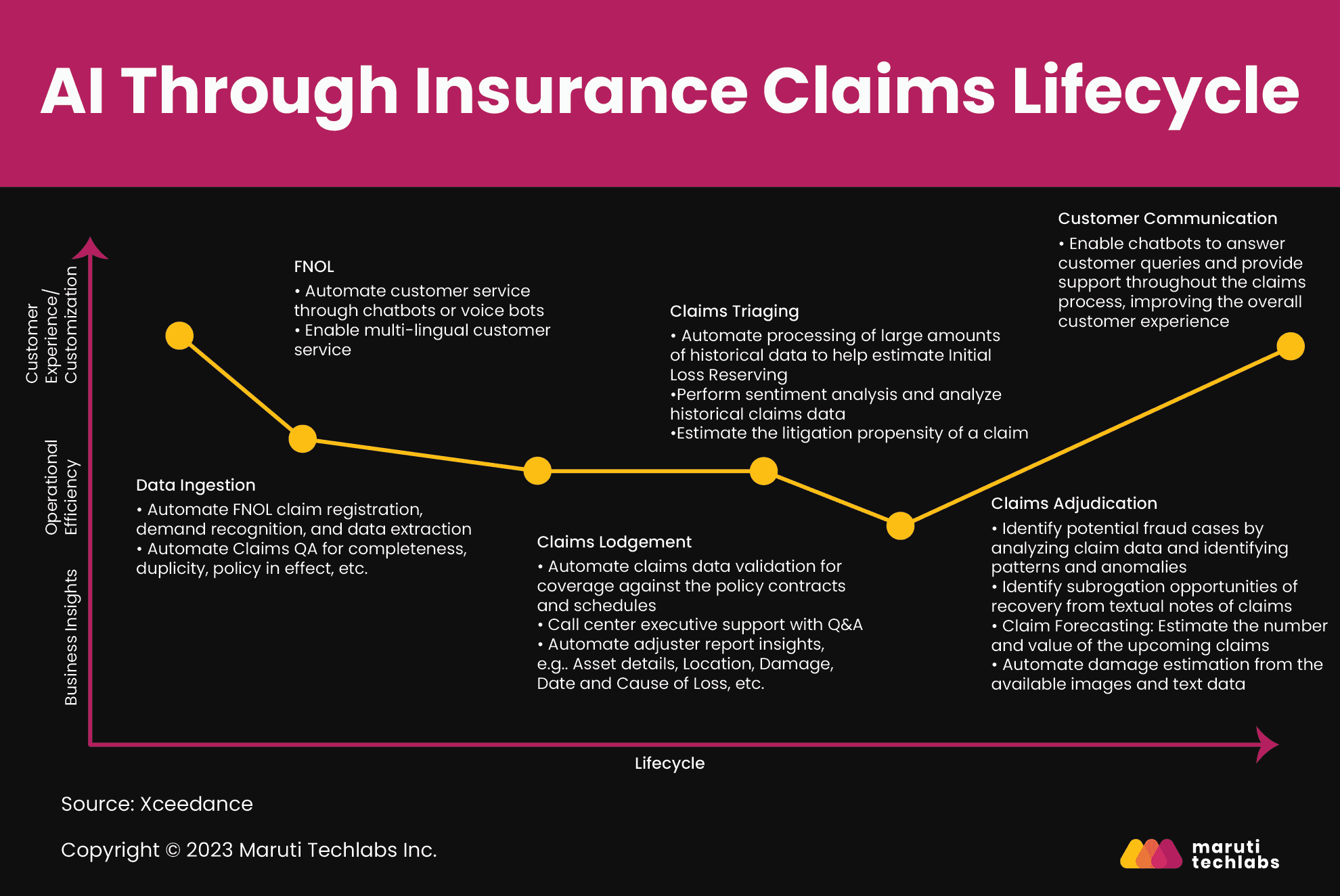
Generative AI can highly contribute to the insurance industry but does have noticeable downsides if not implemented following the proper practices. Let’s explore the advantages of incorporating insurance AI while delving into the obstacles it faces and potential solutions for its implementation.
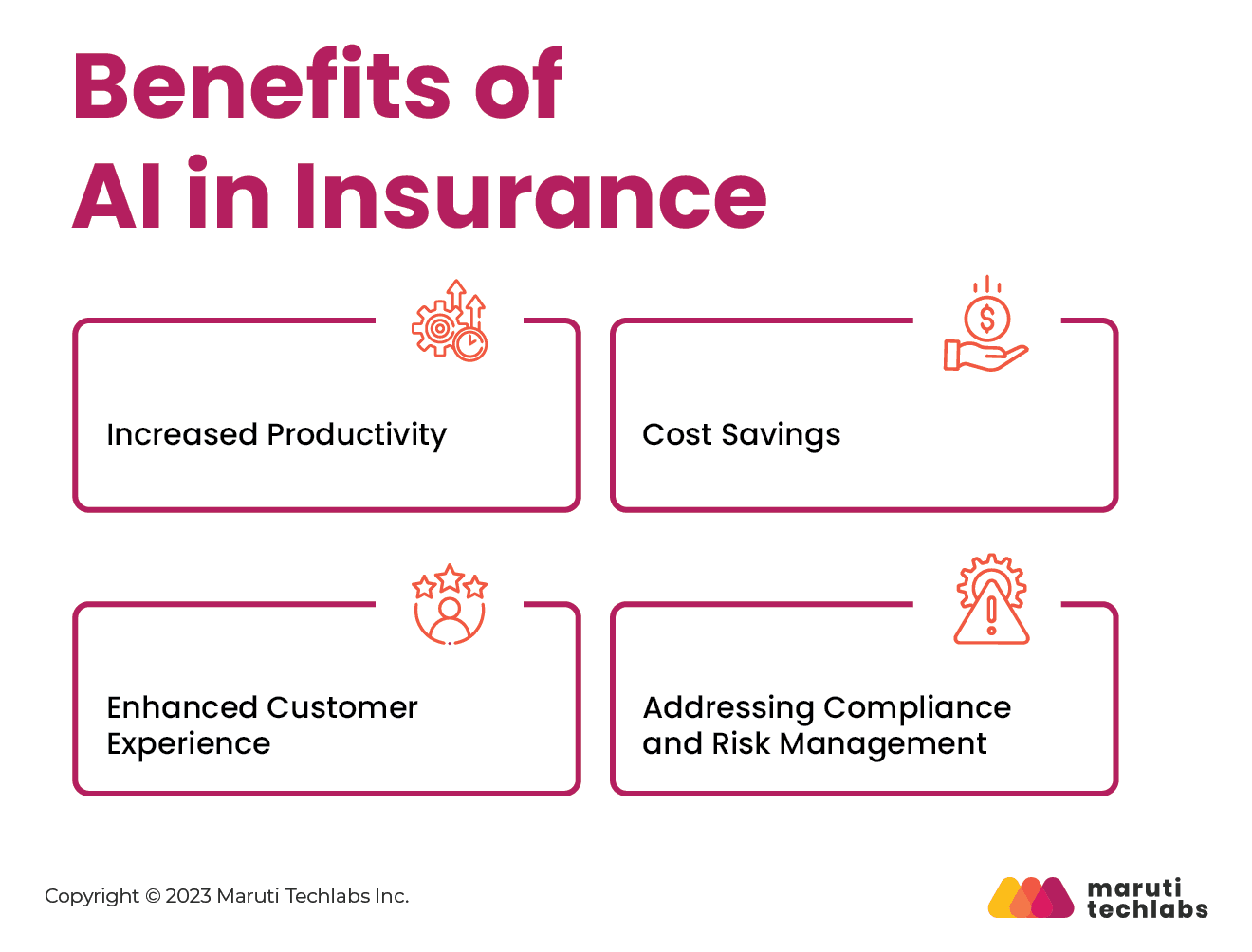
Many business areas within the insurance industry can be revolutionized by leveraging Generative AI for various customer- and employee-related processes. Here are some evident benefits observed by insurers.
Insurance companies are leaning on AI solutions to boost efficiency for industry knowledge workers such as claims adjusters, actuaries, underwriters, and engineers. A significant benefit of gen AI is that it can summarize and synthesize vast data collected through the claims lifecycle, i.e., from call transcripts to legal and medical documentation.
Additionally, insurers can expedite claims processing with swift analysis of photos and policies. Life insurance, significantly, is enhancing decision-making using AI-driven automation. This results in insurers issuing policies to a broader customer base without conducting in-person examinations.
Generative AI can sift through historical claims data, customer information, and supplementary variables such as weather and economic trends. Doing so can help insurers identify and price risks more precisely, reducing losses and improving profitability. Furthermore, AI facilitates real-time risk alerts and recommendations to policyholders, helping them take measures to avoid accidents or losses. This proactive approach helps reduce the number of claims and associated costs.
Integration of AI can foster personalized and empathetic interactions, enhancing overall customer, agent, and staff experiences. It automates mundane tasks, allowing insurance professionals to focus on high-value tasks. Additionally, AI-driven insights can streamline operations and fuel innovation to develop new products. Notably, generative AI is reimagining customer service and product development approaches.
AI solutions tailored for the insurance sector can continually monitor and ensure compliance with changing regulatory requirements. Furthermore, these AI systems can generate content through training materials and interactive modules for staff to stay updated with the latest regulatory developments in areas the company is actively exploring.
Generative AI has taken the world by storm, and every industry is keeping an eye out for introducing the opportunities presented by this cutting-edge technology. In April 2023, Sprout.AI conducted a survey to learn the attitudes, opportunities, and challenges surrounding generative AI in insurance.
Here are the findings observed in this survey.
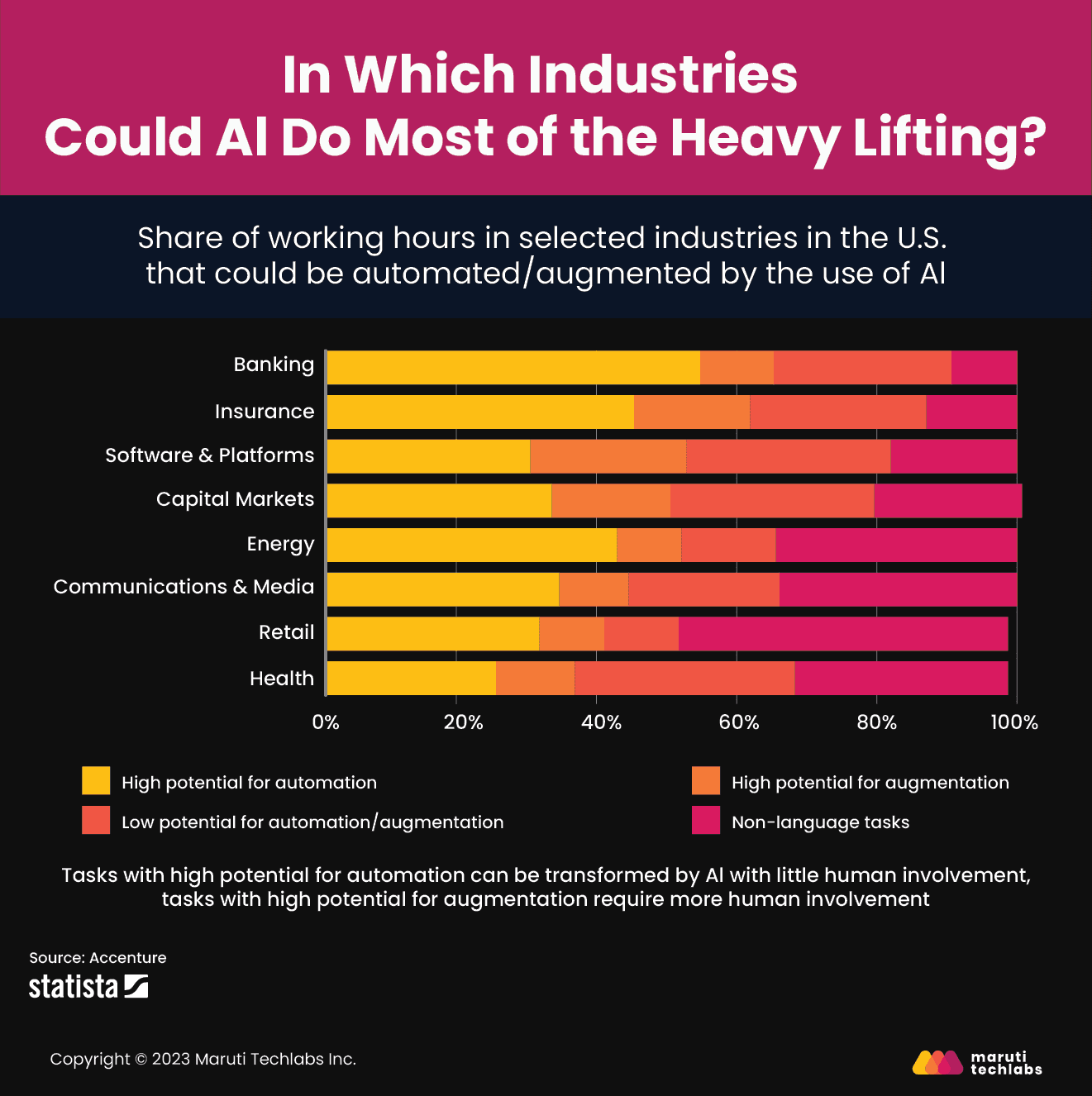
These figures ensure that consumers are aware of generative AI and receptive to its capabilities, making it a potential future expectation from their insurance providers.
One of the most prevailing notions with Generative AI is that it’s primarily used for generating human-like text using tools such as ChatGPT. On the contrary, its capabilities go much further than what meets the eye.
Here are some of the use cases of generative AI for insurance.
Gen AI can be best leveraged to create custom campaigns by extracting data from prospective customer data. Generative AI is extremely good at segregating data based on demographics, online buying patterns, purchase history, and more. It can segment potential customers and devise personalized marketing campaigns using the same.
AI can efficiently handle tasks like data entry, analyzing claims, and identifying new claims with similar patterns. It can also summarize wordy documents and organize claims by priority. This could automate the workflow for claims processing while reducing the time and cost of processing them.
Generative AI can aid underwriters in identifying essential documents and extracting data, thus giving them more time to conduct strategic tasks. It also automates the data calls management structure, allowing more efficient time management.
AI can efficiently verify customer documents such as IDs, passports, and utility bills. It even offers the capability to extract relevant information from these documents. Thus saving time for both employees and customers.
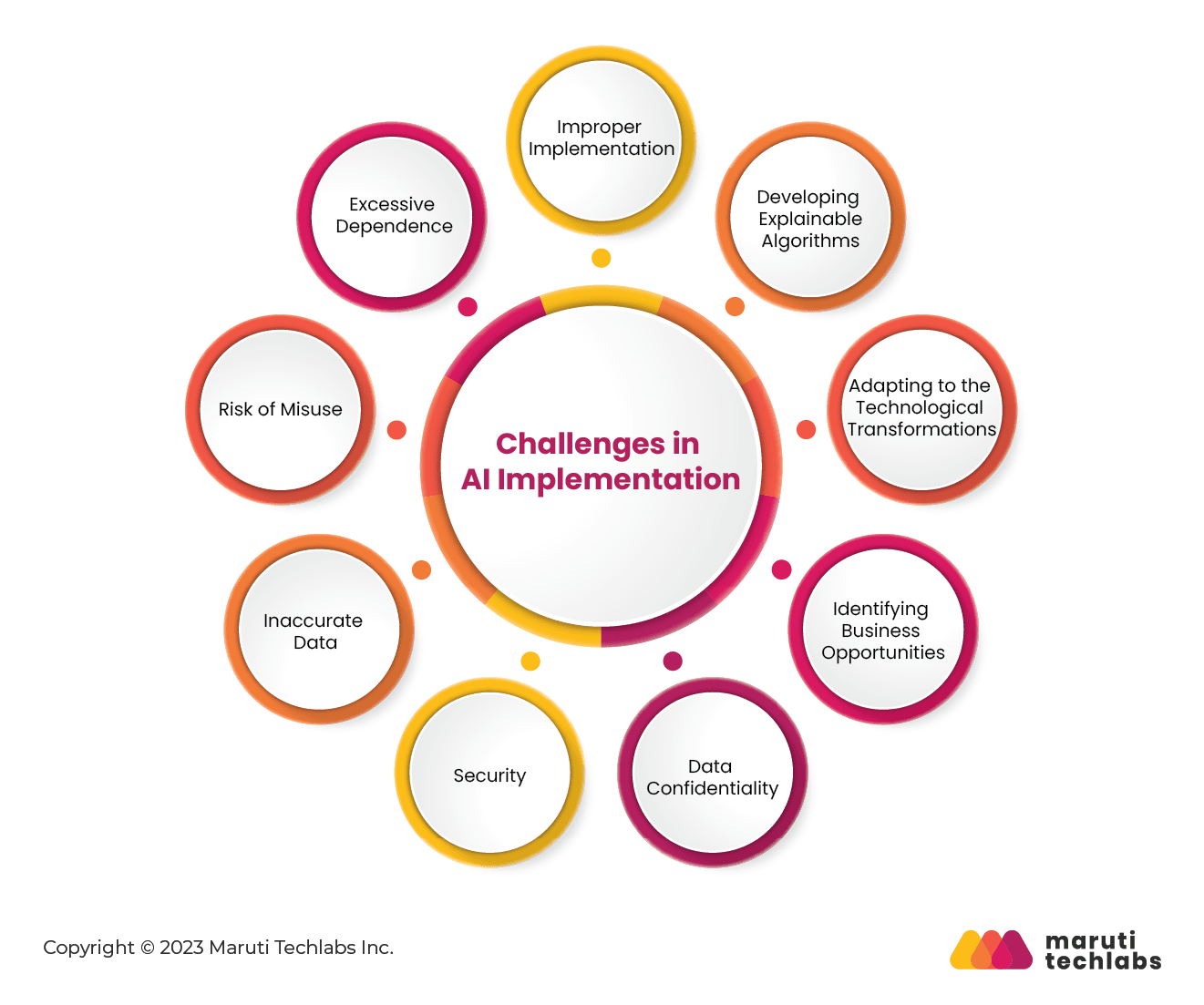
Many feel that the insurance sector and artificial intelligence are mismatched. However, the insurance industry has already observed several use cases with more and more companies integrating this technology into different processes.
Insurers might be concerned about losing the human touch with AI intervention in their processes. This is a legitimate concern as insurance companies prioritize ethical practices and customer commitment. This results in a slower and cautious approach to technology adoption.
Therefore, this sector faces the unique challenge of balancing innovation while maintaining ethical standards. Here’s a list of challenges insurance industries face while catching up with technologies such as AI.
It's expected that when a particular technology receives such high adoption worldwide, it creates an atmosphere of little knowledge and many fantasies.
This misinformation propagates the notion that AI can do anything and everything. Therefore, it becomes essential for insurtechs to educate and confront such misconceptions with well-founded success stories.
The entrepreneurial world is about trying something new, failing or succeeding, and staying on a learning curve forever.
Following this practice, many insurers have integrated AI immaturely and had less favorable outcomes. To overcome this skepticism, insurtechs and insurers should effectively communicate the robustness, maturity, and reliability of implementing AI. It’s crucial to breaking down barriers and earning trust within the insurance industry.
It’s natural for insurers to delve into the intricacies of the decision-making process. They can have questions such as why it’s choosing one estimate over another, how it is performing the permutations and combinations to reach a particular decision, or how they can be sure if the result is not wrong or error-free.
However, AI algorithms are complex creations and often tricky to explain without learning their technicalities. The real challenge is developing explainable algorithms whose internal processes can be described, helping AI insurance companies inculcate the trust of insurers.
Once you apply AI solutions, its benefits are observed from the go. Yet, your teams and processes must adapt to this new environment to extract the most from this upgrade.
Your failure to do so can adversely affect the company’s growth while compromising the benefits offered by AI. As per the Sprout Generative AI report, 47% of insurers feel that staff training is one of the most significant barriers to implementing Generative AI.
You can hire the best tech team by investing millions, but you must identify the right business opportunities to contribute much to your growth.
Insurtechs and insurers must work together when developing this technology, as successful AI deployment needs a complete understanding of the processes, barriers, and advantages.
Insurers can feel reserved before investing in AI because if done wrong, it would affect critical aspects of the insured’s life, such as their home or vehicle. Only when they embrace AI will they be able to unleash its true potential and enhance their policyholder offerings.
The advent of AI fosters the collection of enormous sums of data, thereby making it easy to access personal and professional data without a customer’s consent.
For instance, when AI systems such as ChatGPT are fed confidential corporate data to generate a report summary, it leaves a lasting data footprint on external cloud servers readily accessible to competitors. Therefore, data confidentiality becomes a significant concern when working with AI technologies.
AI cultivates its ability to share insights from the training data fed into the system using different parameters. These parameters, if compromised, can lead to economic and intellectual property loss. Moreover, cyber attackers' unauthorized modifications to these parameters could exploit the AI model, leading to undesirable consequences.
Any AI model’s performance is based on the learnings supplemented by data. If the data fed is plagiarized, prejudiced, or imprecise, it won’t offer the desired results, even if the model’s technically sound.
The risk of abuse or misuse is always a hanging sword, even if the AI system functions as intended. Operators may cause harm by distorting the model’s purposive goal, strategy, or boundaries. For example, facial recognition can be misused to track individuals illegally.
Often, a lack of awareness of AI capabilities leads to over-reliance. This primarily occurs when users start accepting and incorporating false recommendations. The repercussions of this practice induce incapability in a user to tackle new situations or brainstorm different perspectives. Hence, their ability to learn is restricted by AI’s limitations.
The challenges mentioned above emphasize the importance of establishing governance to mitigate both technical and usability risks posed by AI. Here are the potential measures that can be incorporated to constructively address the challenges associated with AI implementation.
Data hygiene is paramount when training your AI models. Machine learning-based models get smarter the more you train them with quality data.
To do this effectively, you must train your artificial intelligence and machine learning models using diverse structured and unstructured data such as historical claims, personal documents, investigative reports, etc. Moreover, this data has to be organized and labeled in their respective datasets.
To orchestrate this process productively, you will need the expertise of proficient data handlers to preserve data fidelity without compromising on quality. You will also have to safeguard your data from dilution while handling data in later stages. This feat can only be accomplished if your team undergoes timely training for managing and preserving data.
From lead-capturing forms to rich media for FNOLs, various touch points capture customer data. An essential prerequisite for enacting AI in insurance is ensuring universal availability of consumer data.
It's necessary to break down data silos and unify storage systems as customer data is collected at various stages. Insurance companies can expect optimal performance from implementing AI if data is located centrally with active data validation and updating systems.
There is a 3-step approach to mitigate usage risks when adopting AI.
It's recommended that you broaden your scope for IT governance to incorporate the following measures to mitigate technological risks effectively.
Artificial intelligence is undoubtedly the new buzzword in the insurance industry. Many vendors are trying to make the most of this tech wave. Investing in AI often demands enormous investments, and service providers worldwide want their piece of this pie. Insurance companies, though unaware of the applications and repercussions of this tech, want to take advantage of it.
Becoming an authentic AI expert for insurance companies is a challenging task. Experienced vendors adhere to the below-mentioned practices:
Organizational support is vital in facilitating the adoption and implementation of new technology. The company's leadership panel has a huge role in helping employees understand the importance of accepting this change.
They must keep the right tools, training, and support programs in place for a smooth transition. Leaders should effectively convey how AI is not an imposed tool but a means to enhance productivity. This top-down trickle approach will help you sustain momentum while observing this technical shift.
“Building trust in the AI models usually takes time. We started the process by extracting assumptions from the historical data and feeding them into the models.”
Many significant problems surround AI adoption in insurance—primarily ethics. There are concerns from individuals and organizations on the fairness of using data to make decisions. Additionally, there is skepticism about how understandable and reliable AI systems are.
Apart from this, it's essential to consider that insurance companies have to follow many rules and laws, such as the Solvency II Directive, the Insurance Distribution Directive, the General Data Protection Regulation, and the Consumer Protection Code.
EIOPA is an EU agency responsible for carrying out specific scientific, technical, and legal tasks for giving evidence-based advice to help shape laws in the EU. They have reflected on the ethical challenges of using AI in insurance and have devised a set of rules to reduce the risks of using AI that can cause harm to insurers or consumers.
AI in insurance is marking a significant shift by offering insurance and other industries transformative capabilities that foster innovation and growth. Implementing AI following standard and tested practices can ultimately lead to enhanced customer experiences, increased retention rates, and lifetime values.
However, insurers must meet this transition mindfully with guardrails in place to adopt AI practices responsibly. As insurers have much at stake when working with customers, they must stay informed about industry trends to manage associated risks and seize opportunities in the AI landscape.
Having worked on several artificial intelligence projects globally, we at Maruti Techlabs understand the challenges one could face when implementing AI in insurance. Our artificial intelligence consulting services are instrumental in unlocking the complete potential of AI technologies. Contact our AI experts to streamline your insurance business processes and design a tailored customer experience.


