

How to Combat eCommerce Fraud Using AI in 2026?






According to a report from Shopify, global e-commerce sales are projected to reach $6.4 trillion in 2026. However, this massive increase in business creates lucrative opportunities for fraudsters. Fraudsters now exploit multiple attack vectors across checkout, payments, refunds, and account access.
An Experian survey shows that nearly 60% of U.S. businesses report higher fraud losses in 2025, driven by more sophisticated attacks and legacy security gaps.
Generally, e-commerce companies rely on rule-based systems to spot fraudulent activities. Rule-based systems rely on predefined conditions to flag suspicious activity. While effective against known patterns, they fail to adapt to evolving and sophisticated fraud techniques.
AI introduces adaptive, data-driven fraud detection capabilities that outperform static, rule-based approaches. AI can identify fraud more quickly than conventional methods while even outsmarting the trickiest fraudsters.
Some of its features, such as real-time behaviour analysis, pattern and anomaly detection, risk scoring, and more, are a boon for e-commerce companies. AI offers an edge in retaliation, with the overall protection needed to fight these clever attackers.
In this blog, we’ll explore the fraud landscape in 2026, common ecommerce frauds, where rule-based systems fall short, and the contribution of AI and ML in fraud detection and prevention.
eCommerce fraud comes in a variety of forms, targeting retailers or merchants. By 2026, fraud tactics might be increasingly automated, AI-assisted, and multi-channel, making traditional perimeter-based defenses ineffective.
These fraudulent activities cost eCommerce businesses millions of dollars annually. Therefore, they demand real-time fraud detection, continual monitoring, and access controls.
Understanding the most common fraud types is the first step toward building effective AI-driven defenses. Let’s observe the top tricks that fraudsters use with eCommerce businesses.
In chargeback fraud, a customer completes a legitimate purchase and later disputes the transaction, falsely claiming fraud or non-delivery. Merchants lose revenue, inventory, and chargeback fees.
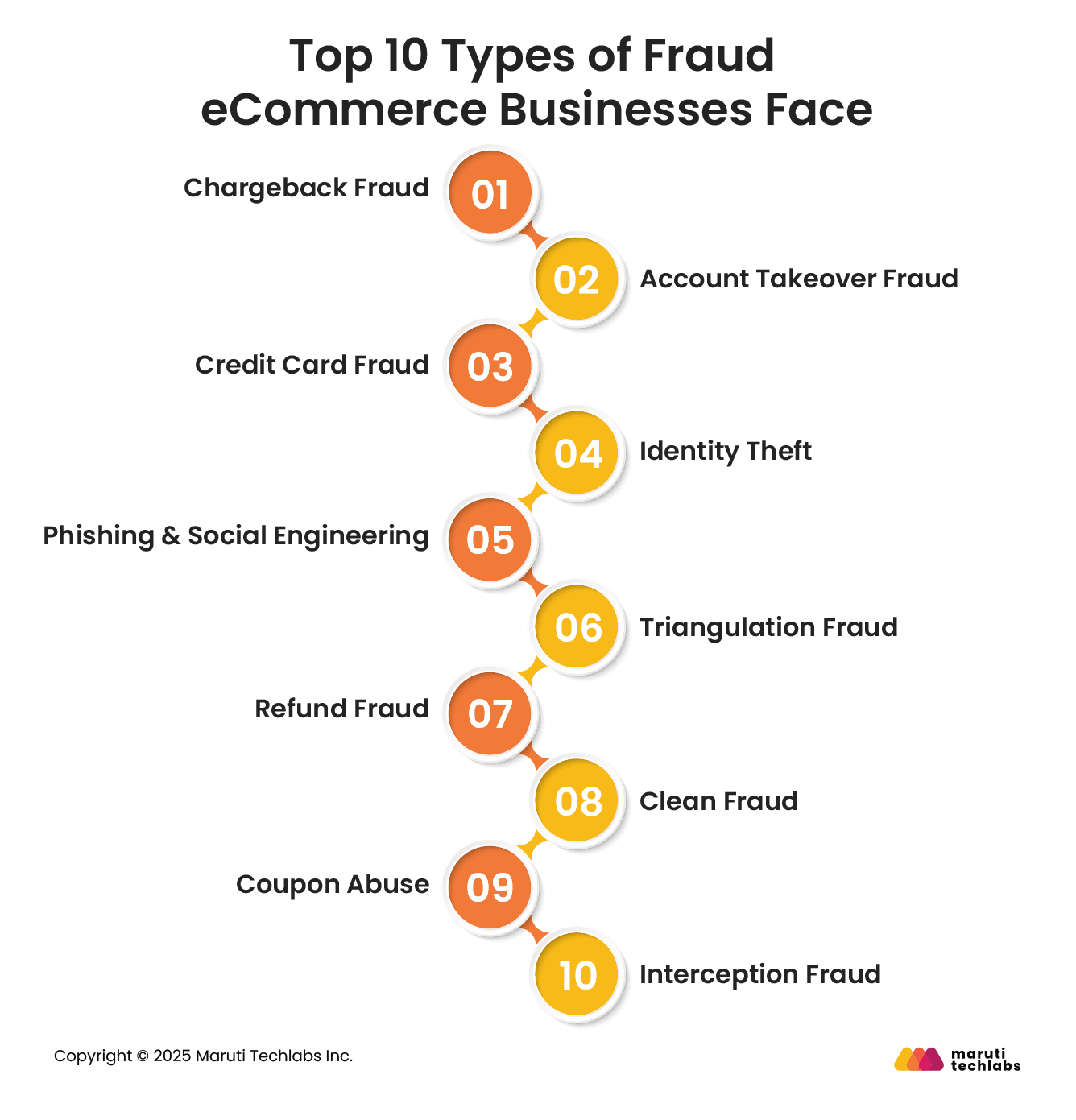
In account takeover fraud, a customer’s login information is compromised, leading to unauthorized purchases. An attacker can also change shipping addresses or use a customer’s sensitive personal information for other purposes.
In addition, many eCommerce companies face card-not-present (CNP) fraud, in which fraudulent transactions result from stolen credit card information. This type of fraud has been happening since the advent of credit cards.
However, with eCommerce, these frauds are explored differently, as physical cards aren’t required for transactions.
Identity theft is a type of fraud in which a user's personal information, such as a billing address, Social Security number, name, or banking information, is used to impersonate that user.
Phishing and social engineering frauds occur when a customer is manipulated into sharing their personal and financial information, such as usernames, passwords, or credit card numbers. This can be done using deceptive emails or website replicas that seem authentic but are actually fake.
Triangulation fraud involves three parties: a buyer, a legitimate retailer, and a fraudster operating a fake storefront. The fraudster uses stolen card details to place orders with legitimate stores, leaving the cardholder and the retailer to absorb the loss.
Here, a fraudster submits a refund request. The scammer may ask for a refund, stating that they have returned the product, even though they haven’t.
In some cases, the scammer purchases a product with stolen credit card information. Then, it reports the product as faulty. Subsequently, the scammer requests a refund even though the product is sold elsewhere.
Clean fraud occurs when the fraudster bypasses all the red flags and perfectly impersonates a cardholder. The transactions are approved as they seem legitimate. It’s only caught when a cardholder notices the fraudulent charge on their bank statement.
Here, scammers leverage coupon codes to observe discounts they aren’t entitled to. This can be done by using single coupons multiple times, or creating new accounts to use ‘new customer’ discount repeatedly, or using bots to use unpublished promotional codes.
This is a unique type of fraud where a scammer places an order with a compromised credit card and then steals the package before it reaches the cardholder’s address. This can be done by re-routing the package through the courier service or by physically receiving it from the cardholder’s property.
Despite their widespread adoption, rule-based fraud systems struggle to keep pace with the complexity of modern eCommerce. Here are the cons of using rule-based security.
Like everything else, fraudsters use new tactics by finding loopholes in your systems. This means continually editing and changing rules.
As your business grows and introduces initiatives like in-store pickup, same-day delivery, or yearly sales, it becomes challenging to keep up.
Rule-based systems don’t foster growth but only focus on preventing fraud. Adding new rules to an already populated rule-based system can be confusing or can even neutralize existing rules.
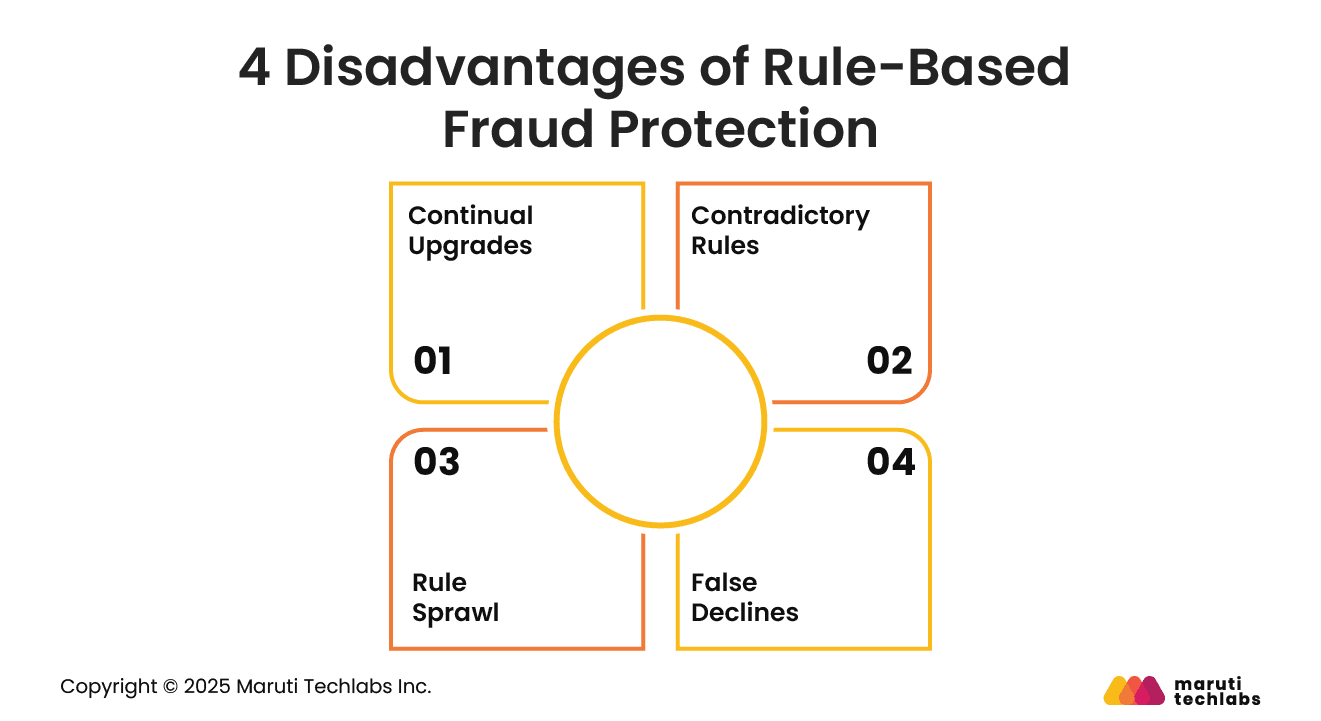
Managing a web of rules can become overwhelming. At times, it can involve investing more energy than creating new initiatives.
Over time, rule sets become either overly restrictive, leading to false declines, or too permissive, allowing fraud to slip through. This rule sprawl often requires companies to hire external security experts.
The problem of false declines often requires companies to conduct manual reviews. This adversely affects customer satisfaction, increases costs, and slows fulfillment. This has a domino effect, with most customers who face such inconveniences not returning to use an eCommerce platform.
Artificial Intelligence and machine learning strengthen fraud detection across the entire transaction lifecycle, from account creation to post-purchase monitoring.
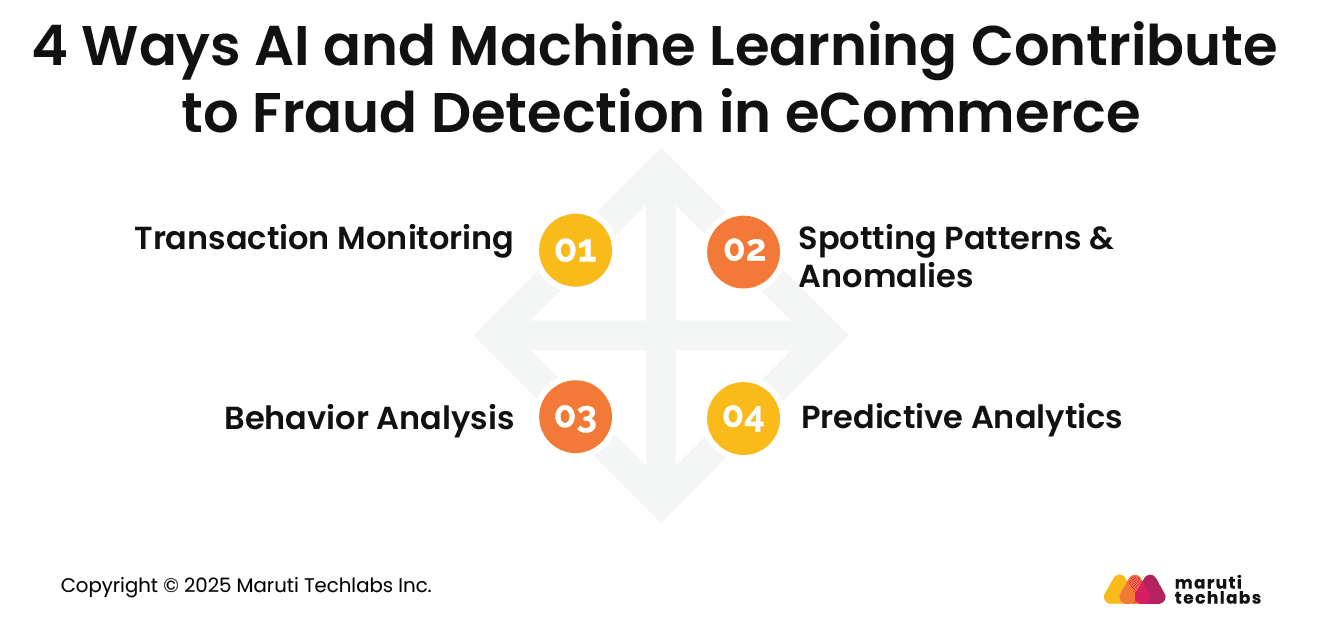
Let’s explore how AI and ML enhance fraud detection for eCommerce organizations.
AI-powered systems are exceptionally fast. They analyze transactions in real time rather than after they are completed. AI continuously monitors data streams, blocking any suspected users.
AI performs a comprehensive risk assessment by analyzing multiple touchpoints. This includes user location, merchant information, transaction history and amounts, device characteristics, and more. All in all, it can process thousands of transactions at one time with accuracy that human analysts cannot ever match.
Algorithms equipped with ML can learn fraudulent patterns in massive datasets. They establish baseline patterns of normal customer behaviour by examining historical data and comparing new transactions against these patterns.
When it observes patterns such as sudden high-value transactions from the same customer across different locations, it alerts the AI system to flag them. These systems can be further enhanced with advanced pattern recognition that identifies complex relationships among vivid touchpoints.
One of the most exquisite features of AI systems is behavioral analytics. This technology studies and stores how customers interact with eCommerce platforms. It includes mouse movements, typing patterns, transaction timings, and the like.
It creates a digital footprint for every user, making it impossible for fraudsters to replicate. When they observe high deviation from standard patterns, they flag them. These systems can even add additional authentication steps or block suspicious users instantly.
Latest fraud detection systems simultaneously process multiple variables and assign risk scores to each transaction. By observing factors such as device information, demographics, customer history, and more, these systems calculate the probability of fraud.
A higher risk score dictates implementing enhanced security measures, while low-risk score transactions are processed seamlessly. Predictive analytics also includes spotting emerging trends and patterns to identify fraudulent behavior.
AI has evolved from a supporting tool to a core capability in modern eCommerce fraud prevention. As fraud tactics become more adaptive and complex, traditional rule-based systems struggle to keep pace.
AI and ML enable real-time fraud detection, behavioral analysis, and predictive risk scoring, helping businesses prevent losses before transactions are completed. Beyond detection, predictive analytics empowers eCommerce leaders to anticipate emerging fraud patterns, optimize controls, and balance security with seamless customer experiences.
To stay resilient, organizations need tailored AI solutions aligned with their data, risk profile, and growth goals.
Explore Maruti Techlabs’ Custom AI/ML Services that are designed to deliver advanced fraud detection and predictive analytics capabilities that scale with your business. Connect with us to leverage intelligent models purpose-built for fraud prevention.
specialized vendors and custom AI service providers like Maruti Techlabs offer AI-based eCommerce fraud detection.
These include fighting fraud using machine learning models for transaction monitoring, identity verification, and behavioral analytics, as well as consulting firms that build tailored AI models aligned to specific business risks and data environments.
Integration typically involves connecting fraud tools or models via APIs to payment gateways, checkout flows, and order management systems.
Businesses must ingest transactional, behavioral, and device data, configure risk rules, train AI models, and establish workflows for automated decisions, alerts, and manual reviews without disrupting customer experience.
Top eCommerce fraud prevention tools include AI-driven platforms for transaction risk scoring, bot detection, chargeback management, and identity verification.
These solutions leverage machine learning, device fingerprinting, and behavioral analysis to detect anomalies in real time and reduce false positives while scaling with transaction volumes.
Choose a service based on fraud detection accuracy, AI and ML capabilities, ease of integration, scalability, and industry experience.
Evaluate transparency of risk models, reporting depth, compliance support, and customization options. A solution should balance fraud prevention with seamless customer experiences and long-term growth.


