

Public Cloud Vs. Private Clouds: The Ultimate Comparison






Whether an MNC or a startup, the past decade has observed a significant upgrade with organizations migrating to the cloud from the conventional practice of on-premise servers. This switch is primarily due to the ‘pay as you go’ convenience these service providers offer.
In contrast, companies using on-premise servers still have to pay even if the server is not in use. According to a forecast by Gartner, global public cloud end-user spending will surpass $675 billion in 2024.
Cloud computing delivers computing resources such as servers, databases, analytics, software, and intelligence over the Internet. This promotes flexibility, cost savings, economies of scale, and innovation, offering your business the potential for growth and adaptability. Cloud service providers have evolved over the years, offering a mix of cloud deployment models that can be used according to your business needs.
Different cloud models possess various advantages and disadvantages. Therefore, it's crucial to weigh the pros and cons before implementing your cloud migration, highlighting the need for careful planning and decision-making in this process.
This blog dives into the intricacies of the different offerings of public and private cloud models, differences, and things to consider when choosing a cloud model. So, we suggest you read on until the end.
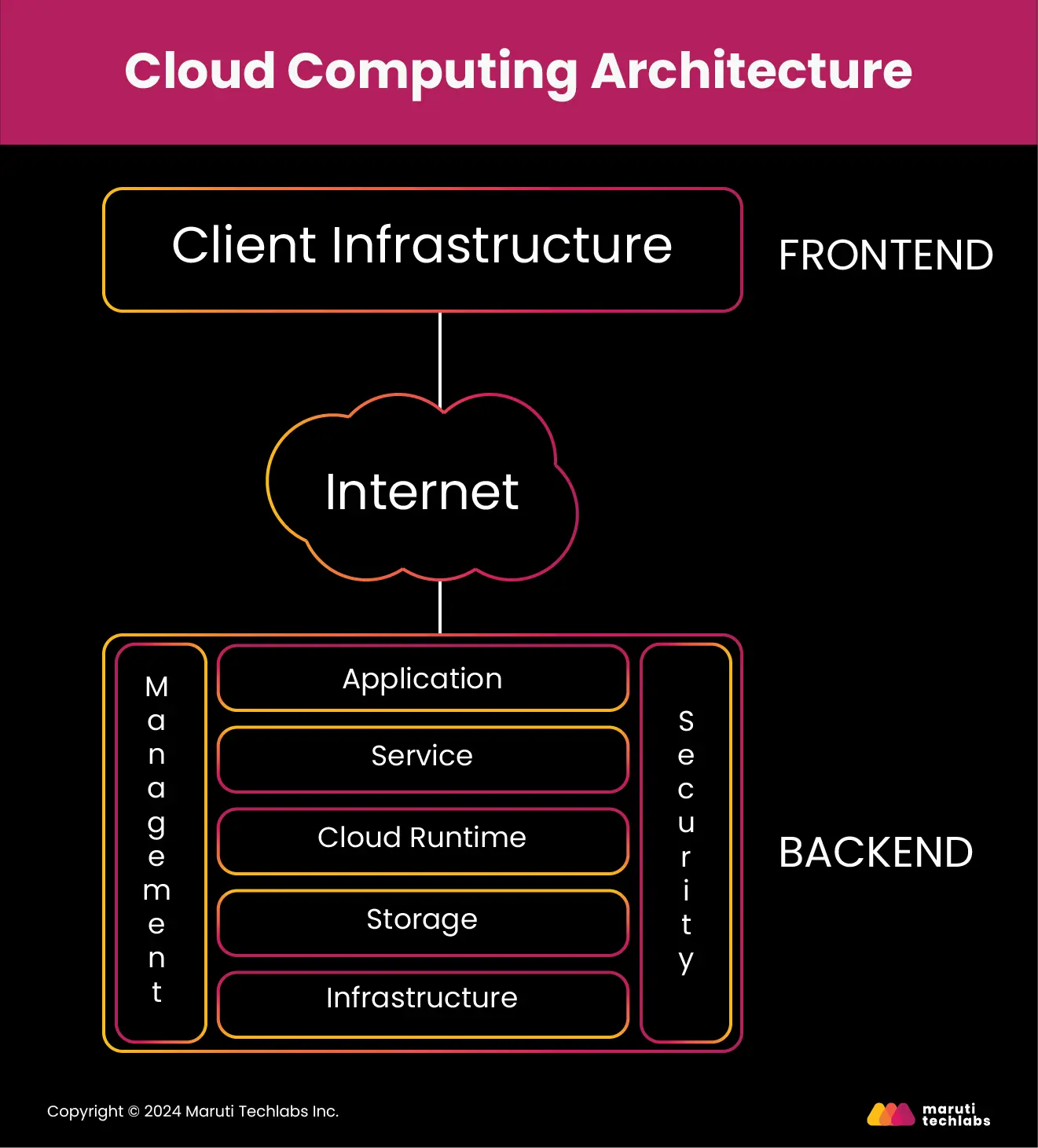
Cloud computing is remote and on-demand access to computing resources like servers, data storage, networking, application development tools, and AI-powered analytics tools that use the Internet instead of relying on local on-premise hardware. It is also known as internet-based computing, where resources are offered as services to end users with pay-per-use pricing models.
Cloud computing enhances flexibility and scalability compared to conventional on-premise infrastructure. We use cloud computing extensively daily, streaming a movie on an OTT platform, accessing emails, or enjoying a cloud-hosted video game.
From small-scale businesses to large enterprises, cloud computing has reached all businesses. It allows employees to work from anywhere worldwide while devising omnichannel engagement for their customers.
Let’s dive into the benefits of cloud computing.
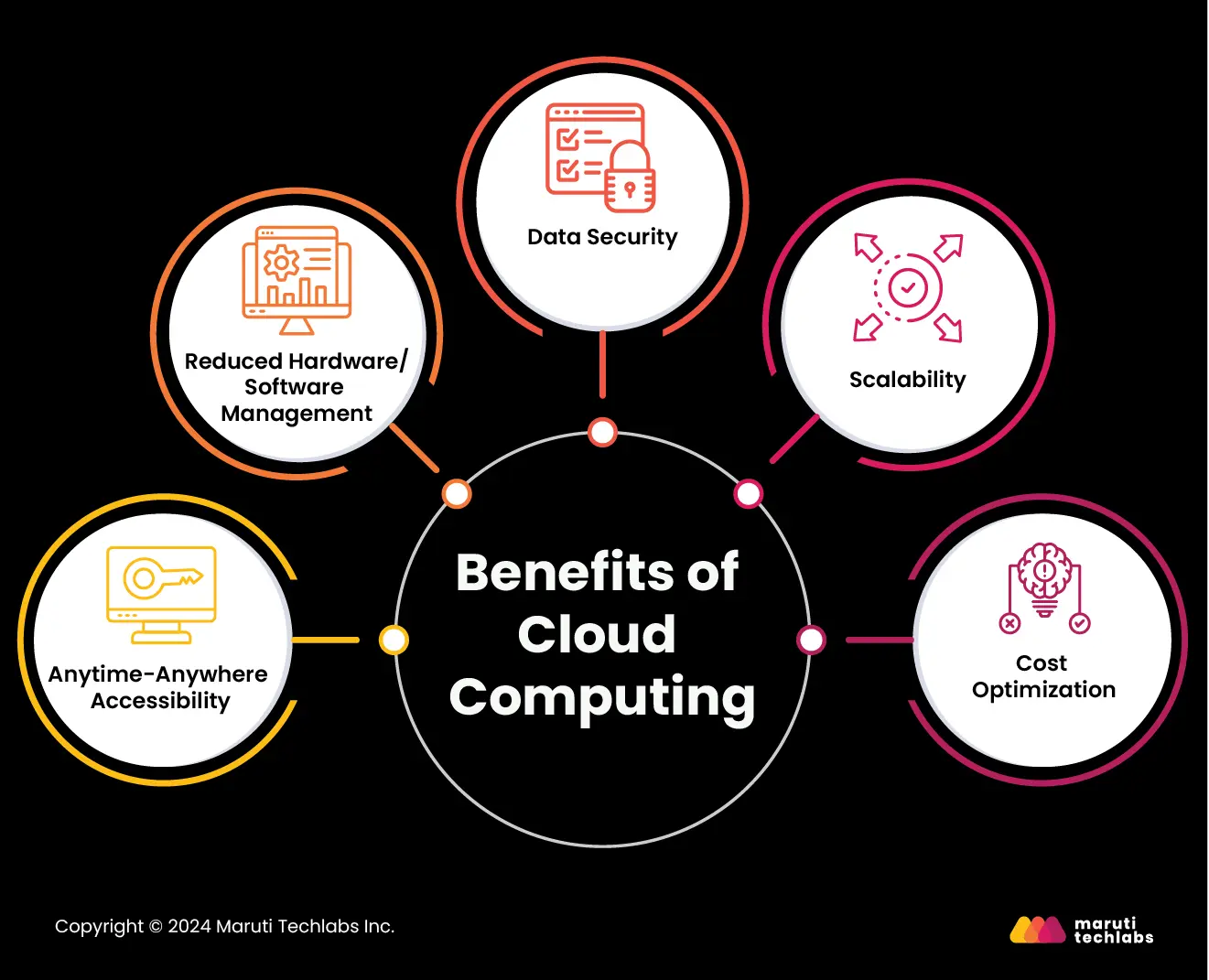
1. Anytime-Anywhere Accessibility: Services hosted on the cloud offer enhanced accessibility to employees and customers. Leveraging cloud services, everyone can access information from anywhere, whether in the office or on the go.
2. Reduced Hardware/Software Management: Cloud computing eliminates the need for servers, cables, routers, etc. Cloud providers can pay a monthly or yearly fee for all of the above, reducing the expense and effort of managing physical hardware.
3. Data Security: Cloud providers offer centralized data backups, eliminating the hassle of keeping on-site and off-site backups. Security features such as two-factor authentication or data encryption ensure greater privacy than what users observe with their equipment.
4. Scalability: With cloud computing, you can support any significant increase in demand while keeping your services up and running. It also offers the convenience of paying only for the period one uses a service rather than having a monthly subscription.
5. Cost Optimization: The initial expense of planning your cloud transition can be costly. However, it can result in substantial savings in the long run as one no longer has to maintain or update expensive hardware and software. Additionally, one can plan an eventual transition, if not an immediate one, including only a few of their services at the start.
When transitioning to the cloud, businesses can choose from four main cloud deployment models depending on their requirements and budget. Let’s learn what each has to offer.
1. Public Cloud
2. Private Cloud
3. Hybrid Cloud
4. Multi-Cloud
Let’s understand each of the above in brief.
A public cloud offers accessibility to everyone. They are designed to serve multiple users rather than just a single customer. Each user requires a virtual computing environment that is separate and typically isolated from others.
This model is the opposite of a public cloud. It eliminates the need to share the hardware with anyone else, offering a one-on-one environment for each user. The organization employs a private cloud that supervises the entire system while observing additional security with robust firewalls.

A hybrid cloud offers the best of both worlds, i.e., public and private. One can host the app in a private, safe environment while saving costs like a public cloud. As per an organization's needs, they can move data and applications between different clouds using cloud deployment methods.
As the name suggests, this model employs multiple cloud providers. However, it uses numerous public clouds rather than a mix of private and public clouds. Multi-cloud environments are safe but less secure than private clouds. Although it's rare for two distinct clouds to get compromised simultaneously, multi-cloud deployment enhances the availability of your services.
Now that we understand different cloud deployment models, let's learn about public and private clouds in detail.
Public cloud services and resources are offered through third-party cloud service providers (CSP) like Amazon Web Services (AWS) or Google Cloud Platform (GCP). These providers deliver their services via the Internet using subscription models such as platform-as-a-service (PaaS), infrastructure-as-a-service (IaaS), or software-as-a-service (SaaS).
Public cloud is the most suitable option because it allows users easy access to systems and services. Such arrangements generally offer free backup and retrieval services. The public cloud follows the multi-tenancy principle, meaning that numerous organizations or tenants can access the same resources, such as servers and storage.
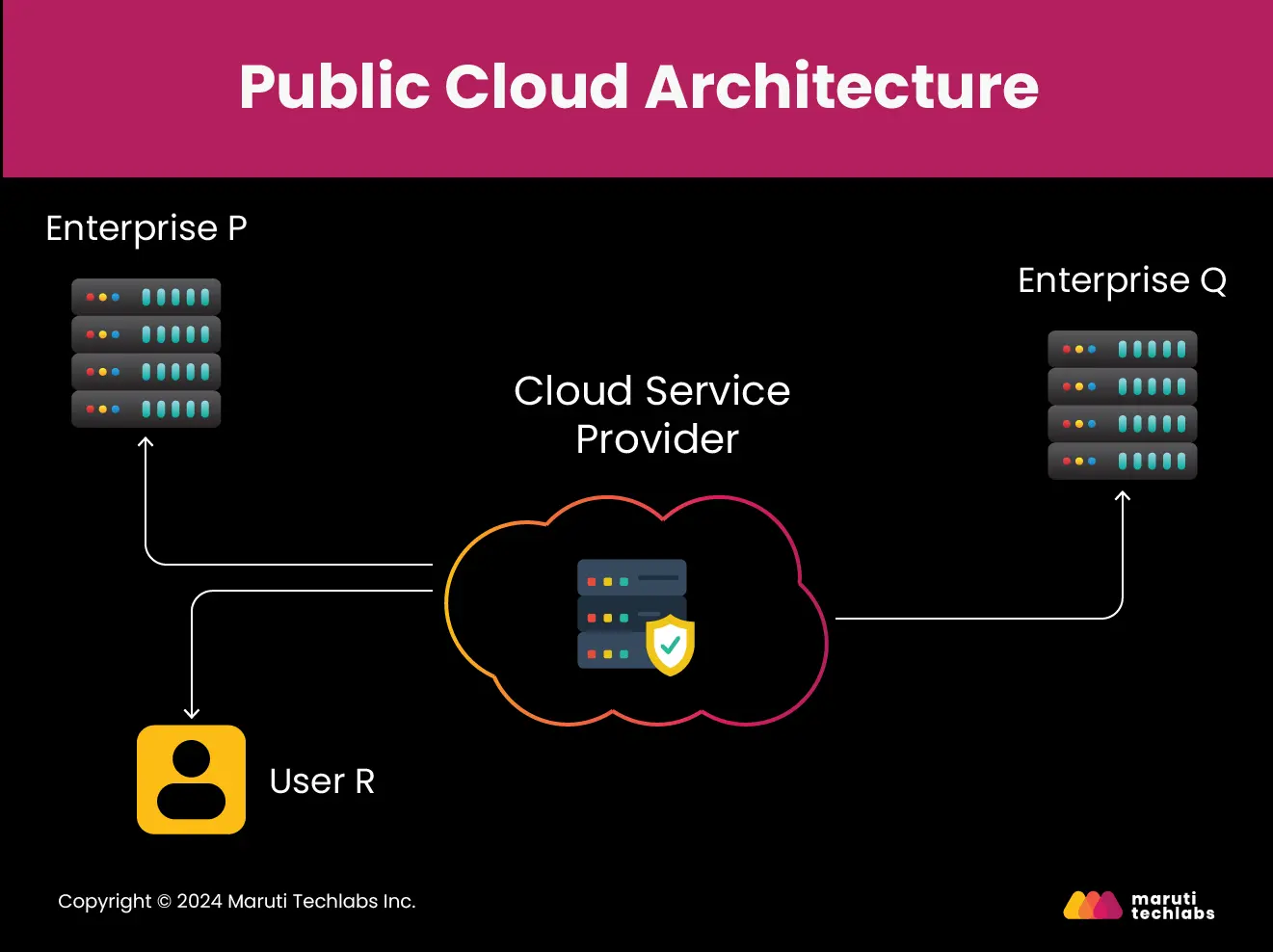
Here is a list of advantages of using a public cloud:
1. Cost-Effective Solution: Public clouds can be offered for lower prices as the same infrastructure is shared by many users. They can be easily expanded to meet demands while reducing IT support and hardware costs for tenants. Additionally, it’s an affordable choice due to the pay-per-use pricing model.
2. No Maintenance Costs: Cloud service providers take end-to-end responsibility for conducting maintenance activities. This allows your in-house IT professionals to perform other essential tasks.
3. Scalability: Businesses can scale their storage according to variations in demand. This convenience allows organizations to deploy products quickly.
4. Enhanced Security: The servers offered by CSPs are located at different locations than the clients'. This adds to the organization's security layer, helping it implement failsafe strategies to protect user data in case of unexpected downtimes or outages.
Let’s observe the disadvantages of using a public cloud.
1. Dynamic Costing: Public clouds are inexpensive. However, their costs can rise exponentially if scaled for extensive usage. Mid and large-sized organizations are more likely to face this challenge if their demand increases rapidly.
2. Lack of Visibility: The vendor conducts complete public cloud management and offers little control over the tenant's infrastructure. This results in a lack of visibility and poses serious problems with compliance.
3. Data Integrity: Public cloud providers do not provide information on where and how they store user data, and users are also unaware of how the vendors use their data.
4. Lack of Customization: The public cloud follows a multitenant approach, offering users limited to no customization. This hinders organizations with complicated network architectures.
A private cloud, sometimes called an on-premise private data center, offers an organization exclusive use of the cloud, its services, and its infrastructure. Here, the servers are accessed
using a private network and act as isolated components.
Private clouds provide a secure and isolated infrastructure, delivering a single-tenant environment where a single customer has exclusive access to its dedicated resources. They are traditionally hosted on the client’s on-premise data center. However, they can also be hosted on offsite rented data centers or the infrastructure of an independent cloud provider. Private clouds can be self-managed or outsourced to the service provider.
This model best suits organizations with high potential for sensitive data, such as fintech or healthcare. Its best use is protecting confidential personal and business information from cyber attacks, adding additional layers of security. Tech giants and government agencies needing complete control over their infrastructure can use private clouds. A private cloud offers more control over cloud resources while enhancing its scalability.
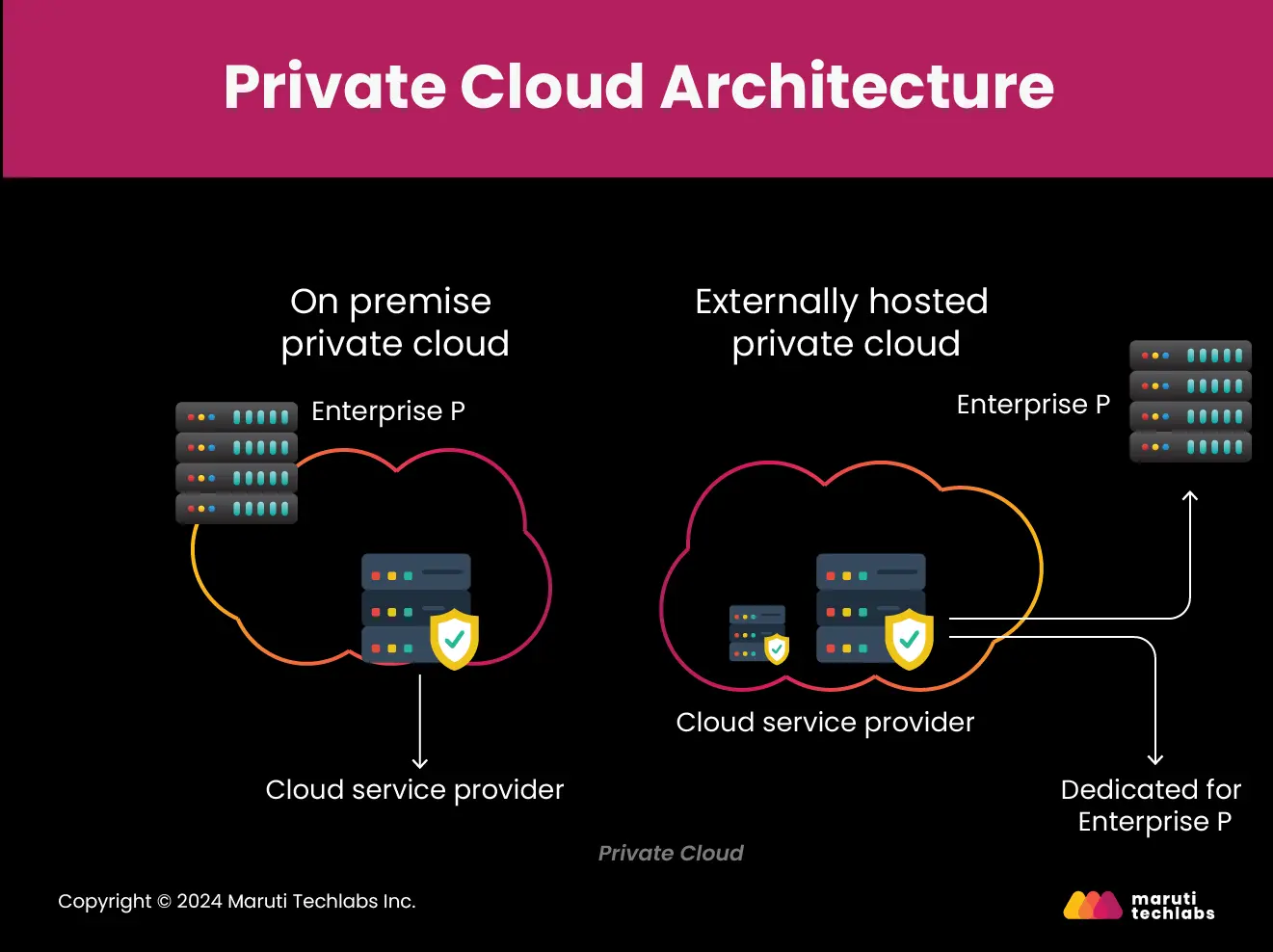
The advantages of using a private cloud include,
1. Customizable Compliance Protocols: Private clouds offer the freedom to customize compliance protocols per their requirements. This is an ideal model for businesses that must adhere to strict privacy regulations like GDPR or CCPA. It’s also suitable for organizations that must follow HIPAA or Sarbanes-Oxley regulations.
2. Increased Control: It offers more control over your cloud infrastructure as it doesn’t support multi-tenancy. This adds to the security, customizability, and control over the infrastructure.
3. Scalability: A private cloud can increase or decrease storage depending on the tenant's needs. It also facilitates the execution of mission-critical applications, where a dedicated server can be used as a virtual server.
Here are the disadvantages observed with a private cloud.
1. Expense: Private clouds are expensive compared to public clouds, even more so when used for the short term.
2. Limitations for Mobile Users: Private clouds pose limitations for users accessing mobile with ample security layers.
3. Incapability to Handle Unexpected Surge: Private clouds can fail at handling unpredictable demands if the cloud data center is restricted to on-premise computing resources.
4. Accessibility: Private clouds offer restricted accessibility, so they can only be accessed in particular areas.
Here are the core differences between public cloud and private cloud.
Public Cloud | Private Cloud |
| 1. This cloud computing infrastructure is used only by a single enterprise and is shared by service providers over the Internet.
|
| 2. It offers single-tenancy, storing data of a single enterprise. |
| 3. Private cloud providers offer specific services and hardware per an organization’s requirements. |
| 4. The enterprise or service provider site is the host. |
| 5. It can be only connected over a private network. |
| 6. It offers limited scalability but high reliability. |
| 7. A single enterprise performs its management and use. |
| 8. It is more expensive than the public cloud. |
| 9. Private cloud offers top-grade security. |
| 10. It delivers high performance. |
| 11. Private cloud runs on dedicated servers. |
| 12. Examples of private cloud include Red Hat, VMWare, HP, and Microsoft KVM. |
When choosing among cloud computing models, it’s important to consider factors such as:
Security is a primary concern when switching to any new service. Below is the list of questions one should have clarity on before choosing their cloud service provider.
Regulatory compliance is essential for organizations that deal with confidential data, such as fintech or healthcare. Let’s learn the critical questions you should consider before your cloud transition.
Scalability is vital to meet evolving business needs. Let’s consider the essential scalability of the cloud.
Your tech investments mustn’t burn a hole in your pocket. Therefore, it’s crucial to ask the questions below before deciding.
Public and private cloud models have received the most attention and adoption, especially since COVID-19. While public clouds are affordable, accessible, and easy to set up, private clouds offer excess control, customization, isolation, and privacy.
Small organizations or startups can opt for the pay-as-you-go public cloud model. An evident use case for this could be IT service companies searching for an environment for development and testing.
Private cloud models best suit large enterprises seeking higher control, enhanced privacy and security, and customization. This can further be improved by incorporating cloud-native technologies. Cloud-native app development facilitates a need-per-basis model that supports fast and frequent changes for business-critical applications.
Depending on your needs, you may have to choose a combination of public and private clouds. This task demands thoughtful attention and planning with your IT strategy, necessitating the expertise of cloud application development service professionals.
Our experts assist you in devising a tech ecosystem that serves your present clientele and paves the way for future growth backed by technological advancements.
Want to estimate the cost of your cloud transition or hybrid setup? Use our Cloud Migration Cost Calculator to plan smarter and make informed decisions.
A cloud deployment model refers to how the cloud is organized and controlled. It offers options like public, private, hybrid, and multi-cloud, each possessing different cost structures and characteristics.
The disadvantages of private cloud include expensiveness, limitations for mobile users, incapability to handle unexpected surges, and accessibility.
Microsoft Azure is a public cloud. Office 365 is one of the world’s most popular cloud solutions: Software as a Service.
Different companies have their cloud infrastructure to store their data. Salesforce is one of them.


