

Code Refactoring in 2025: Best Practices & Popular Techniques






Code refactoring is the secret weapon for keeping your codebase clean and efficient without changing how it works. It streamlines the structure of existing code and removes duplicate code, making it more readable, maintainable, and ready for future updates. By refining what’s already there, refactoring reduces technical debt and minimizes bugs, saving time and effort in the long run.
In this blog, we’ll explore the significance of code refactoring and when and how to approach it. We’ll also explore ways to tackle common challenges and strategies that transform your codebase into an efficient and adaptable asset!
To explore this concept further, let’s start with learning the definition and significance of code refactoring.
Code refactoring involves restructuring existing code to improve its internal structure while maintaining its external behavior. This practice focuses on enhancing the code's readability, eliminating redundancies, and optimizing performance without introducing new features or modifying the system's outward functionality.
Refactoring is especially valuable for long-term projects where code may accumulate technical debt over time. Technical debt is the future costs associated with cutting corners in software development, such as writing inefficient code or skipping testing to meet deadlines. Like financial debt, technical debt can compound, making it more complex and costly to maintain and scale a project in the future.
To fully appreciate its value, let’s explore the key benefits of effective code refactoring.
Code refactoring offers numerous advantages that significantly enhance software development.
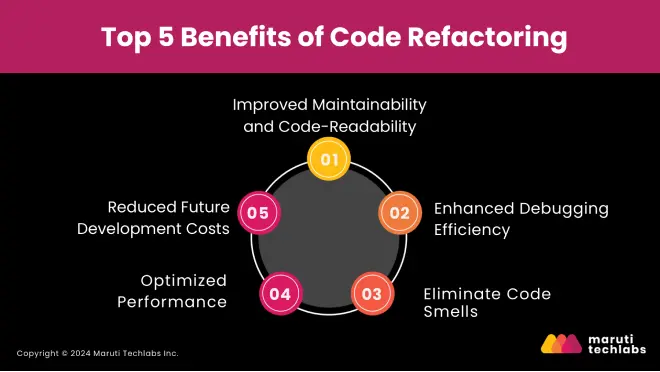
Here are the top 5 benefits of code refactoring:
Well-organized code is easier to understand, which is crucial when multiple developers collaborate on the same project. Refactoring improves readability by organizing the code logically and reducing complexity.
Debugging becomes simpler when the code is well-structured and easy to follow. Refactoring helps developers quickly identify bugs and abnormalities in the code, reducing the time spent on troubleshooting.
Code smells are indicators that something is wrong with the code's design or structure. While not necessarily bugs, they suggest underlying issues that could lead to problems in the future.
Refactoring can improve performance by identifying and removing redundant code, optimizing algorithms, and ensuring efficient memory usage. This contributes to faster and more reliable applications.
Although refactoring requires upfront investments of time and resources, it later pays off with huge savings after some period. Clean and maintainable code is less likely to be bug-prone, making it easier to add new features, fix bugs, and scale the application without extreme rewrites.
Implement code refactoring at the right time to maximize its impact. Let’s learn when code refactoring delivers optimal value.
Refactoring should be part of your regular development cycle, but there are specific scenarios when it becomes crucial.
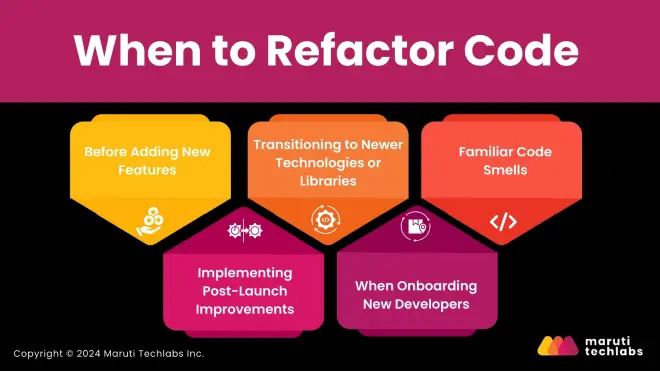
Let’s explore when businesses or organizations should prioritize refactoring.
Before planning significant feature additions, it is essential to refactor the existing codebase. If the code is messy, it’s challenging to integrate new features without causing conflicts or introducing bugs. Refactoring cleans up legacy code, providing a stable foundation for incorporating new features and enhancements.
For example, adding a new payment method to an e-commerce platform might involve multiple touchpoints across the system (database, frontend, API integrations). Refactoring beforehand ensures a smooth integration process, minimizes potential issues, and enhances scalability.
Performance issues may arise once a product is live, or new features may be requested. Refactoring can help prepare the codebase for enhancements without jeopardizing existing functionality. For example, X (formerly Twitter) famously refactored their backend from Ruby on Rails to a Java-based stack to improve scalability and performance.
As technologies evolve, upgrading to newer frameworks or libraries can offer better performance and enhanced features. Refactoring is crucial during these transitions, as it helps adapt the existing codebase to new paradigms and optimizes the integration.
For example, moving from an older JavaScript library to a modern framework like React requires refactoring the UI components for better compatibility, performance, and maintainability.
When new developers join a team, well-structured code makes the onboarding process smoother. Refactoring ensures the codebase is clean and easy to understand, allowing new team members to contribute more quickly.
With a clear understanding of when to refactor, we can now focus on the methodologies that guide an effective refactoring process.
Refactoring requires a thoughtful approach to avoid breaking the existing functionality.
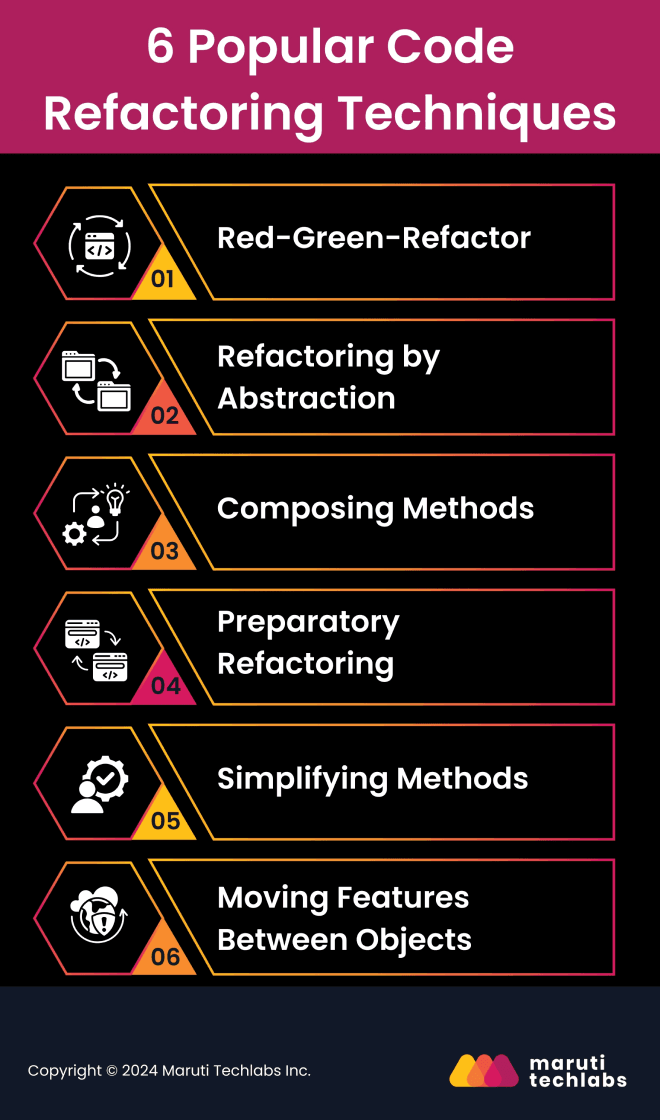
Here are some widely used refactoring techniques:
The Red-Green-Refactor technique is widely used in Agile development, particularly in Test-Driven Development (TDD). TDD emphasizes writing tests before the code is developed, ensuring that the code is built to meet specified requirements from the start. This approach consists of three main steps:
The Red-Green-Refactor method is particularly beneficial in several scenarios:
This approach promotes continuous, incremental improvement while ensuring the code remains functional.
Refactoring by abstraction is used to eliminate redundancy and enhance modularity. This includes:
Refactoring by abstraction is most beneficial when developers need to manage and refactor large amounts of code. It is particularly effective in scenarios where:
By leveraging refactoring by abstraction, developers can create a more modular and scalable architecture. This makes extending the system easier and maintains consistency across the codebase.
This technique may be the right choice if you need to make significant changes while keeping the system stable.
Long, complex methods can be challenging to maintain. Composing methods involves breaking them into smaller, well-named, and focused methods. Benefits include:
By simplifying large methods, the overall clarity and maintainability of the codebase are significantly improved.
Before implementing new features, it's often wise to refactor existing code to make it easier to modify. Preparatory refactoring involves:
This technique ensures that the codebase is healthy, making future changes less error-prone and more accessible to implement.
Implementing the proper techniques is vital, but adhering to best practices can further enhance refactoring.
Simplifying methods focuses on reducing the complexity of individual methods by:
This approach improves the codebase's readability and usability, making it easier for developers to maintain and extend it.
Sometimes, as requirements change or the code evolves, certain functionalities may be better suited in other parts of the system. This technique involves:
Moving features between objects helps create a well-balanced system in which each class or module has a clear and specific purpose.
Now that you know the best approaches to code refactoring, let’s learn the challenges of implementing them.
While code refactoring offers numerous benefits, it’s not without challenges.
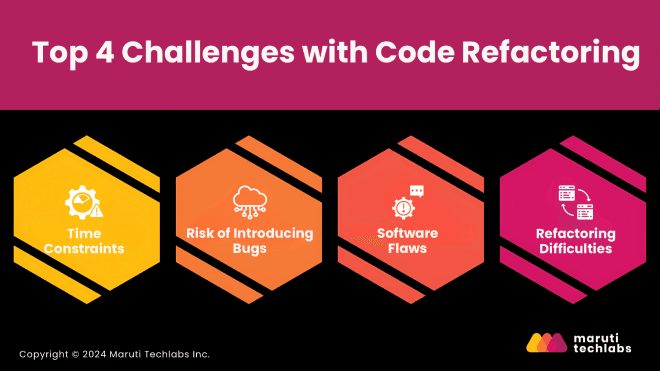
Developers should be aware of the potential risks and complexities associated with the process.
Refactoring requires an upfront investment of time, which can be challenging to justify in projects with tight deadlines. However, neglecting refactoring can lead to higher costs in the long run as technical debt accumulates.
If not carried out carefully, the refactoring process can introduce new complexities or unintended issues, including the risk of introducing new bugs. It requires a deep understanding of the codebase and close collaboration with QA teams to identify potential risks and trade-offs.
Simply reorganizing code structure through refactoring will not resolve underlying software defects. While refactoring enhances code organization and maintainability, it doesn't correct functional problems. Teams need dedicated debugging efforts and thorough testing protocols to address software issues adequately.
Undertaking refactoring work carries its risks. Improving code structure may create new problems or unexpected side effects without careful planning and deep technical knowledge. Success requires a comprehensive understanding of the existing system and carefully evaluating potential impacts.
Addressing these challenges head-on requires strategic planning and proactive measures.
Now that you have a clear idea of the challenges of code refactoring let’s learn the solutions that can deliver the best results.
Challenge | Strategy |
|---|---|
Time Constraints | Prioritize refactoring in development schedules. Use Agile sprint planning to include refactoring tasks and break them into smaller, manageable parts. |
Risk of Introducing Bugs | Implement automated testing frameworks (e.g., JUnit, pytest) and code review processes to catch bugs early. Collaborate with QA teams. |
Software Flaws | Use static code analysis tools to detect and resolve software flaws early in development. Perform code reviews regularly to maintain code quality. |
Refactoring Difficulties | Break down complex refactoring tasks into smaller steps and perform incremental refactoring. Focus on maintaining functionality at each step. |
While refactoring has substantial advantages, there are specific scenarios in which it may be prudent to refrain from this practice.
Let’s now observe the best practices that can be used for code refactoring.
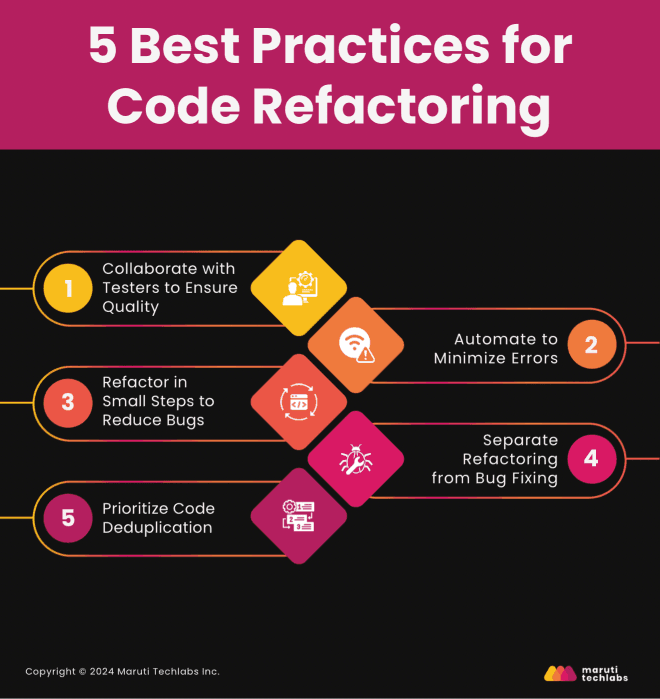
Developers should follow the 5 best practices below to refactor effectively, minimize risk, and maximize the process's benefits.
Here’s what needs to be done.
Involving the QA team during the refactoring process is crucial for maintaining the integrity of the code. QA teams thoroughly evaluate both functional and non-functional aspects of the code. They perform frequent testing to ensure consistency with code behavior, even as the internal structure evolves.
In addition, automated tests can help catch regressions and verify that refactoring efforts do not introduce new bugs.
Utilizing automated tools can significantly enhance refactoring by speeding up routine tasks such as variable renaming, method extraction, and class restructuring. These tools also reduce the potential for human error, allowing developers to focus on more complex refactoring tasks. Automation ensures that changes are consistently applied and helps maintain a high standard of code quality.
Adopting an incremental approach to refactoring minimizes the risk of introducing bugs. By breaking down the process into smaller, manageable changes, developers can test and validate each modification more easily. This controlled method ensures that the code remains functional throughout the refactoring process, making identifying and addressing any issues easier.
Maintaining a clear distinction between refactoring and bug fixing is essential for an effective development process. Refactoring aims to improve the code structure without altering functionality, while bug fixing addresses issues within the code’s behavior. Mixing the two can lead to confusion and make tracking progress more difficult.
Keeping these activities separate ensures developers can concentrate on each task's objectives.
Focusing on reducing code duplication is vital for enhancing the maintainability of a codebase. Duplicate code can lead to inconsistencies and complicate future updates across different parts of the system. By prioritizing eliminating redundant logic during refactoring, developers simplify the codebase, making it easier to understand, modify, and maintain in the long run.
Despite its many benefits, code refactoring presents several challenges that developers must navigate carefully. Let’s observe them in brief.
Code refactoring is essential for maintaining a healthy, efficient, and scalable codebase. While it requires an upfront investment, disciplined approach and careful planning, the long-term benefits far outweigh the initial investment. By following best practices such as collaborating with QA teams, automating processes, refactoring in small steps, and more developers can ensure that their codebase remains clean, maintainable, and free from technical debt.
As software systems grow in complexity, the importance of refactoring will only continue to increase. Embracing refactoring as a regular practice will help you build a strong foundation for the future, ensuring your codebase remains adaptable and efficient.
Consider partnering with experts to maximize the benefits of refactoring and stay ahead in the software landscape. Upgrade your software development with Maruti Techlabs! Our expert team can help you determine the most accurate refactoring strategies for your needs.
Our Software Code Audit Services can offer crucial insights into your code quality and identify areas for improvement! Contact us today to find out how we can help build scalable, efficient, and maintainable software foundations for your business's growth.
Code refactoring improves the internal structure of the code without changing its external behavior. It increases readability, removes redundancy, optimizes performance, and builds reliability for easy maintenance and scalability.
Code refactoring should be prioritized before adding new features, after a product launch, when fixing bugs or addressing technical debt, and when onboarding new developers to ensure a clean, maintainable codebase.
While refactoring can introduce bugs, this risk can be mitigated by thorough testing during the process, including the use of automated testing frameworks and involving quality assurance (QA) teams to ensure the code’s functionality remains intact.
Key benefits include improved readability and maintainability, easier debugging, elimination of code smells (e.g., duplicated code, large classes), optimized performance, and reduced future development costs by preventing technical debt.
Yes, many refactoring automation tools are available, such as those integrated within IDEs like IntelliJ and Visual Studio Code and specialized platforms like SonarQube and CodeClimate, to streamline the refactoring process and reduce manual effort.
![SL-103020-37400-03[1].jpg](/_next/image/?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcdn.marutitech.com%2F%2Fsmall_SL_103020_37400_03_1_9ef554f0fb.jpg&w=640&q=75)

