

Fundamentals of Cloud Audit: Challenges and Best Practices






As cloud adoption deepens in 2026, organizations face growing pressure from regulators, customers, and boards to prove security, cost control, and accountability. Rapid expansion, remote work, and complex vendor ecosystems increase risk exposure.
Regular cloud audits help businesses maintain trust, reduce financial waste, and ensure cloud environments remain secure, compliant, and well governed.
This blog provides a clear and practical guide to conducting effective cloud audits. It explains a step-by-step audit framework, essential checklists, useful tools, measurable indicators, and real risk scenarios, helping organizations strengthen security, control costs, and build a sustainable cloud governance practice.
A cloud audit is a chronological review of a company’s cloud infrastructure, security, and compliance. It aims to thoroughly examine a cloud provider's security practices, data access controls, and risk mitigation strategies.
Cloud audits can be conducted internally or externally. Internal audits are conducted by a company’s cloud professionals, who evaluate their security policies, procedures, and resources. External audits are assessments performed by third-party experts in cloud security and compliance.
Given cloud environments' dynamic and distributed nature, comprehensive cloud audits have become the need of the hour. Traditional audits manage the physical and logical controls of an on-premise infrastructure.
Cloud audits encompass many verticals, such as the divided responsibilities between customers and cloud providers, scalability, and security risks. Nearly 65% of 3000 respondents to a 2024 Thales Global Data Threat Report identify cloud security as a top current and future priority. In addition, 72% consider it a future concern.
Here are the three main types of audits that are crucial for cloud migration.
A security audit shields businesses against unauthorized access and data breaches. They ensure:
They ensure all services and performance metrics crucial to business operations are adhered to. Performance audits analyze different facets of cloud environments to ensure efficiency and reliability.
Compliance audits assure clients that their cloud services meet legal and regulatory requirements. This is imperative to avoid any legal issues post-migration. Some of these compliances include risk management and governance (ISO & NIST), data privacy and protection (GDPR & CCPA), and access management (HIPAA).
Conducting regular cloud audits is a necessity for all organizations. A thorough audit can render the following benefits to businesses in the long run.
Timely audits help organizations identify potential threats, vulnerabilities, and areas of improvement in their cloud’s performance, security, compliance, and reliability. This assists them with implementing mitigation strategies before these threats become a reality. It also helps them learn the effectiveness of their strategy and revamp them as required.
Customers using your services expect their financial and personal data to be safe and compliant with relevant standards. Conducting private cloud audits and sharing certifications with customers helps inculcate trust. It also showcases a company’s willingness to adhere to best practices. Subsequently, this process adds to an organization's reputation, loyalty, and retention.
Cloud investments can produce a lot of waste regarding resources and costs. A comprehensive audit can offer invaluable insights into the efficacy and performance of infrastructure, platforms, and applications. This helps companies eliminate inefficiencies, waste, and redundancy within their cloud environment.
A structured cloud audit framework ensures consistent evaluation of security, compliance, and cost controls. Following clear steps helps organizations identify gaps, reduce risk, and maintain continuous visibility across cloud environments.
Define what the audit will cover and why it is being conducted. Identify cloud accounts, services, and regions in scope. Set clear objectives such as security posture improvement, compliance validation, or cost optimization.
Well-defined scope prevents audit sprawl and ensures results align with business and regulatory priorities.
Create a complete inventory of cloud resources, including compute, storage, networks, and identities. Classify assets based on sensitivity, business criticality, and data type.
Accurate inventory and classification enable focused controls, reduce blind spots, and support consistent risk evaluation across environments.
Identify potential threats based on asset type, access patterns, and data sensitivity. Assess the likelihood and impact of misuse, exposure, or failure.
This step helps prioritize risks, focus audit efforts on high-impact areas, and align controls with real-world threat scenarios.
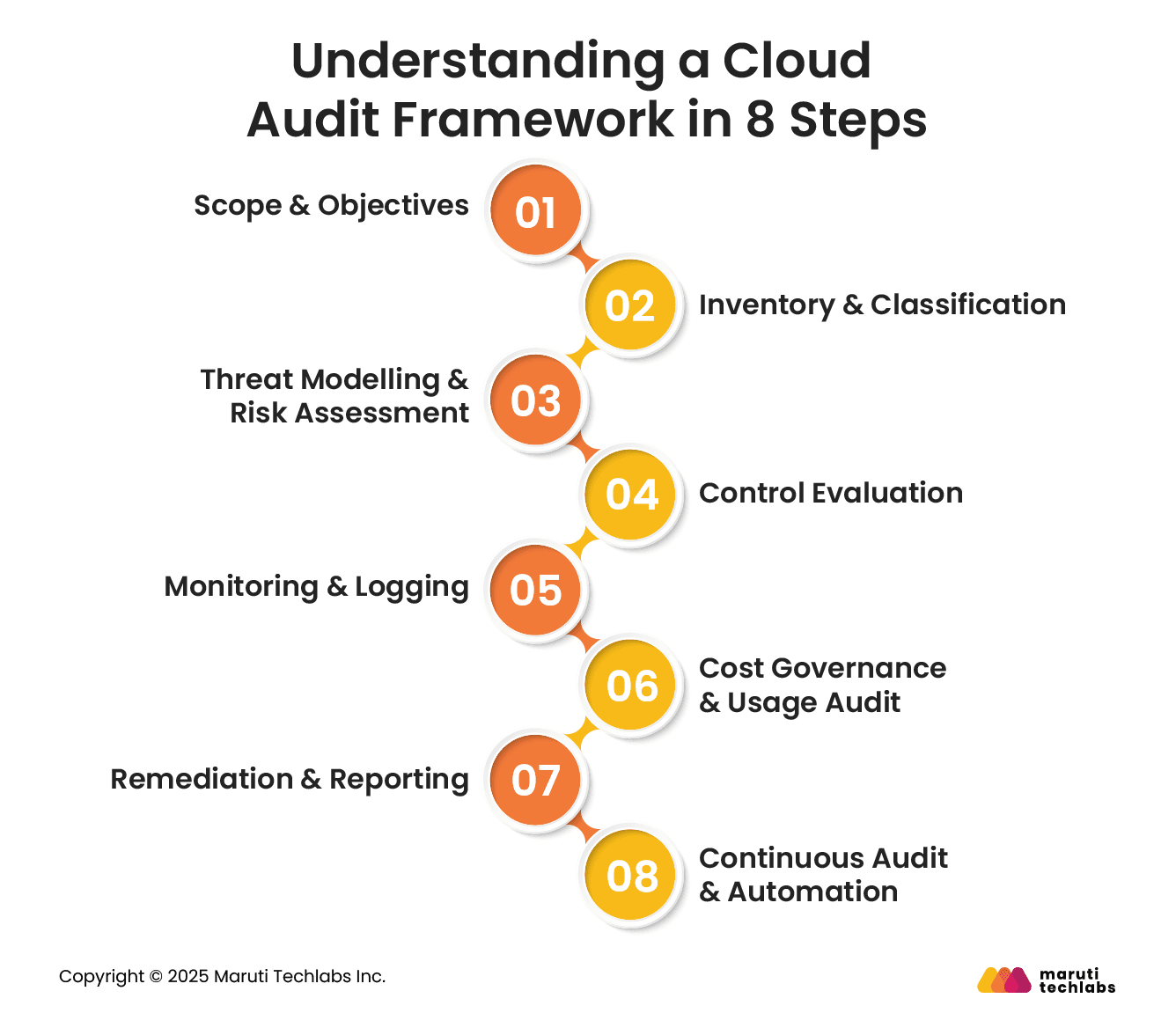
Review existing security and governance controls against internal policies and regulatory requirements. Validate access restrictions, encryption settings, backups, and configuration standards.
Control evaluation highlights weaknesses, outdated practices, and areas where enforcement is inconsistent or missing across cloud resources.
Assess whether activity logs, alerts, and monitoring systems are enabled and retained properly. Verify coverage for user actions, system changes, and security events.
Effective monitoring provides visibility into abnormal behavior and supports investigations, accountability, and timely incident response
Review resource usage, billing patterns, and allocation practices. Identify unused services, oversized resources, and missing ownership details.
Cost governance audits help control spending, improve forecasting, and ensure cloud investments align with actual business needs.
Document findings clearly with risk levels, evidence, and recommended actions. Assign ownership and timelines for remediation.
Clear reporting ensures stakeholders understand issues and progress, while structured remediation reduces repeat findings and strengthens overall cloud governance maturity.
Move from periodic audits to continuous assessment using automated checks and alerts. Regular validation helps detect drift, enforce standards, and reduce manual effort.
Continuous auditing supports faster issue resolution and keeps cloud environments aligned with evolving requirements.
Audit checklists provide consistency and completeness, ensuring critical areas are reviewed systematically and evidence is collected reliably during every cloud audit.
Verify identity access restrictions, encryption for data at rest and in transit, secure network configurations, backup policies, and incident response readiness. Ensure default settings are reviewed and hardened.
This checklist helps confirm that basic security protections are consistently applied across all cloud resources.
Confirm availability of audit logs, access records, configuration snapshots, and policy documents. Validate retention periods and the integrity of evidence.
This checklist ensures organizations can demonstrate compliance during reviews and respond confidently to regulatory or customer audit requests.
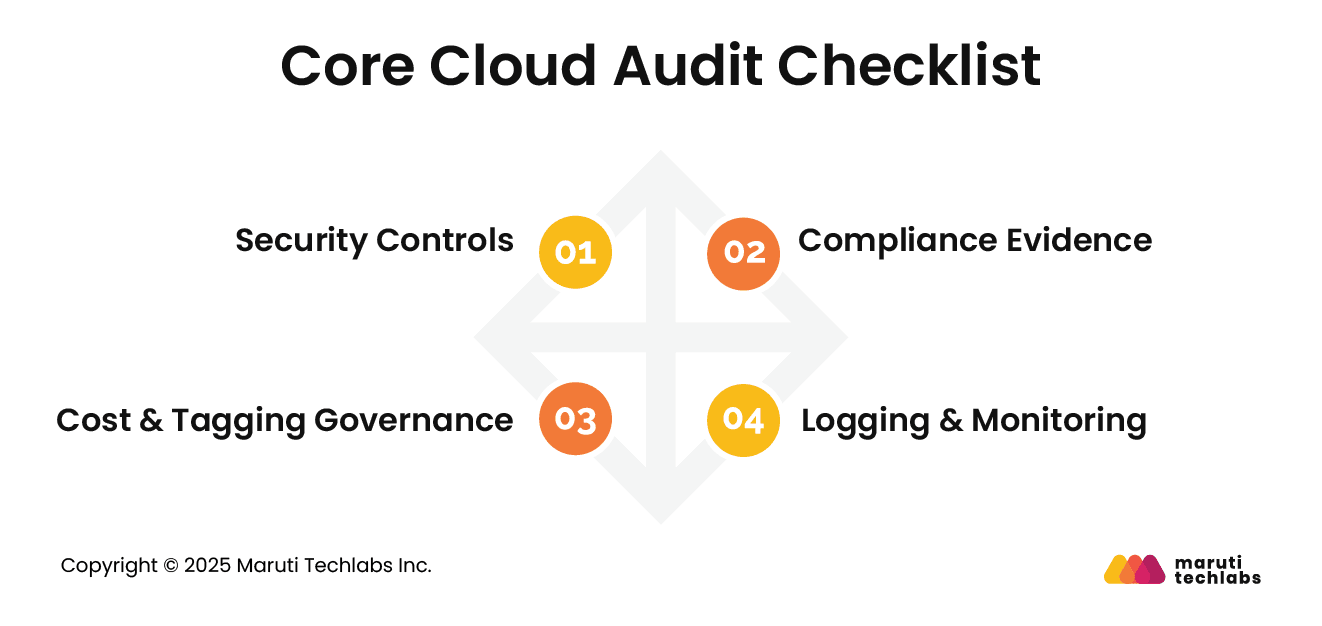
Check that all resources have clear ownership tags, environment labels, and cost centers. Identify unused or idle services. Review budgets and alerts. Strong tagging and governance improve cost visibility, accountability, and reduce unnecessary cloud spending.
Ensure logging is enabled for key services, access events, and configuration changes. Verify alerts for suspicious activity and system failures. Confirm log retention meets policy needs.
This checklist supports faster detection of issues and reliable forensic analysis.
Effective cloud audits rely on tools that provide visibility, automation, and consistency. The right technologies reduce manual effort and help teams maintain ongoing oversight across dynamic cloud environments.
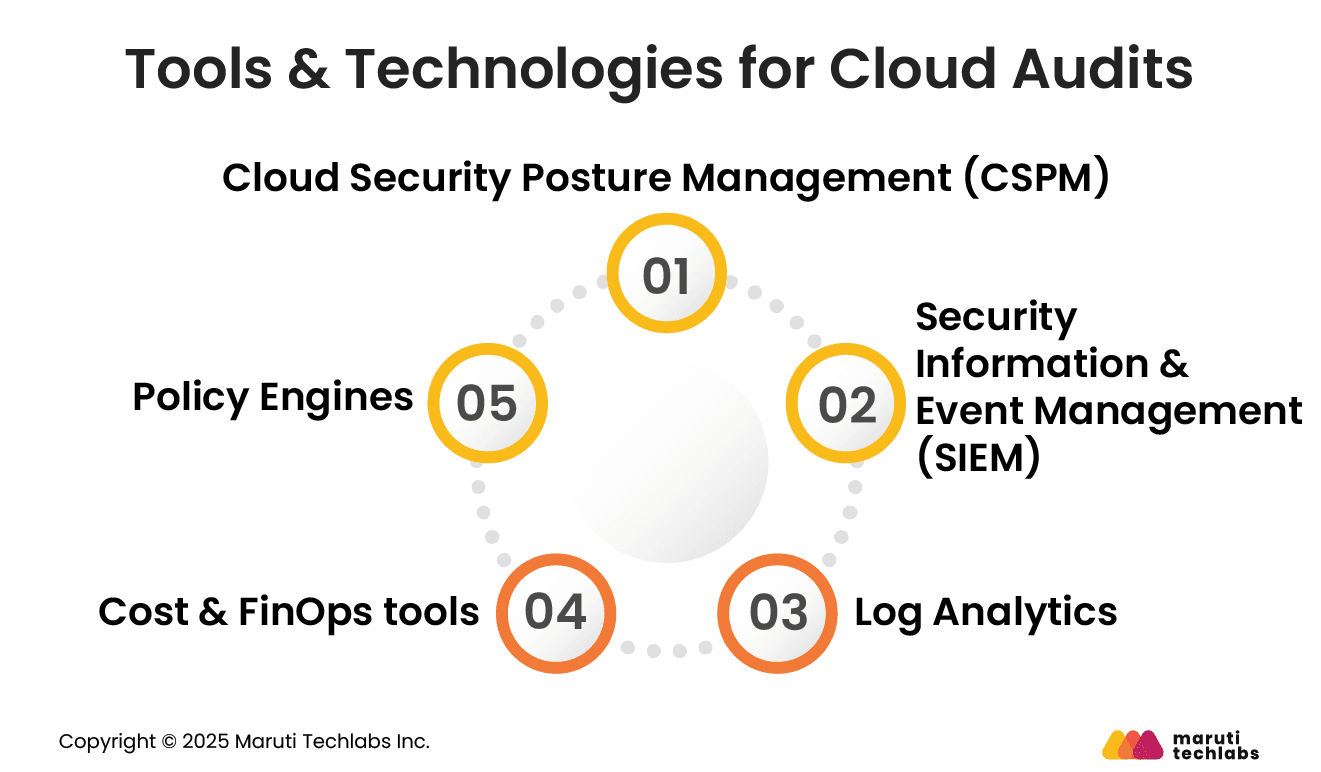
CSPM tools continuously assess cloud configurations against best practices and policies. They identify misconfigurations, risky permissions, and exposed resources. CSPM supports proactive risk reduction and helps auditors detect issues before they lead to incidents.
SIEM systems collect and correlate security events from cloud services. They provide centralized visibility into activity patterns and alerts. SIEM tools support incident detection, investigation, and compliance reporting during and after cloud audits.
Log analytics tools analyze large volumes of cloud logs to identify trends, anomalies, and operational issues.
They help auditors understand usage behavior, detect suspicious actions, and verify monitoring effectiveness across environments without relying on manual log reviews.
Cost management tools provide detailed insights into spending, usage patterns, and anomalies. They help auditors identify waste, enforce budgets, and validate cost allocation practices.
These tools support financial accountability and informed decision-making in cloud environments.
Policy engines enforce rules automatically across cloud resources. They prevent non-compliant configurations and support consistent standards.
During audits, policy engines provide clear evidence of enforcement and help organizations maintain alignment with security and governance requirements.
Measuring the right indicators helps organizations understand audit effectiveness, track improvement, and communicate cloud risk and governance health to leadership clearly.
Track time to detect and respond to security issues. Measure alert accuracy and resolution speed. These metrics indicate how effectively monitoring and response processes work and whether cloud teams can act quickly to reduce potential impact.
Measure the percentage of controls meeting policy or regulatory requirements. Track changes over time to identify improvement or regression.
Compliance pass rates provide a simple view of audit readiness and highlight areas needing focused remediation.
Monitor unexpected spikes or unusual usage patterns. Track how quickly anomalies are identified and addressed. These trends help assess cost governance maturity and prevent prolonged waste or budget overruns.
Evaluate how many resources follow standards for tagging, access, and configuration. High hygiene scores indicate disciplined cloud management. Low scores reveal sprawl, weak ownership, and increased operational risk.
Cloud audits help identify common risk scenarios early. Regular reviews reduce the likelihood of security incidents, financial loss, and compliance failures across cloud environments.
Excessive access permissions increase the risk of misuse and breaches. Audits identify users and services with unnecessary privileges.
By enforcing least access principles, audits reduce attack surfaces and limit potential damage from compromised accounts.
Sensitive data stored without encryption can lead to serious exposure. Audits verify encryption settings and access controls. Early detection ensures data protection measures are applied consistently and regulatory expectations are met.
Unused development resources often remain active and generate ongoing costs. Audits identify idle services and outdated environments. Removing them reduces waste, improves cost efficiency, and encourages better lifecycle management.
Missing logs or incomplete documentation weaken compliance posture. Audits highlight evidence gaps before formal reviews. Addressing these gaps improves readiness, reduces stress during regulatory checks, and strengthens organizational accountability.
Transitioning to the cloud or making new enhancements to your current cloud settings isn’t easy. Here are the challenges that one can encounter when auditing cloud-based systems.
On-premise hardware and infrastructure can always be monitored physically. However, this isn’t the case with the cloud. As the cloud infrastructure and environment are owned and maintained by cloud service providers, physical inspection is impossible for auditors. Without physical inspections, the security and integrity of infrastructure can be compromised.
Cloud providers typically follow the shared responsibility model. This model observes a practice where customers and cloud providers handle the different security aspects. This division makes it cumbersome for auditors to learn if both parties adhere to their obligations and maintain adequate security.
Different cloud resources can be allotted and decommissioned on demand, making the cloud environments highly dynamic. This constant commissioning and de-provisioning of resources make it difficult to maintain an inventory and ensure optimal security in real-time.
Cloud providers offer the multi-tenancy option, where different customers utilize the same infrastructure. This poses a security risk, demanding adequate data segregation between tenants to maintain security and compliance. In addition, it makes verification difficult for auditors.
Cloud providers have limited visibility into their infrastructure and operations. This makes it challenging for auditors to assess the effectiveness of security controls and potential vulnerabilities.
Here is a list of best practices that can assist companies with conducting a thorough cloud audit.
The first step is to fully understand the scope of the audit, its timeline, and the necessary resources and tools. Your scope should be aligned with your business strategies and regulatory requirements to conduct an efficient and effective audit. This focused approach helps you observe results that are congruent with your vision.
It’s essential to know your current cloud environment. This paints the right picture of learning the necessities per your defined scope.
To begin with, you can make a list of all assets, such as databases, applications, servers, and data. Learning the data flows and underlying configuration of these assets helps auditors better identify issues and areas for improvement.
The next step is discovering the security risks that make your cloud environment vulnerable. This encapsulates non-technical risks like human error, technical misconfigurations, and unpatched systems.
According to the Thales study, 65% of respondents identify cloud security as a current concern. To diligently address security risks and potential weaknesses in the cloud, auditors should leverage a mix of automated scanning tools, manual review, and penetration testing.

Enforcing mitigation measures includes access management, network segmentation, incident response procedures, and data encryption. Implementing all the above measures together can be cumbersome. Therefore, it’s best to choose and prioritize calculating their risk score and impact on the organization.
An auditor’s job doesn’t end with implementing control measures. Real-time monitoring is crucial to ensure your cloud environment stays secure and compliant. To quickly be notified and respond to threats or compliance problems, one must have security information, event management (SIEM), intrusion detection, and log analysis tools in place.
The last step in a cloud audit is preparing a comprehensive report that includes your findings, inferences, and recommendations. The report should consist of a summary and be presented to stakeholders like IT teams, management, and compliance officers. After concluding your audit, you must plan and execute follow-ups while scheduling future audits to examine its effectiveness.
Cloud audits are the key to ensuring your budget is spent on the right cloud provider, offering perfect security and necessary compliance. However, performing these audits can be confusing and complicated, and errors may have dire consequences.
The best practices outlined in the blog can help you fully understand your needs, discover risks and gaps, and enforce mitigation strategies.
Consider partnering with a cloud consulting company like Maruti Techlabs to make this process easier and quicker.
Our comprehensive cloud audit services can provide a detailed report of your cloud environment in 2 weeks. Our experts conduct a 360-degree examination of your cloud ecosystem and suggest ways to enhance your performance and security while eliminating waste or underutilized resources. These audits are further strengthened by our specialized cloud security services, designed to address vulnerabilities and ensure compliance across your cloud infrastructure.
Don’t worry about your cloud audit. Contact us today, and we’ll do the work for you.
To audit a cloud environment assess security controls, data encryption, identity management, and access policies. Review compliance with standards, monitor logs for anomalies, evaluate backup strategies, and ensure proper resource allocation, cost optimization, and incident response procedures.
To access audit logs in Strata Cloud Manager, navigate to Settings > Audit Logs. Here, you can view user-initiated actions, including changes made, the responsible user, date and time, and descriptions. To refine your search, use filters for date range, user, category, and change type.
To audit AWS - review IAM roles, policies, and permissions. Examine CloudTrail logs for user activities, assess CloudWatch for resource monitoring, and analyze GuardDuty alerts. Verify data encryption, backup policies, and security groups and ensure compliance with AWS best practices.


